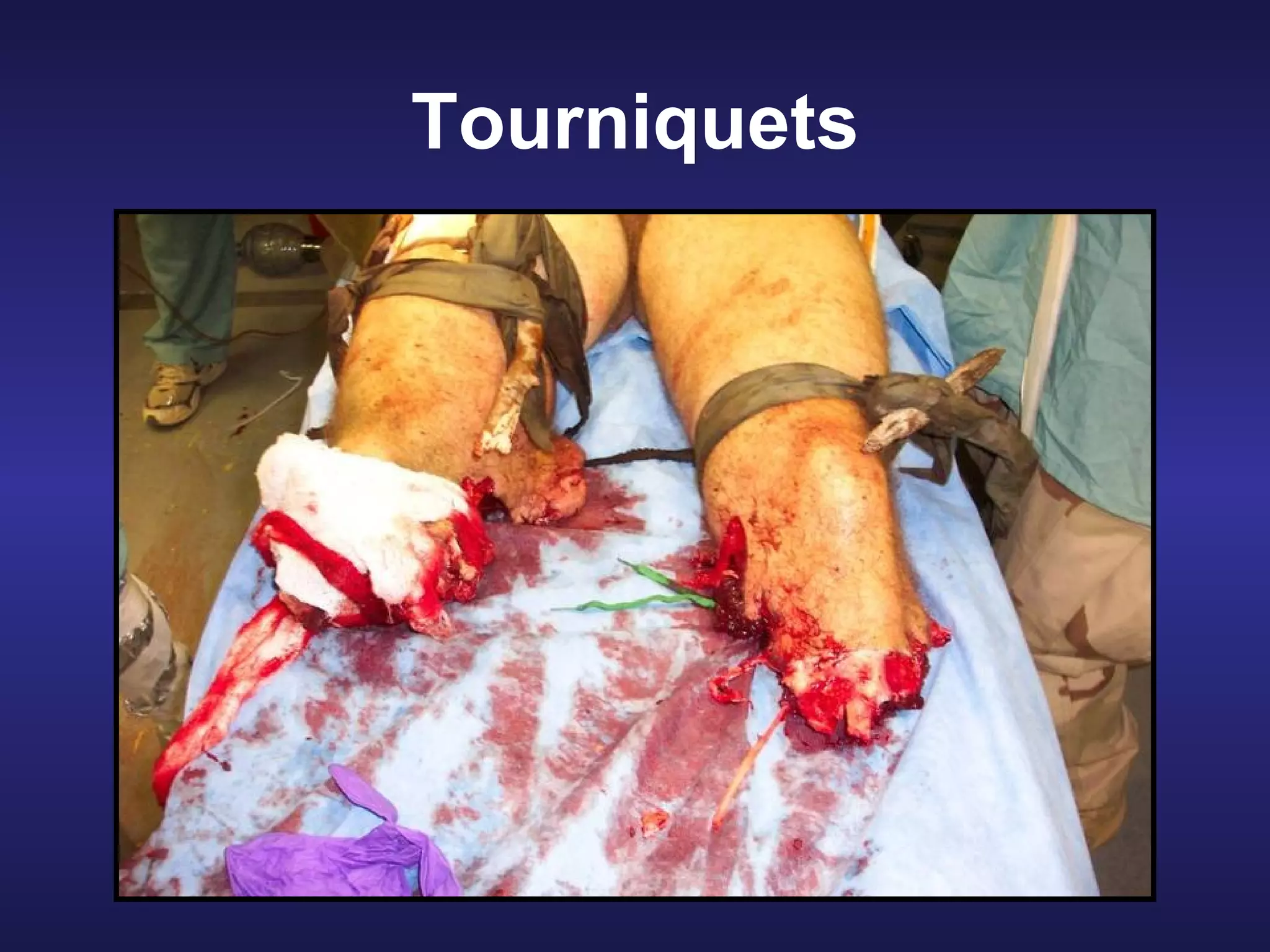
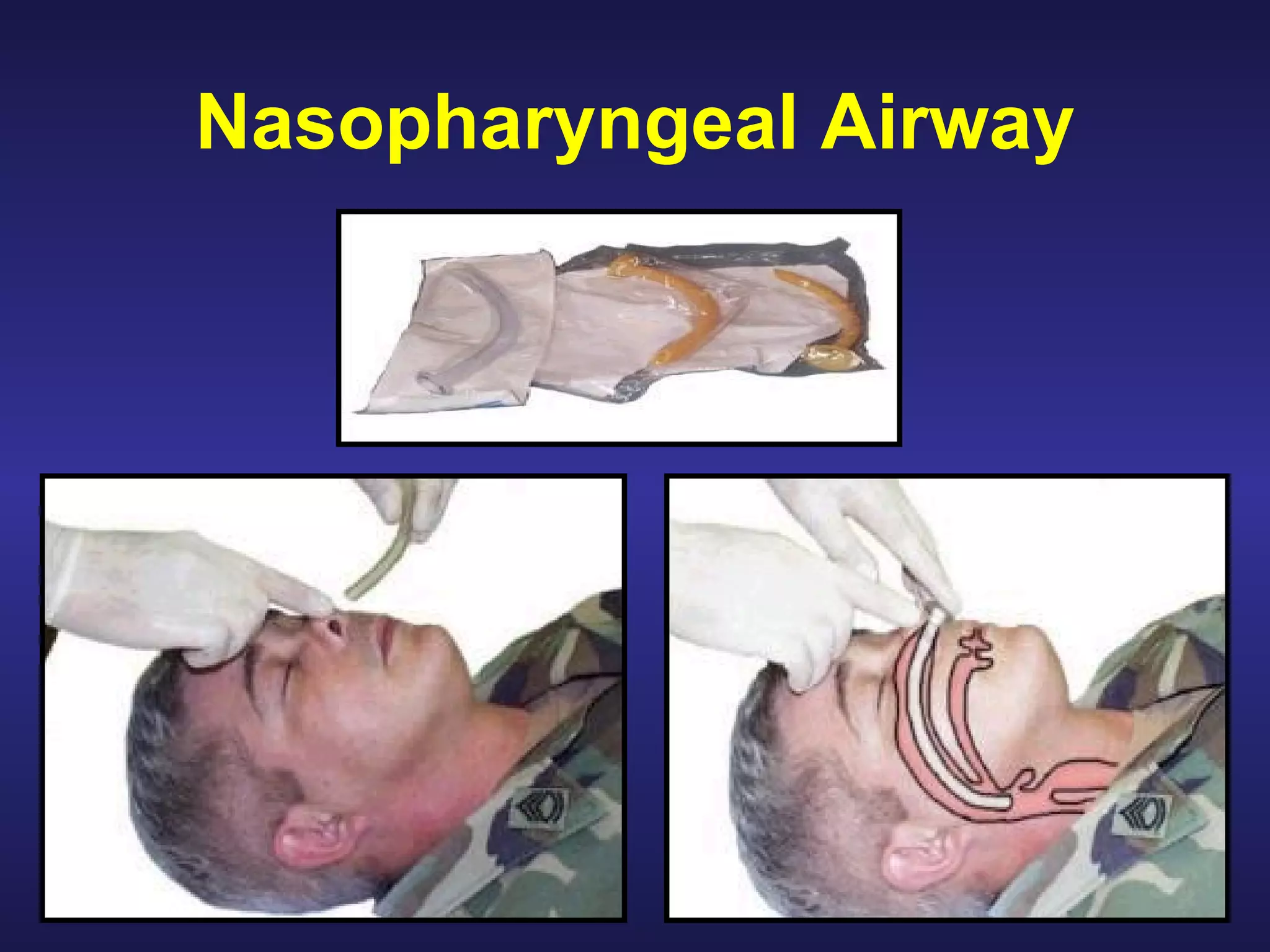
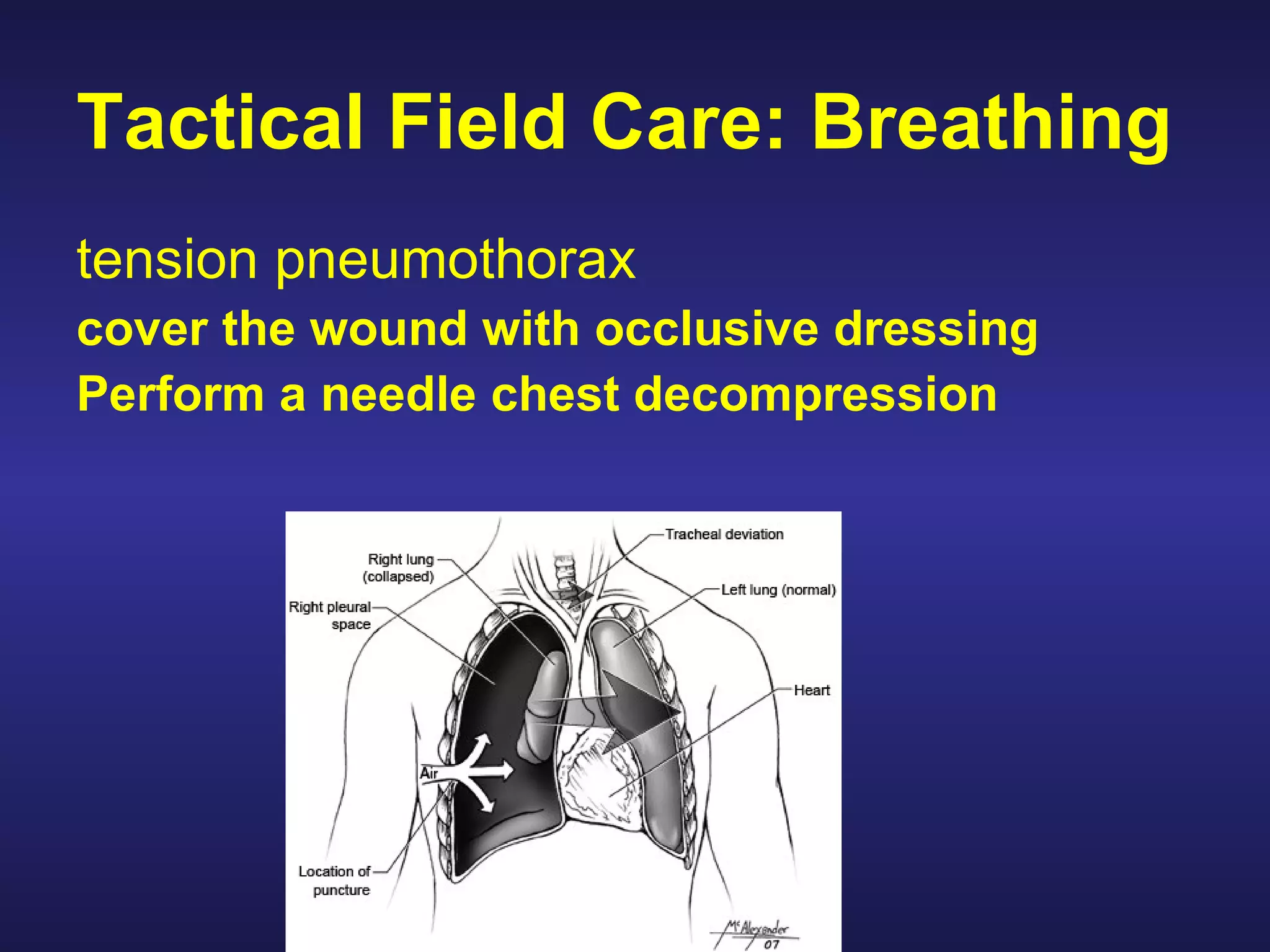
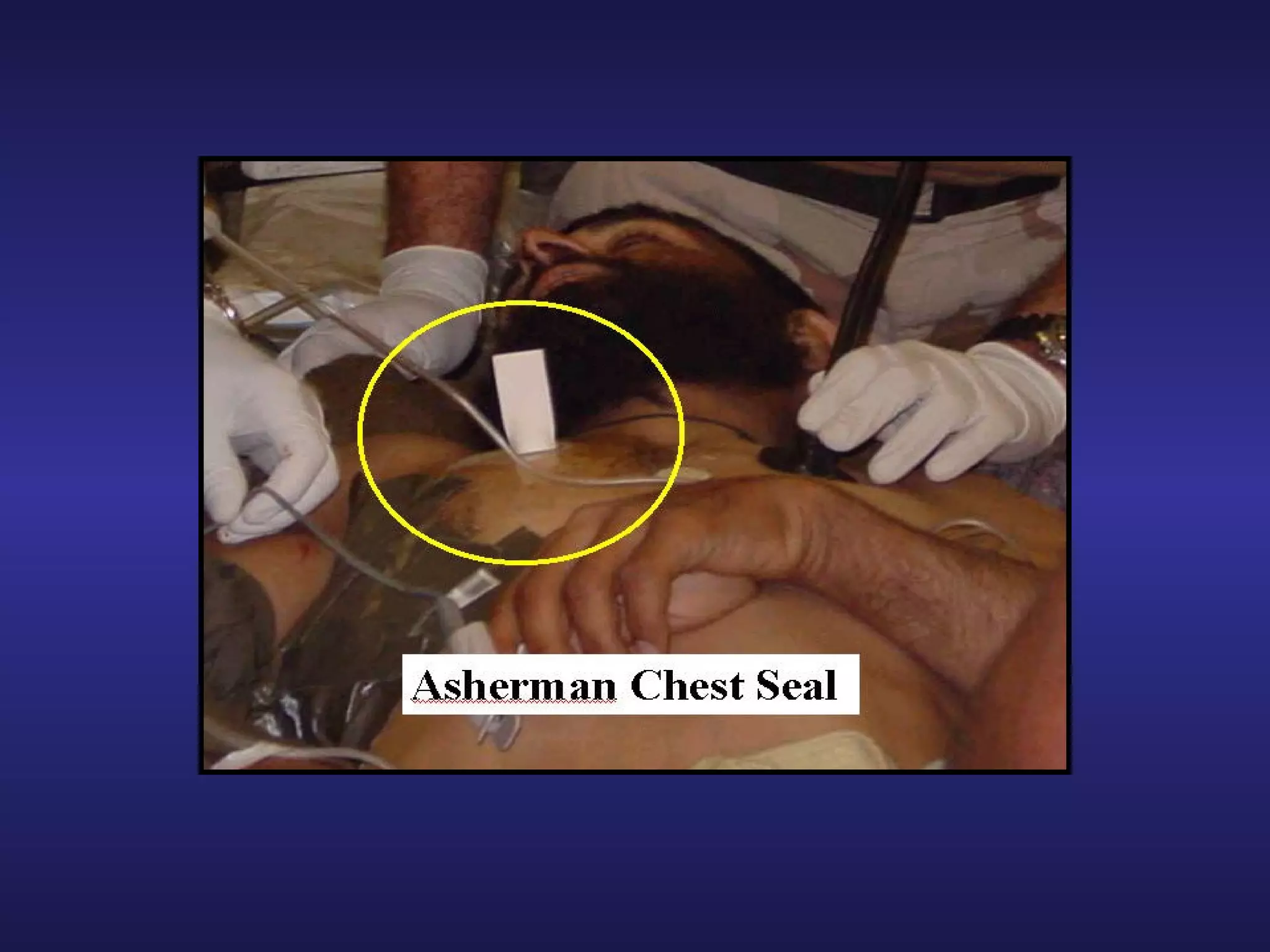
