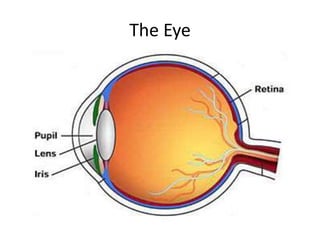
The document discusses how vision and perception work. It explains that light bounces off objects and enters the eyes, triggering a reaction in the retina that sends a signal along the optic nerve to the brain. The key parts of the eye are identified as the retina, rods, cones, and optic nerve. Rods detect low light and movement while cones detect fine details and color. The lesson objectives are to understand the parts of the eye and how they work.