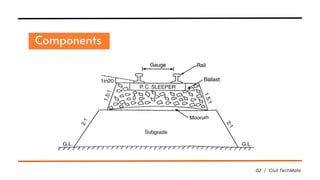
A permanent way refers to the infrastructure of rails, sleepers, ballast, and subgrade that supports train operations, contrasting with temporary tracks used for construction. Key requirements for a permanent way include uniform gauge, level rails, proper load distribution, well-designed curves for passenger comfort, effective drainage, and ease of maintenance. These factors are crucial to ensure safety, durability, and efficiency in railway systems.