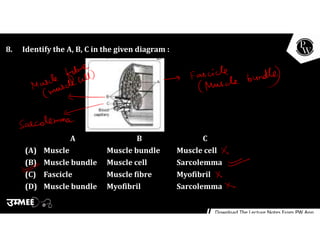
(1) Skeletal muscles are made of bundles of muscle fibers. Each fiber contains many myofibrils, which are made of repeating contractile units called sarcomeres.
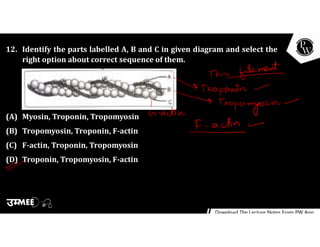
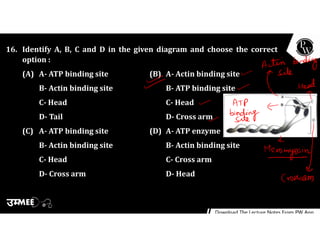
(2) Sarcomeres contain overlapping thin actin filaments and thick myosin filaments. During muscle contraction, myosin heads bind to and pull on actin filaments, causing the filaments to slide towards each other.
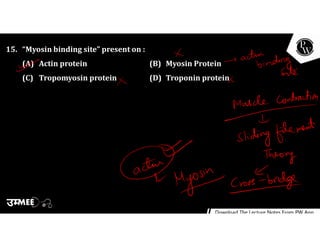
(3) Muscle contraction is initiated by motor neurons stimulating the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcium binds to troponin, exposing actin binding sites for myosin to form cross-bridges and drive contraction.