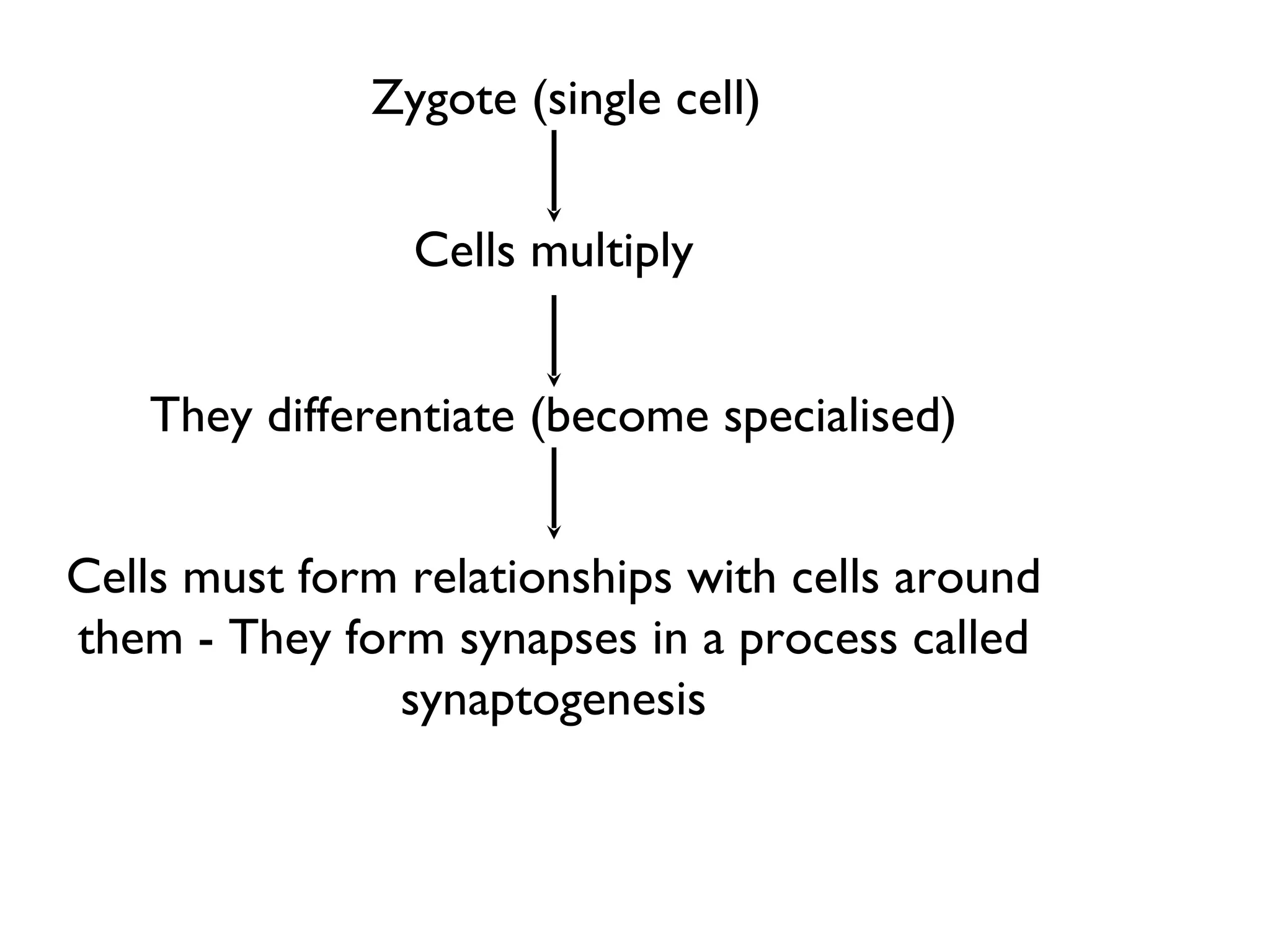
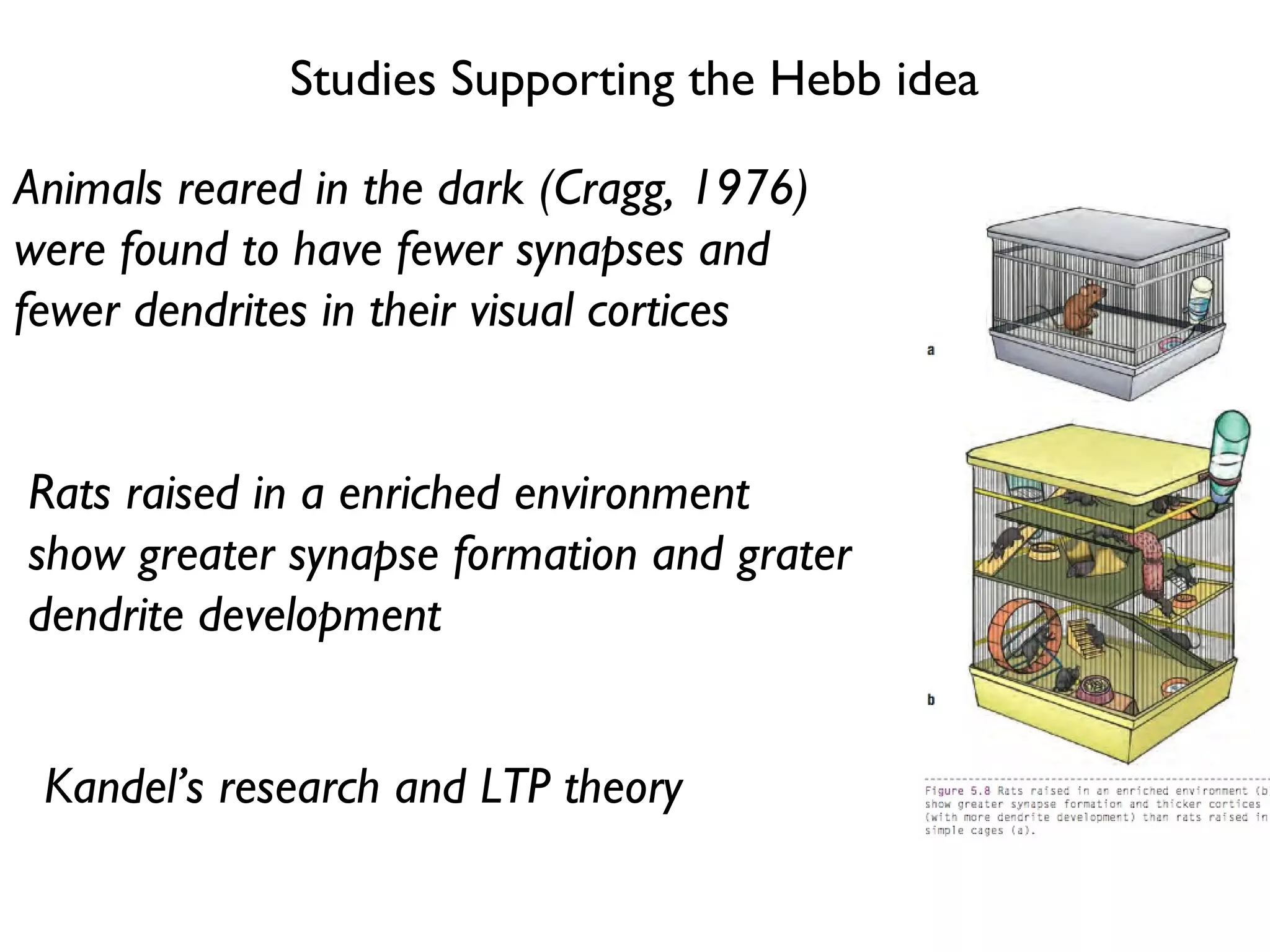
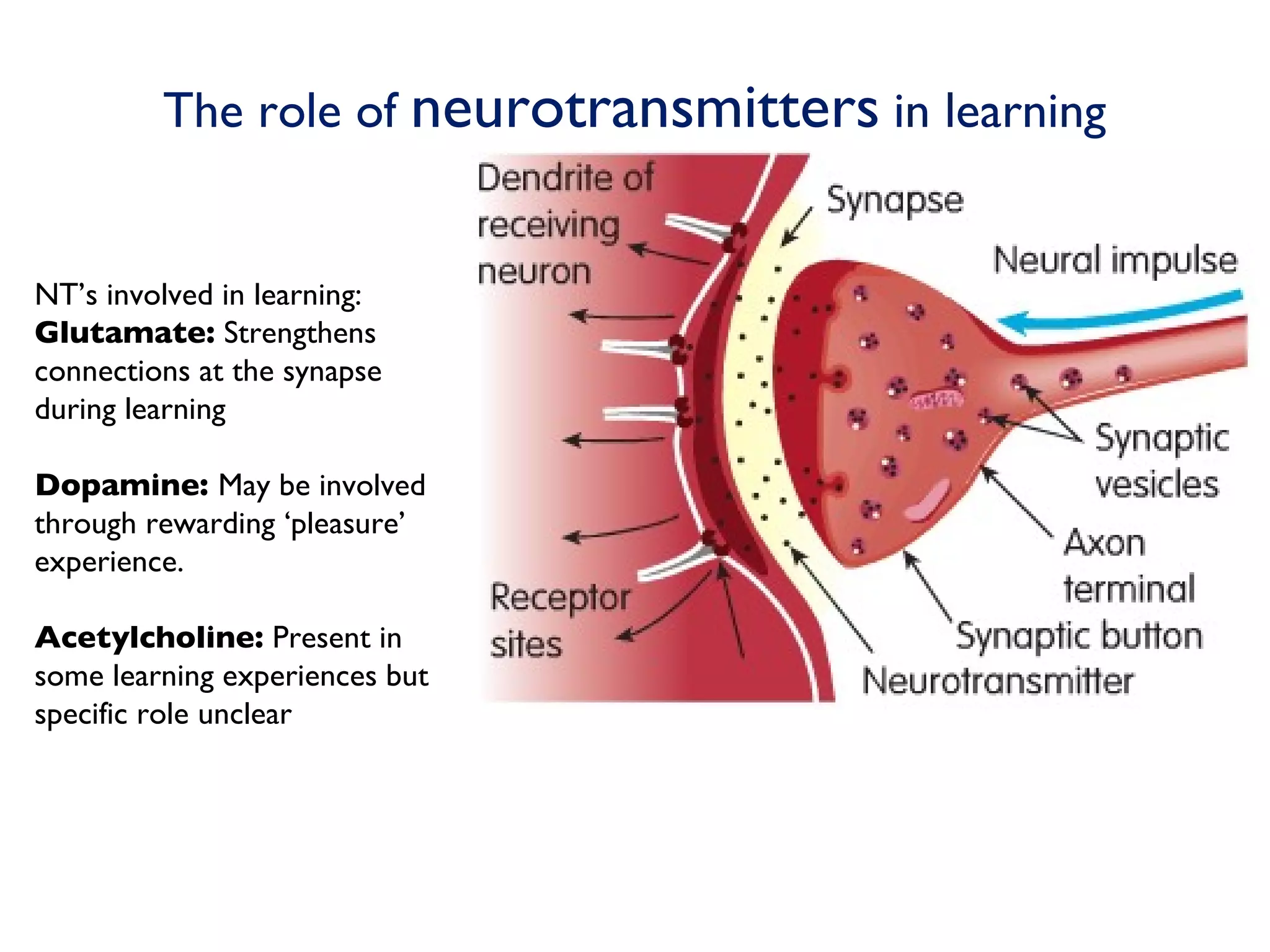
The document discusses the phases of neural development involved in learning. It explains that genetics alone do not determine neural development and that experience plays a role through strengthening neural connections. When neurons fire together they become more closely linked, creating neural pathways that are active during learning. Studies show animals reared in enriched environments have greater synapse formation and dendrite development, supporting the idea that use of neurons improves their function. Long-term potentiation is identified as a crucial mechanism of learning, strengthening synaptic connections and enhancing neuronal function along pathways when activated.