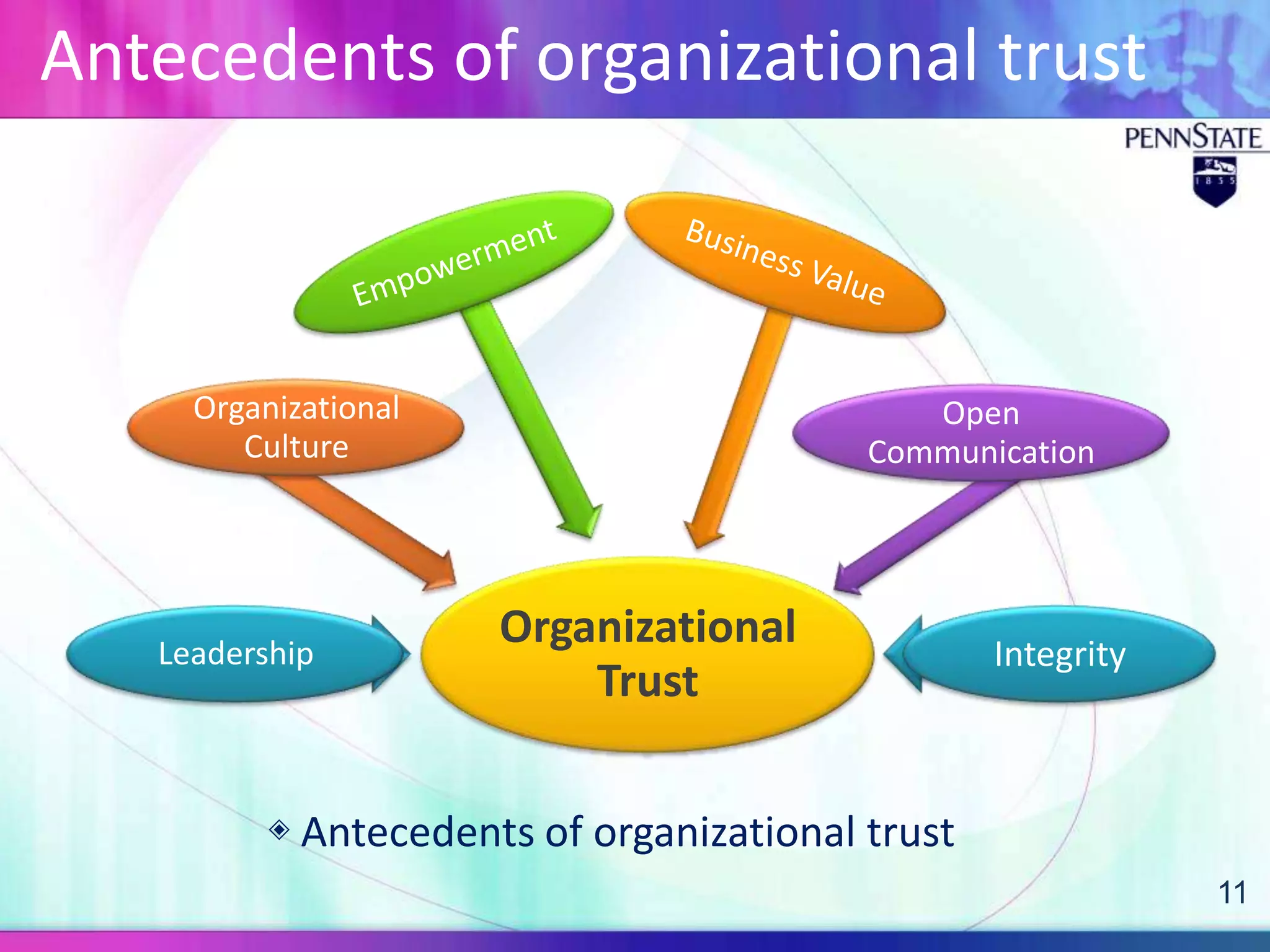
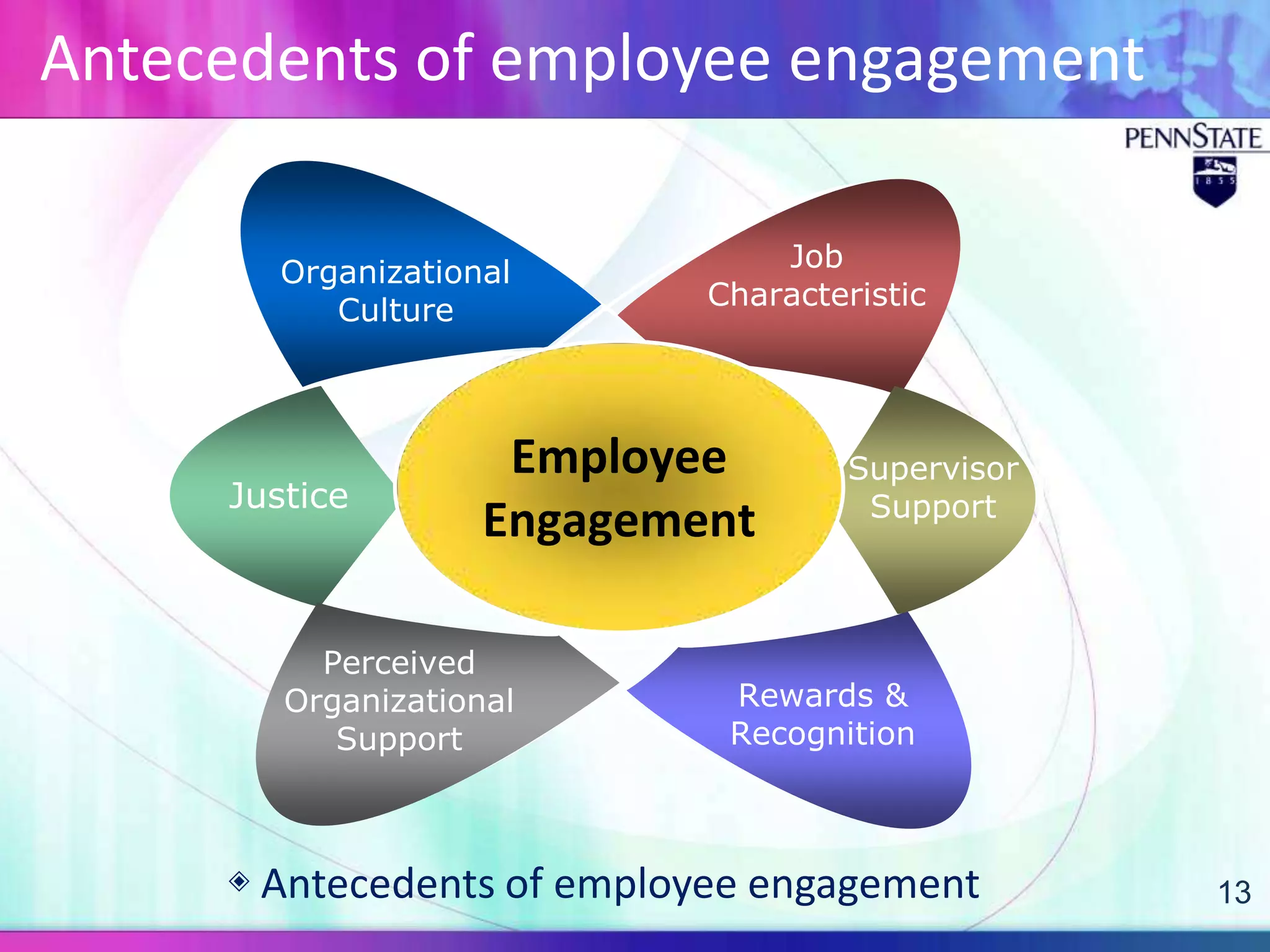
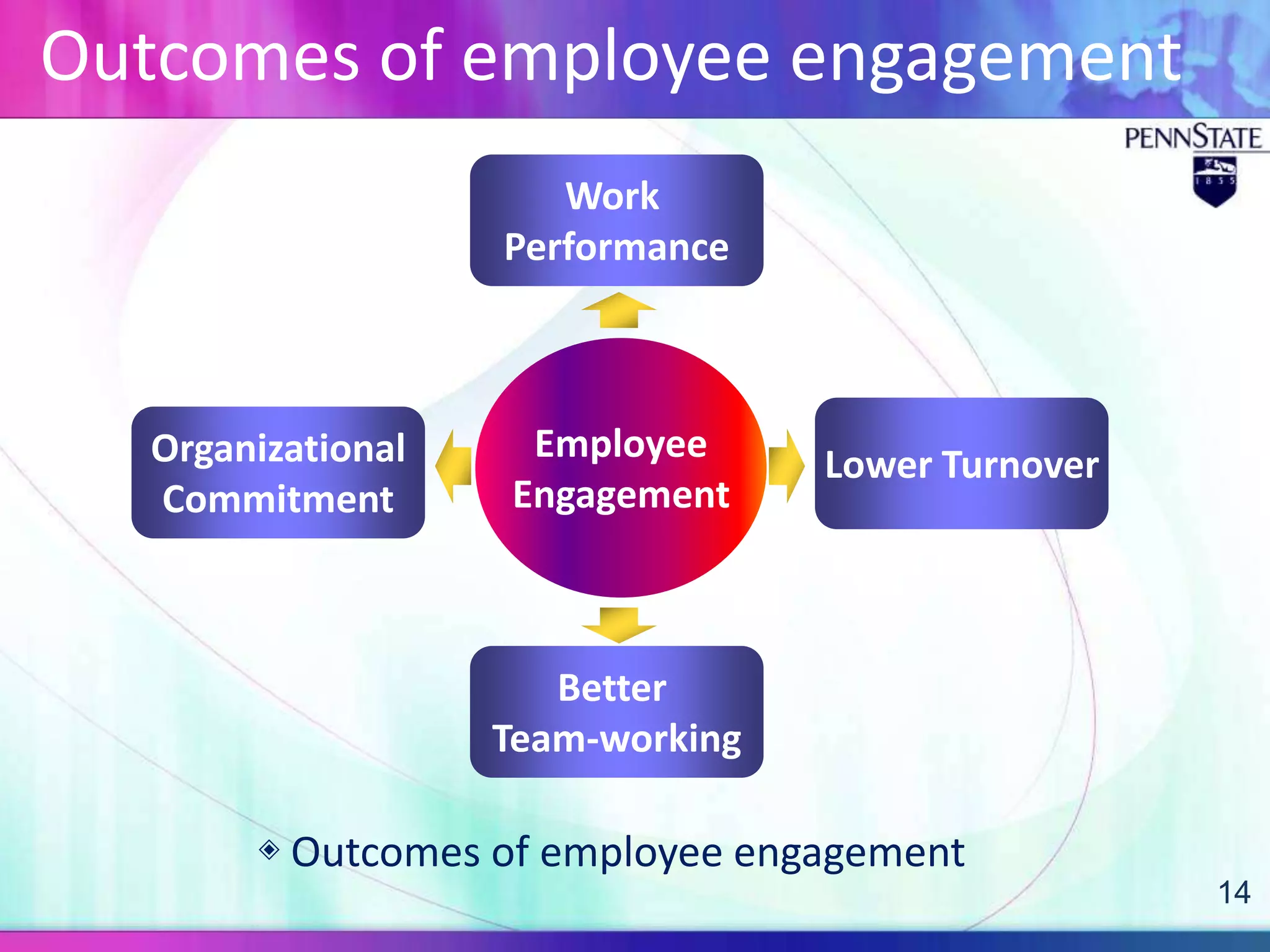
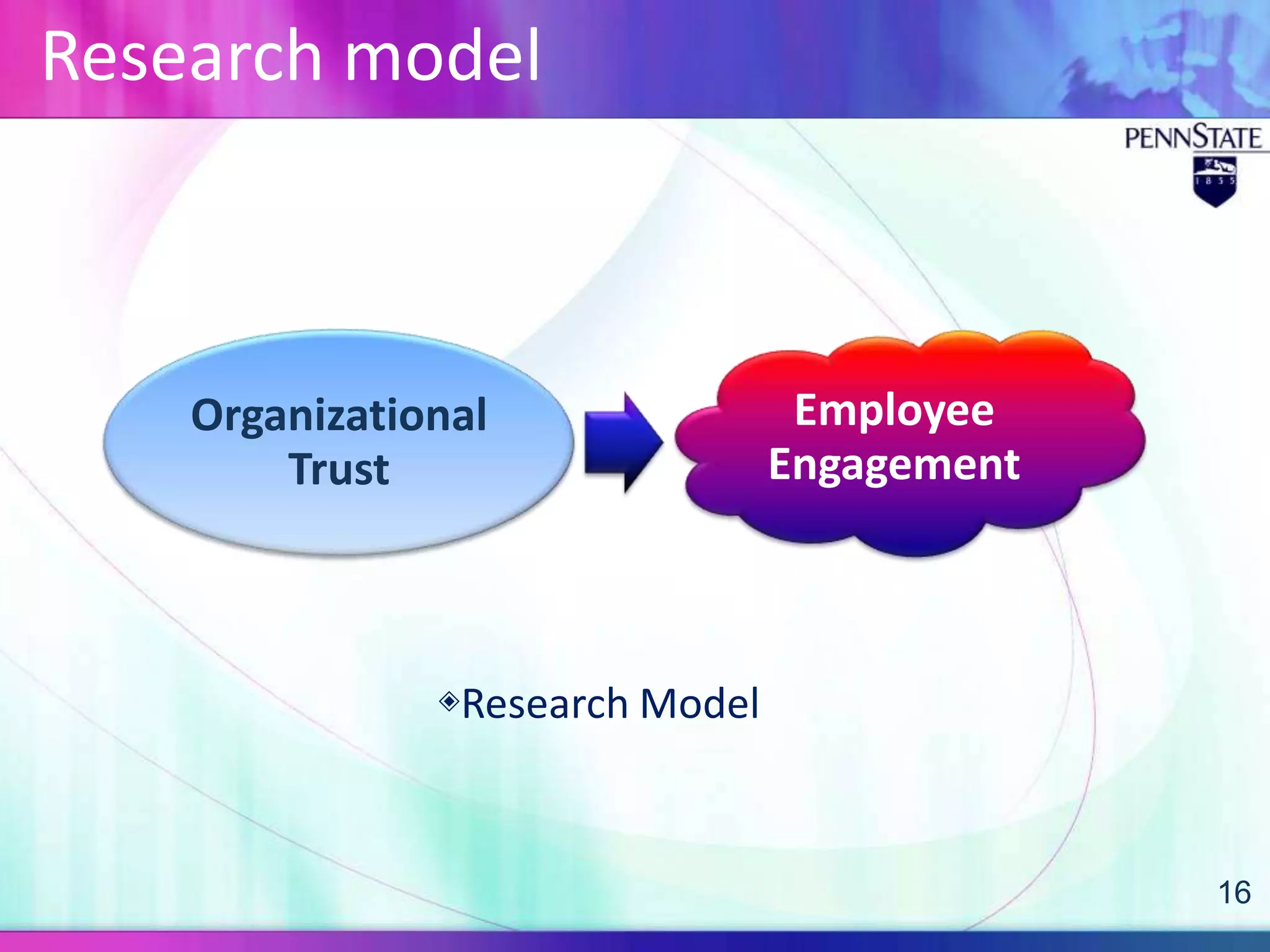
This document discusses organizational trust and employee engagement. It provides definitions of organizational trust as an employee's confidence in an organization, and employee engagement as a positive work-related state of mind. The significance of both constructs is explored, with organizational trust linked to effectiveness, and employee engagement predicting outcomes like performance and commitment. Antecedents and outcomes of organizational trust and employee engagement are presented in models. The research question examines the relationship between organizational trust and employee engagement in a Korean business context, with a quantitative methodology proposed.