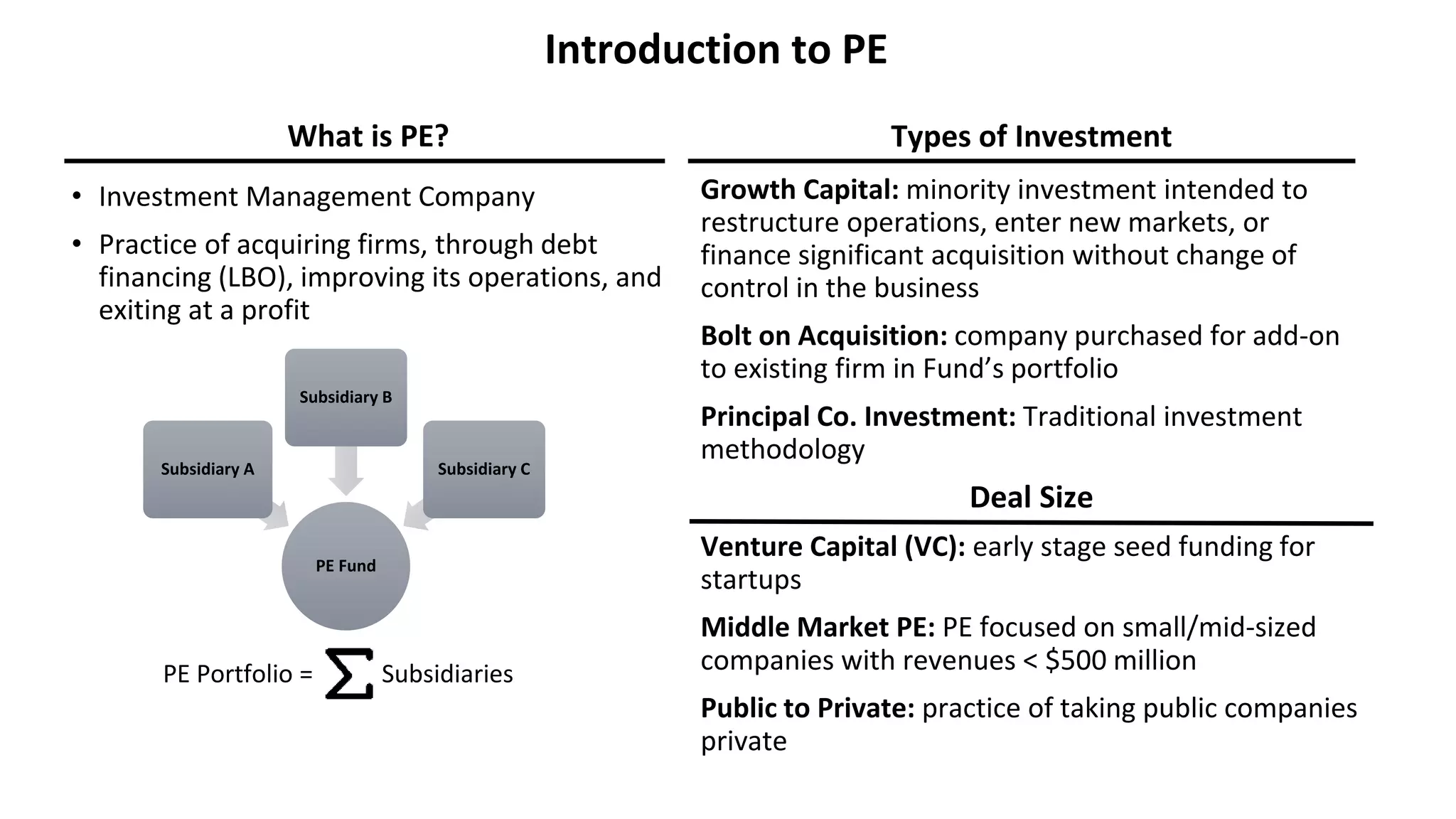
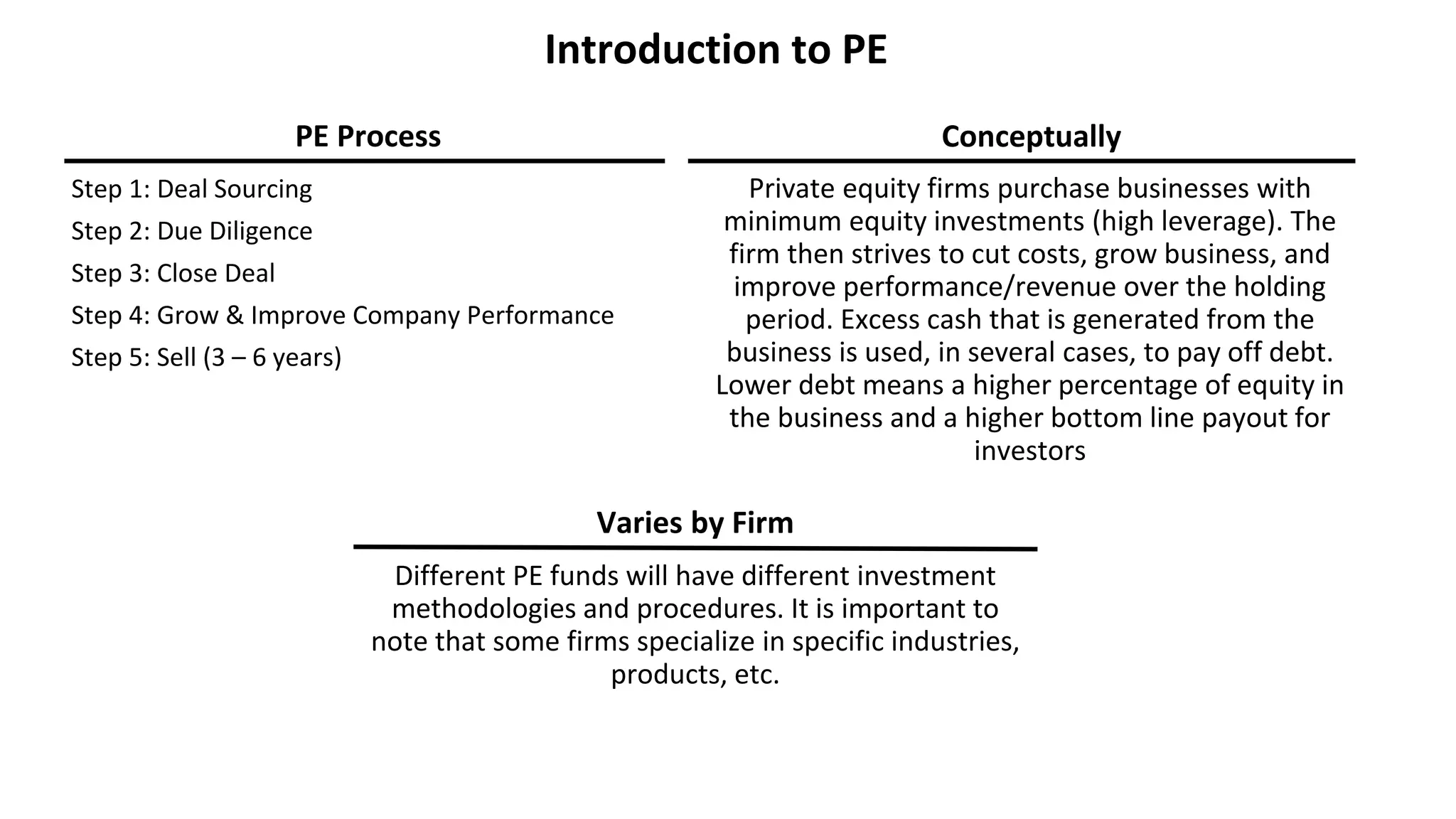
This document provides an introduction to private equity (PE). It defines PE as investment management companies that practice acquiring firms through debt financing (leveraged buyouts or LBOs), improving their operations, and exiting at a profit. PE funds look for companies with stable cash flows, low cyclicality, growing industries, sustainable competitive advantages, and low capital expenditures. The PE process typically involves deal sourcing, due diligence, closing the deal, growing the company's performance over 3-6 years, and then selling the company. Leveraged buyouts involve acquiring companies primarily through debt financing to provide higher returns with minimal equity investments. Debt financing for LBOs includes senior secured bank debt and subordinated mezzanine financing