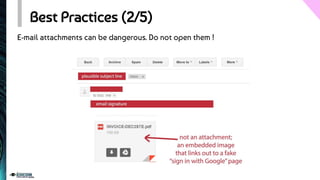
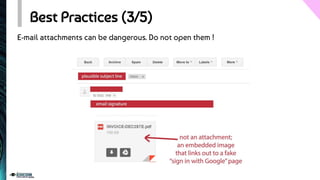
The document provides an overview of phishing, detailing its design, motivations, and types, including spear phishing and vishing. It explains the risks associated with clicking malicious links and outlines best practices to enhance online security, such as verifying email links and maintaining antivirus software. The document emphasizes the importance of awareness and vigilance in preventing phishing attacks.