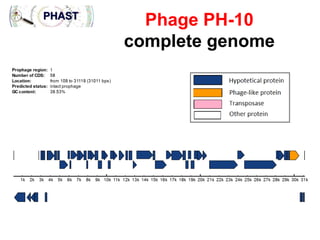
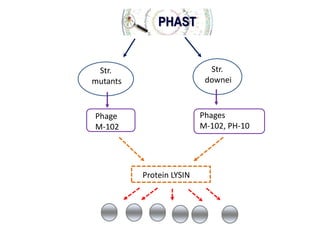
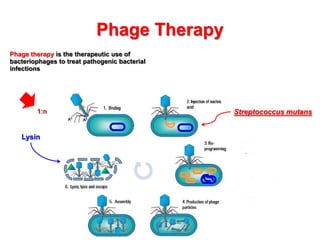
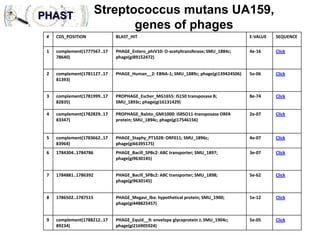
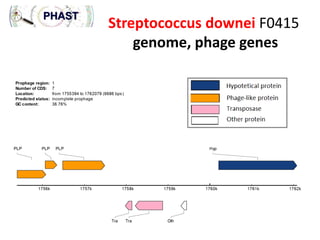
1) The document discusses using bacteriophages and their lysin proteins as a potential approach for dental medicine. It explores using synthetic bacteriophages engineered with lysin genes as a targeted treatment for the oral pathogen Streptococcus mutans, a primary cause of tooth decay.
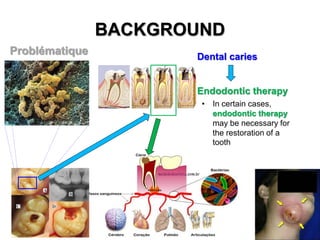
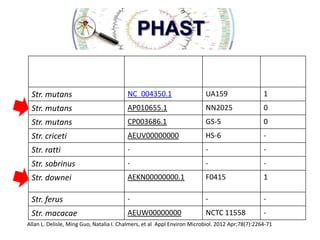
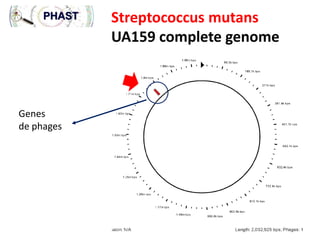
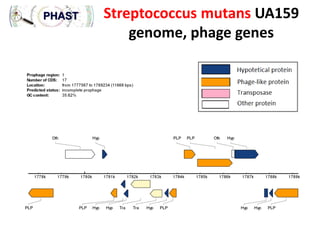
2) The background provides information on dental caries as the most prevalent chronic disease. It identifies S. mutans as the most important bacteria associated with tooth decay.
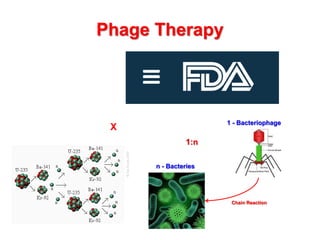
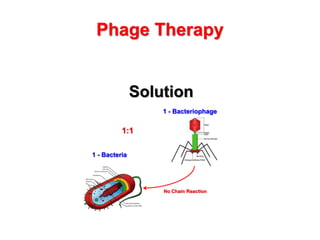
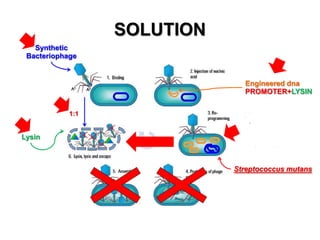
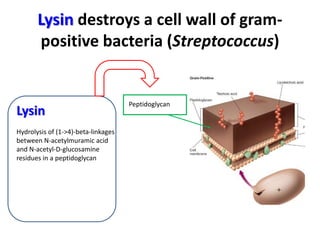
3) The solution proposes engineering a synthetic bacteriophage containing a lysin gene under a strong promoter for targeted killing of S. mutans. The engineered lysin would destroy the cell wall of gram-positive S. mutans bacteria.







![Result BLAST
endolysin phage M-102
•lysin [Streptococcus mutans]
•NCBI Reference Sequence: WP_002287207.1
•LOCUS WP_002287207 171 aa linear BCT 12-MAY-2013
•DEFINITION lysin [Streptococcus mutans].
•ACCESSION WP_002287207 VERSION WP_002287207.1 GI:488215999
•SOURCE Streptococcus mutans
•ORGANISM Streptococcus mutans Bacteria; Firmicutes; Bacilli; Lactobacillales;
Streptococcaceae; Streptococcus.
•COMMENT REFSEQ: This record represents a single, non-redundant, protein sequence which
may be annotated on many different RefSeq genomes from the same, or different, species.
•FEATURES Location/Qualifiers source 1..171 /organism="Streptococcus mutans"
/db_xref="taxon:1309" Protein 1..171 /product="lysin" /calculated_mol_wt=18727 Region
54..165 /region_name="CHAP" /note="CHAP domain; pfam05257" /db_xref="CDD:218523"
•ORIGIN 1
•mlkktltflg lsvgllivsp hanahtsrlt ldqtnelytr laaegrgvdt dqqygmqcvd 61 idtdltnnyv gvpisgnaid
lldsaraagy eivpaskppr agdlfvmdts tvyghpfght 121 gyiyrvnpdg sfetveqnvg ddsnlytgtv
akfmhrtrdy mlgyirlayr k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phagosodonto-131205101953-phpapp02/85/Phagos-odonto-25-320.jpg)