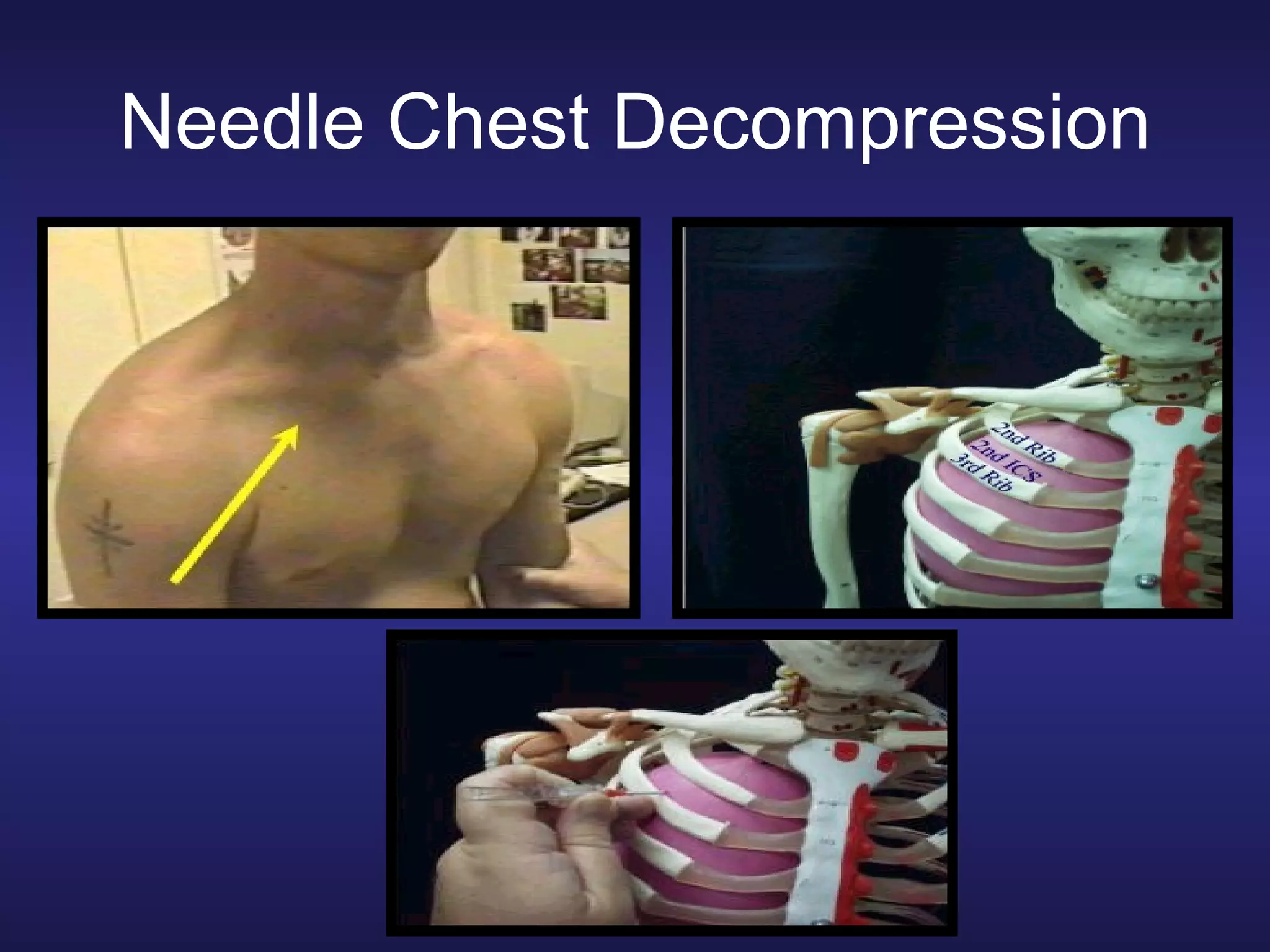
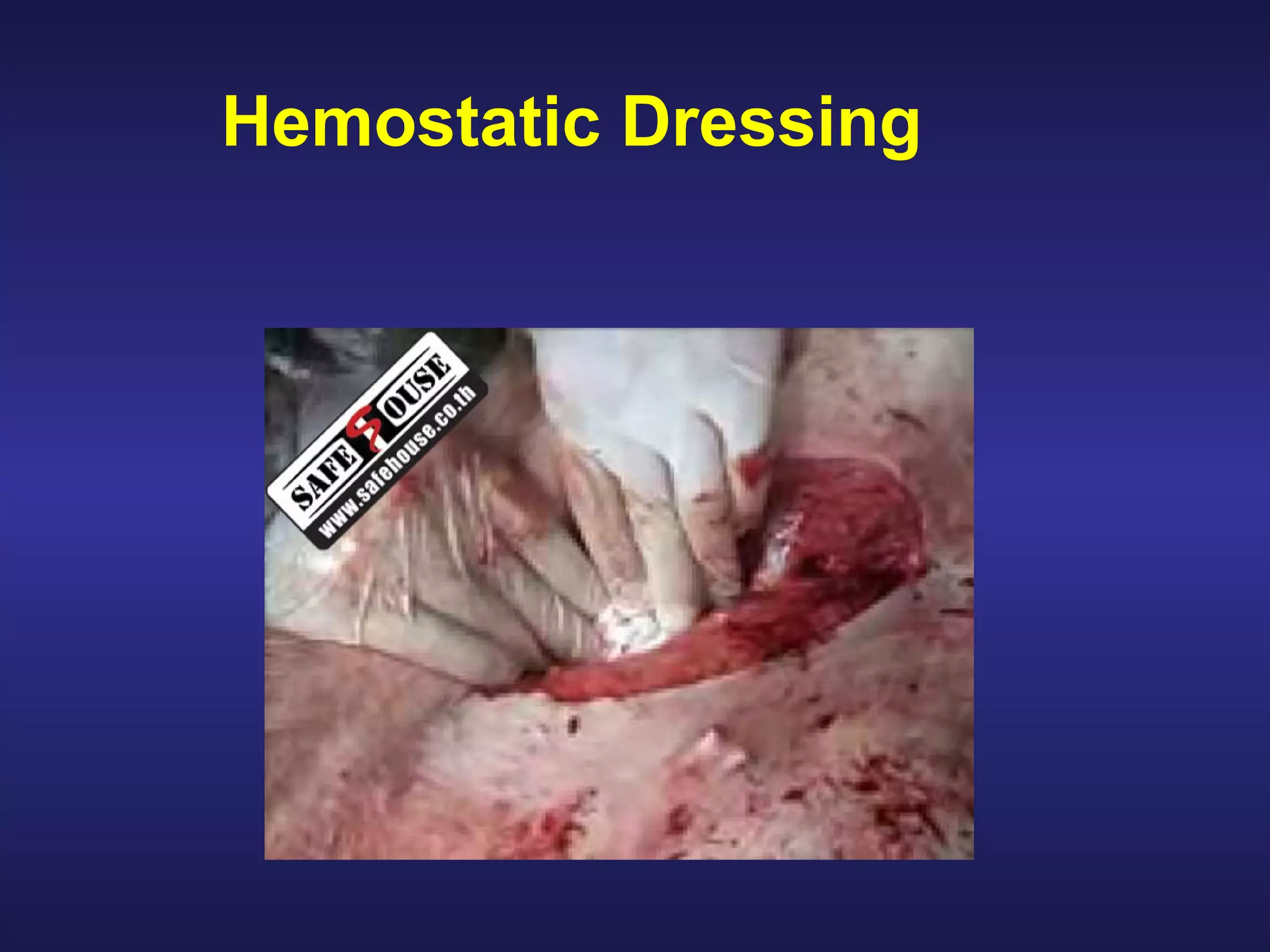
Over 2500 soldiers died in the Vietnam conflict due to blood loss from wounds to the arms and legs despite having no other serious injuries. As a combat lifesaver, one's primary mission is combat duties, but rendering medical care is secondary when it does not jeopardize the primary mission. For care under fire, if a casualty can return fire or move to safety, direct them to do so or tell them to play dead if unable; do not attempt CPR for casualties without signs of life. Prompt use of tourniquets in this phase may save lives since hemorrhaging from extremities is a leading cause of preventable combat death.