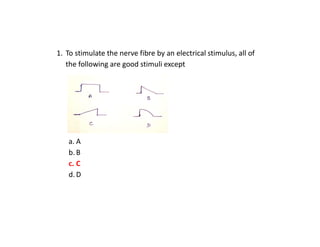
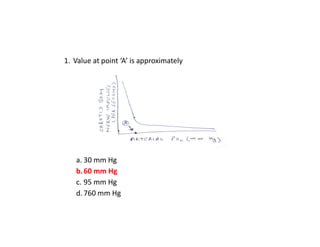
This document contains multiple choice questions (MCQs) about muscle physiology, respiratory system, gastrointestinal system, and kidney physiology. The questions cover topics like muscle contraction, structure and function of respiratory and digestive systems, kidney filtration, reabsorption in nephron segments, and countercurrent mechanisms.












































































![1. All are true of juxtamedullary nephrons except [wrt cortical
nephrons]
a. Form 15% of total nephrons
b. Have vas recta
c. Have long loops of Henle
d.Have high blood flow
e. Have large O2 extraction
f. Have larger glomeruli and narrower efferent arterioles](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mcqpptcombinedwithanswerspdf-230504201122-135b22e3/85/Physiology-MCQS-pdf-78-320.jpg)