1. Waves transmit information or energy from one point to another through a medium without the medium itself moving.
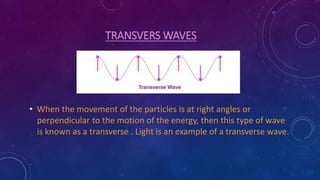
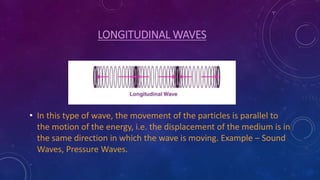
2. There are two main types of waves: transverse waves, where the particle motion is perpendicular to the wave motion, and longitudinal waves, where particle motion is parallel.
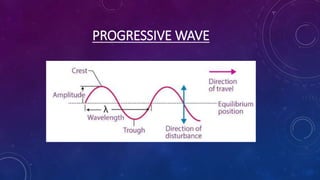
3. Key wave properties include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, speed, and period. The relationship between wavelength, frequency, and speed is described by the wave speed formula.