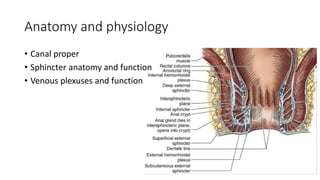
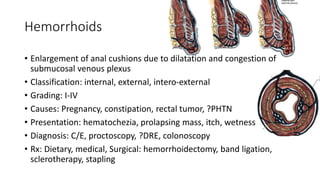
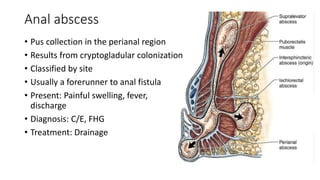
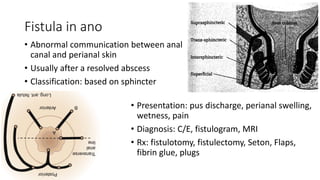
The document discusses various benign perianal diseases, including hemorrhoids, anal abscesses, fistulas, pilonidal disease, fissures, rectal prolapse, and pruritus ani. It covers definitions, anatomical considerations, common presentations, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for each condition. The lecture aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the perianal region and its associated diseases.