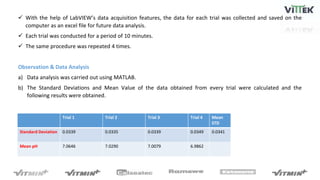
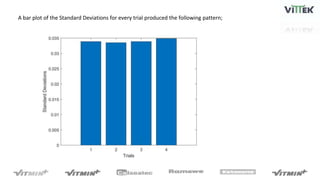
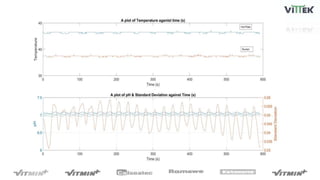
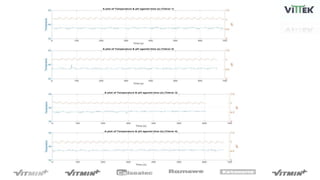
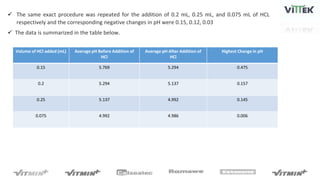
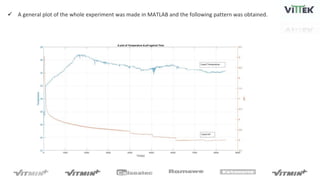
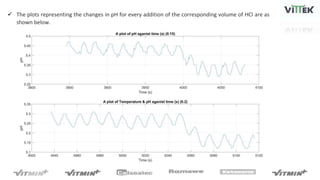
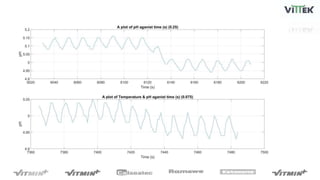
The pH sensor was tested for repeatability, accuracy, and resolution. For repeatability, measurements of a pH 7 solution were taken over 4 trials and analyzed. The standard deviation between trials was 0.0341 and the mean pH values were close to 7. For accuracy, the sensor measured a pH 6.17 solution as pH 7, indicating relatively poor accuracy. The resolution test found the smallest detectable pH change was around 0.006 pH units when 0.075mL of HCl was added.