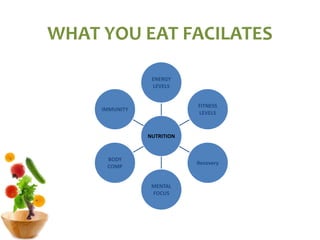
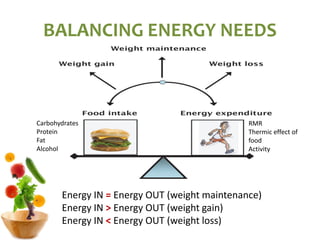
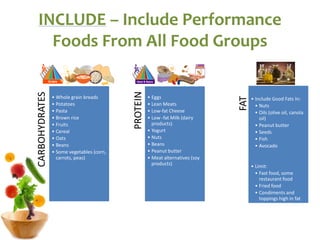
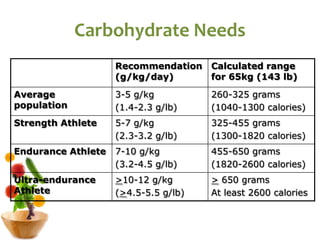
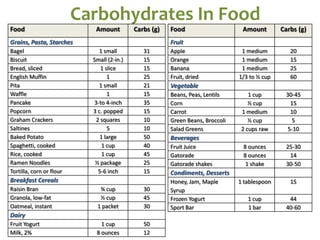
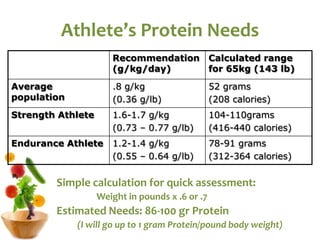
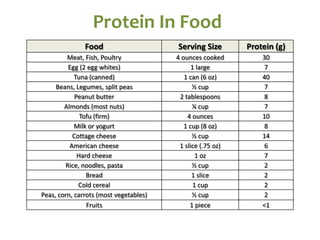
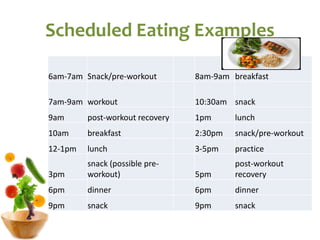
The document covers the essentials of performance nutrition, emphasizing the significant impact of nutrition on fitness and recovery, with a model suggesting that body shape is influenced by 50% nutrition, 40% workout, and 10% genetics. It provides guidelines for healthy eating, including moderation, balance, variety, and specific recommendations for macronutrients and hydration, along with strategies for fueling before, during, and after workouts. Additionally, it highlights the importance of meal timing, hydration, and the need to approach dietary supplements with caution.