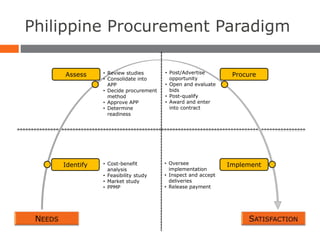
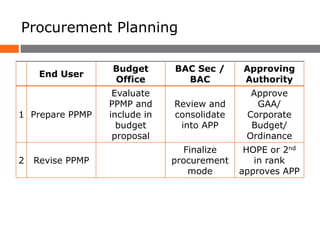
The document provides an overview of the Philippine government procurement system, including problems it previously faced and reforms implemented. Key reforms include enacting the Government Procurement Reform Act (GPRA) in 2003, which established standards and transparency. It created the Government Procurement Policy Board to set procurement policies and required use of the Philippine Government Electronic Procurement System. The GPRA and its implementing rules and regulations now govern procurement of infrastructure, goods, and consulting services for all national and local government agencies and seek to address prior issues like lack of transparency, standards, and oversight.