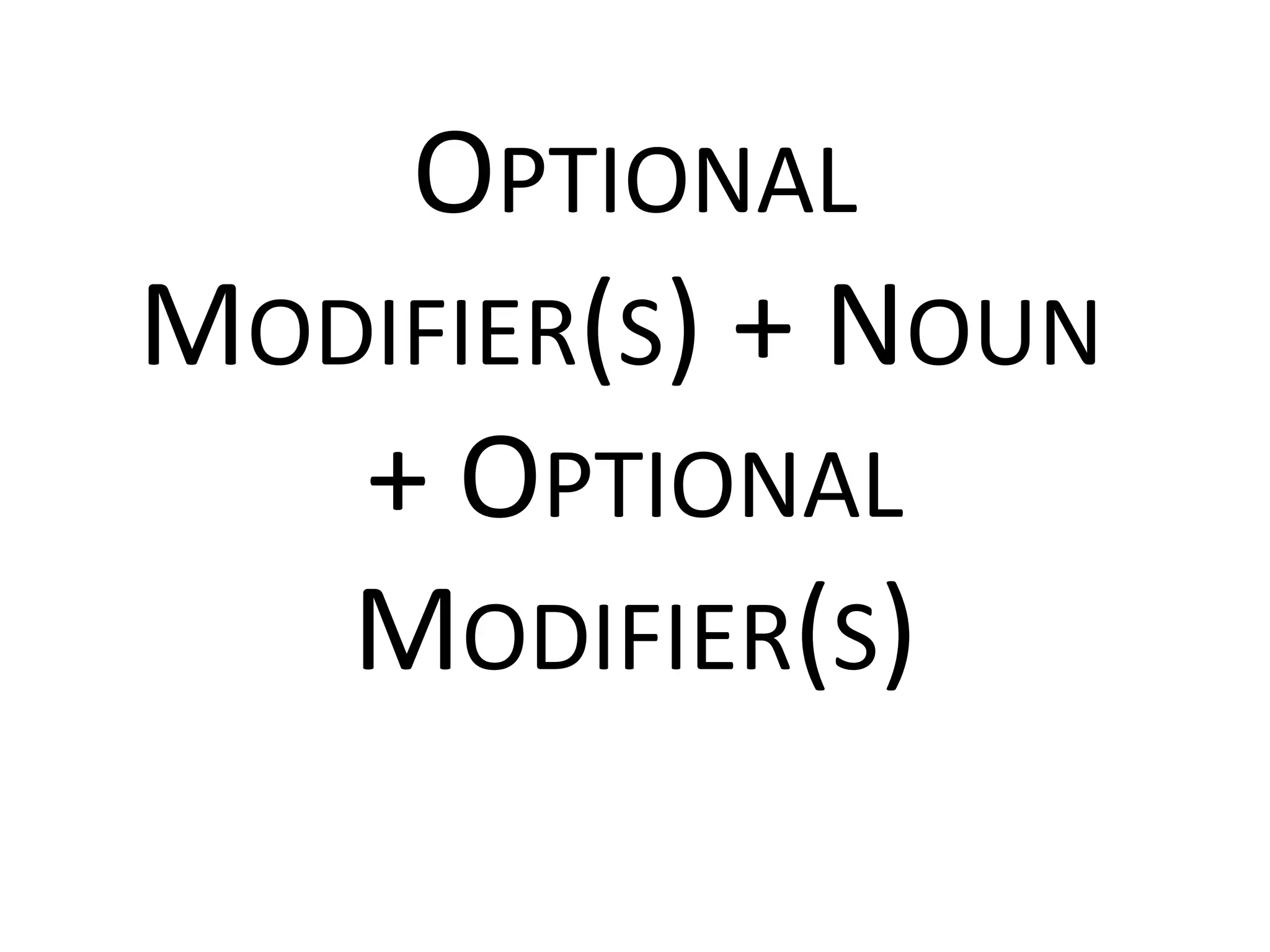
The document does not contain a narrative or story, but rather discusses linguistic concepts such as phrases and verb phrases. It provides examples of different types of phrases, including noun phrases which contain a noun and optional modifiers, and verb phrases which can contain auxiliary verbs and verb endings. It also gives directions to identify phrases in sample sentences.