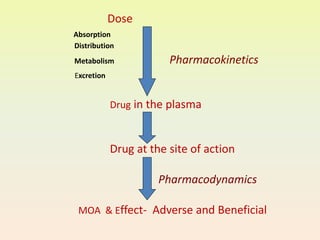
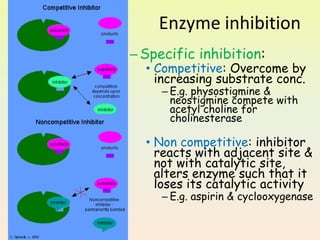
The document provides an overview of pharmacodynamics, which examines the actions of drugs on the body and their mechanisms of action, categorizing drug effects into stimulation, depression, irritation, replacement, cytotoxic actions, and immune modification. It discusses receptor-mediated and non-receptor mediated mechanisms, including the role of receptors, enzyme actions, and the impact of factors such as dose response and drug interactions. Additionally, it highlights the significance of therapeutic index and the combined effects of drugs, including synergism and antagonism.



![PRINCIPLES [Types] OF DRUG ACTION
1. Stimulation
– Adrenaline
– Pilocarpine
2. Depression
– Quinidine
– Morphine
– Barbiturates
3. Irritation
– Bitters
– Counter irritants
4. Replacement
• Insulin
• Iron
• Levodopa
5. Cytotoxic action
•Penicillin,
•Chloroquine
• cyclophosphamide
6. Modification of
immune status
•Vaccines
•Sera](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-5-320.jpg)







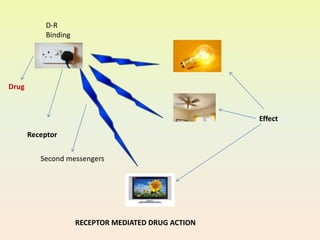
![Mechanism of Drug Action - Receptor
Mediated
• Receptor:
Protein macromolecules
Present on cell wall or
Inside the cell
To which drug binds, interacts and
produces action
• Drug[D]+Receptor[R]↔D-R-Complex→Action
Eg. Adrenergic, Muscarinic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-14-320.jpg)

![endocrine and the sensory systems.
References:
G-Protein coupled[GPCR]
Ligand gated ion channels
Nuclear receptors
Enzymatic receptors
Receptor Super Families](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-17-320.jpg)

![Receptor Regulation
Downregulation Upregulation
• Prolonged use of agonists
[Salbutamol]
↓
Receptor no. and sensitivity
[β2 receptors] ↓ ↓
↓
Drug effect ↓ ↓
[Decreased effect on chronic
use]
• Prolonged use of
antagonists
[Propranolol]
↓
Receptor no. and sensitivity
[β2 receptors] ↑↑
↓
[Sudden withdrawal →
Increased sensitivity of
adrenoreceptors→ Angina](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-19-320.jpg)



![Dose response
• Dose-Response relationship: Relationship
between Pharmacological effect and dose
[Concn.of drug at site of action]
• Graded or quantitative: As the dose
administered in a single sub or tissue is
increased, response increases in a graded
fashion
Graded
• Quantal or all or none: frequency with
which any drug evokes a all or none
response in a population
Quantal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-23-320.jpg)





![Combined effect of drugs
Indifferent Synergism Antagonism
One facilitates
the action of
other
One opposes the
action of other
Additive
Supra-additive
[Potentiation]
Competitive
Non-
competitive
Physical
Chemical
Physiological
Receptor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-29-320.jpg)







![Competitive[Surmountable] Noncompetitive[Unsurmountable]
1. Binds with the same site
on the receptor
2. Resembles the agonist
3. Surmountable by
incresing the concn. Of
agonist
4. Rightward shift of DRC
5. Eg.
Ach – atropine
Morphine - Naloxone
1. Binds to another site or
same site covalently
2. No resemblance
3. Not surmountable
4. Flattening of DRC
5. Eg.
Diazepam –Bicuculline
Phenoxybenzamine-
Noradrenaline
Antagonism](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pharmacodynamics-1-230426061019-42a4f138/85/PHARMACODYNAMICS-1-37-320.jpg)