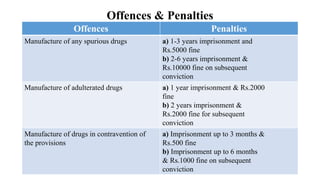
This document provides an overview of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act of 1940 and its rules of 1945 in India. It discusses the history and objectives of the act, key definitions, schedules, provisions around importing and manufacturing drugs, licensing requirements, and offenses and penalties. The act was implemented to regulate the drug industry and ensure safety, quality and standards through licensing and inspection. It covers allopathic, ayurvedic, siddha and unani medicines.