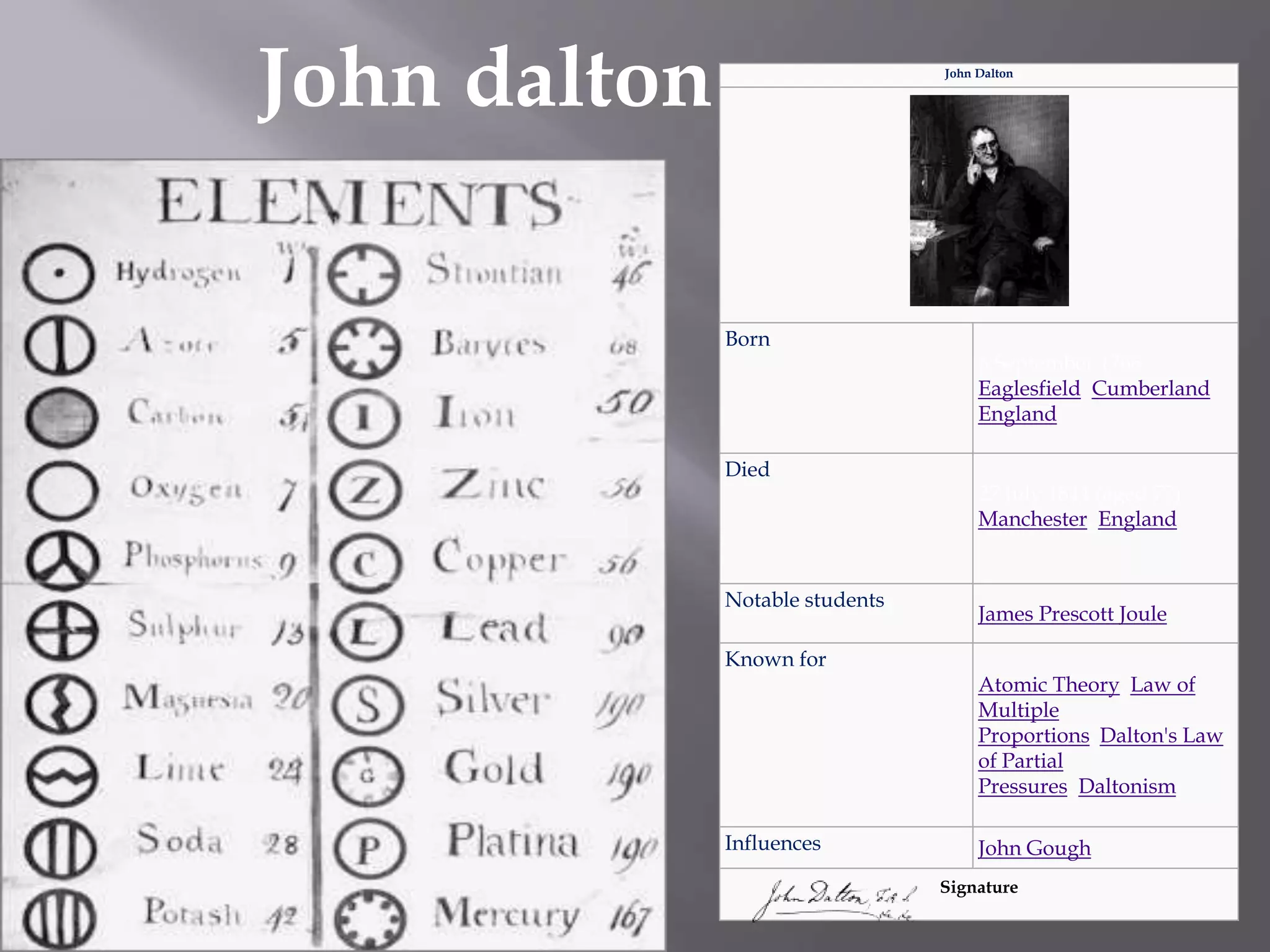
John Dalton was an English scientist born in 1766 who is considered the founder of modern atomic theory. He proposed that all matter is composed of small indivisible particles called atoms and that different atoms have different weights. His atomic theory included the ideas that atoms of a given element are all identical, atoms cannot be created, destroyed, or divided, and atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form chemical compounds. Dalton's atomic theory was groundbreaking and laid the foundation for modern chemistry, though some of his specific assumptions, like his rule of simplest composition, were later found to be incorrect. He made many contributions in the fields of mathematics, meteorology, and gas behavior.



![Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit (symbol: u), also called the dalton (symbol: Da), is
a unitused for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one
twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and
electronic ground state. The CIPM have categorised it as a "non-SI unit whose values
in SI units must be obtained experimentally".[1]
It’s value
of 1.660538782(83)×10
−27 kg.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicspowerpointpresentation-101120192837-phpapp02/85/Physics-powerpoint-presentation-5-320.jpg)


![Family
Statue of Berzelius in the center ofBerzelii Park, Stockholm
In 1818 Berzelius was ennobled by King Carl XIV Johan; in
1835, at the age of 56, he married Elisabeth Poppius, the 24-
year old daughter of a Swedish cabinet minister, and in the
same year was elevated to friherre.[3]
Berzeliusskolan, a school situated next to his alma mater,
Katedralskolan, is named for him. In 1939 his portrait
appeared on a series of postage stamps commemorating the
bicentenary of the founding of the Swedish Academy of
Sciences.
He died on 7 August 1848 at his home in Stockholm, where
he had lived since 1806..[4]
Chemical compound
A chemical compound is a pure chemical substance consisting of two or more
different chemical elements[1][2][3] that can be separated into simpler substances
by chemical reactions.[4] Chemical compounds have a unique and defined chemical
structure; they consist of a fixed ratio of atoms[3] that are held together in a defined
spatial arrangement by chemical bonds. Chemical compounds can
be molecularcompounds held together by covalent bonds, salts held together by ionic
bonds, intermetallic compounds held together by metallic bonds, orcomplexes held
together by coordinate covalent bonds. Pure chemical elements are not considered
chemical compounds, even if they consist of molecules which contain only multiple
atoms of a single element (such as H2, S8, etc.),[5] which are called diatomic
molecules orpolyatomic molecules.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicspowerpointpresentation-101120192837-phpapp02/85/Physics-powerpoint-presentation-8-320.jpg)

![Chemical structure
A chemical structure includes molecular geometry, electronic structure and crystal
structure of molecules. Molecular geometry refers to the spatial arrangement of atoms in
a molecule and the chemical bonds that hold the atoms together. Molecular geometry can range
from the very simple, such as diatomic oxygen or nitrogen molecules, to the very complex, such
as protein or DNA molecules. Molecular geometry can be roughly represented using
a structural formula. Electronic structure describes the occupation of a molecule's molecular
orbitals.
Ions
For ions, the charge on a particular atom may be denoted with a right-hand superscript. For
example Na+, or Cu2+. The total charge on a charged molecule or a polyatomic ion may also be
shown in this way. For example: hydronium, H3O+ or sulfate, SO4
2−.
For more complex ions, brackets [ ] are often used to enclose the ionic formula, as in [B12H12]2−,
which is found in compounds such asCs2[B12H12]. Parentheses ( ) can be nested inside brackets to
indicate a repeating unit, as in [Co(NH3)6]3+. Here (NH3)6 indicates that the ion contains
six NH3 groups, and [ ] encloses the entire formula of the ion with charge +3.
Isotopes
Although isotopes are more relevant to nuclear chemistry or stable isotope chemistry than to
conventional chemistry, different isotopes may be indicated with a left-hand superscript in a
chemical formula. For example, the phosphate ion containing radioactive phosphorus-32 is32PO4
3-.
Also a study involving stable isotope ratios might include the molecule 18O16O.
A left-hand subscript is sometimes used redundantly to indicate the atomic number. For
example, 8O2 for dioxygen, and 16
8O2 for the most abundant isotopic species of dioxygen. This is
convenient when writing equations for nuclear reactions, in order to show the balance of charge
more clearly.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicspowerpointpresentation-101120192837-phpapp02/85/Physics-powerpoint-presentation-10-320.jpg)
![Isobutane
Molecular formula:
C4H10
Semi-structural
formula: (CH3)3CH
Butane
Molecular formula:
C4H10
Semi-structural
formula:
CH3CH2CH2CH3
Chemical symbol
A chemical symbol is a 1- or 2-letter
internationally agreed code for a chemical
element, usually derived from the name of the
element, often in Latin. The first letter, only, is
capitalised. For example, "He" is the symbol
for helium (English name, not known
in ancient Roman times), "Pb"
for lead (plumbum in Latin), "W"
for tungsten (wolfram in German, not known
in Roman times). Temporary
symbols assigned to newly or not-yet
synthesized elements use 3-letter symbols.
For example, "Uno" was the temporary
symbol for Hassium which had the
temporary name of Unniloctium.
Chemical symbols may be modified by
the use of superscripts or subscripts to
specify a particular isotope of an atom.
Additionally superscripts may be used
to indicate the ionization or oxidation
state of an element.
Attached subscripts or superscripts specifying a
nucleotide or molecule have the following
meanings and positions:
The nucleon number (mass number) is shown in
the left superscript position (e.g., 14N)
The proton number (atomic number) may be
indicated in the left subscript position
(e.g., 64Gd)
If necessary, a state of ionization or an excited
state may be indicated in the right superscript
position (e.g., state of ionization Ca2+).
Inastronomy, non-ionised atomic hydrogen is
often known as "HI", and ionised hydrogen as
"HII".[1]
The number of atoms of an element in
a molecule or chemical compound is shown in
the right subscript position (e.g., N2 or Fe2O3)
A radical is indicated by a dot on the right side
(e.g., Cl· for a chloride radical)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/physicspowerpointpresentation-101120192837-phpapp02/85/Physics-powerpoint-presentation-11-320.jpg)
