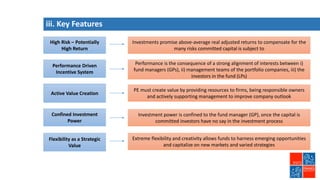
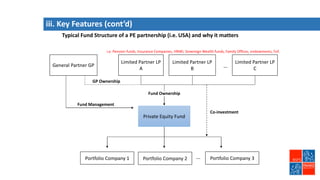
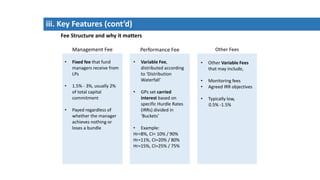
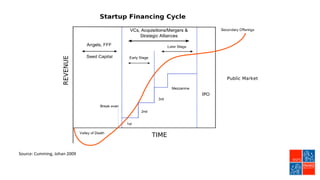
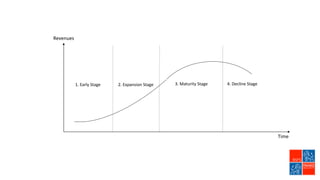
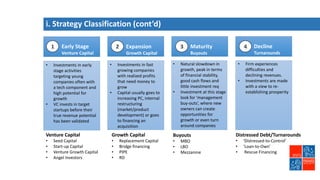
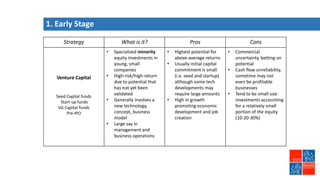
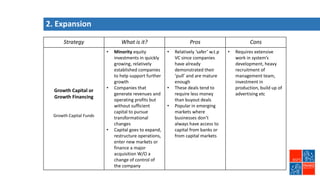
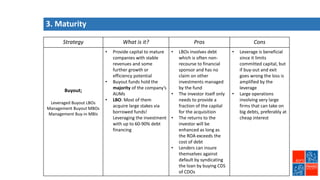
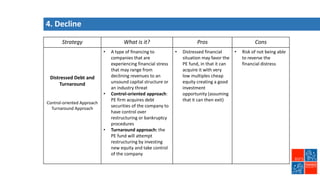
Private equity involves investing in companies that are not publicly traded, with the goal of improving financial performance and selling at a profit. There are various private equity strategies based on a company's stage of development, including venture capital for early stage companies, growth capital for fast-growing firms, buyouts of mature companies, and distressed debt investments in struggling firms. While high risk, private equity aims to generate above-average returns. Most exits are trade sales to other companies in the same industry, rather than initial public offerings. Private equity requires active involvement to create value through specialization, flexibility, and strong performance incentives.