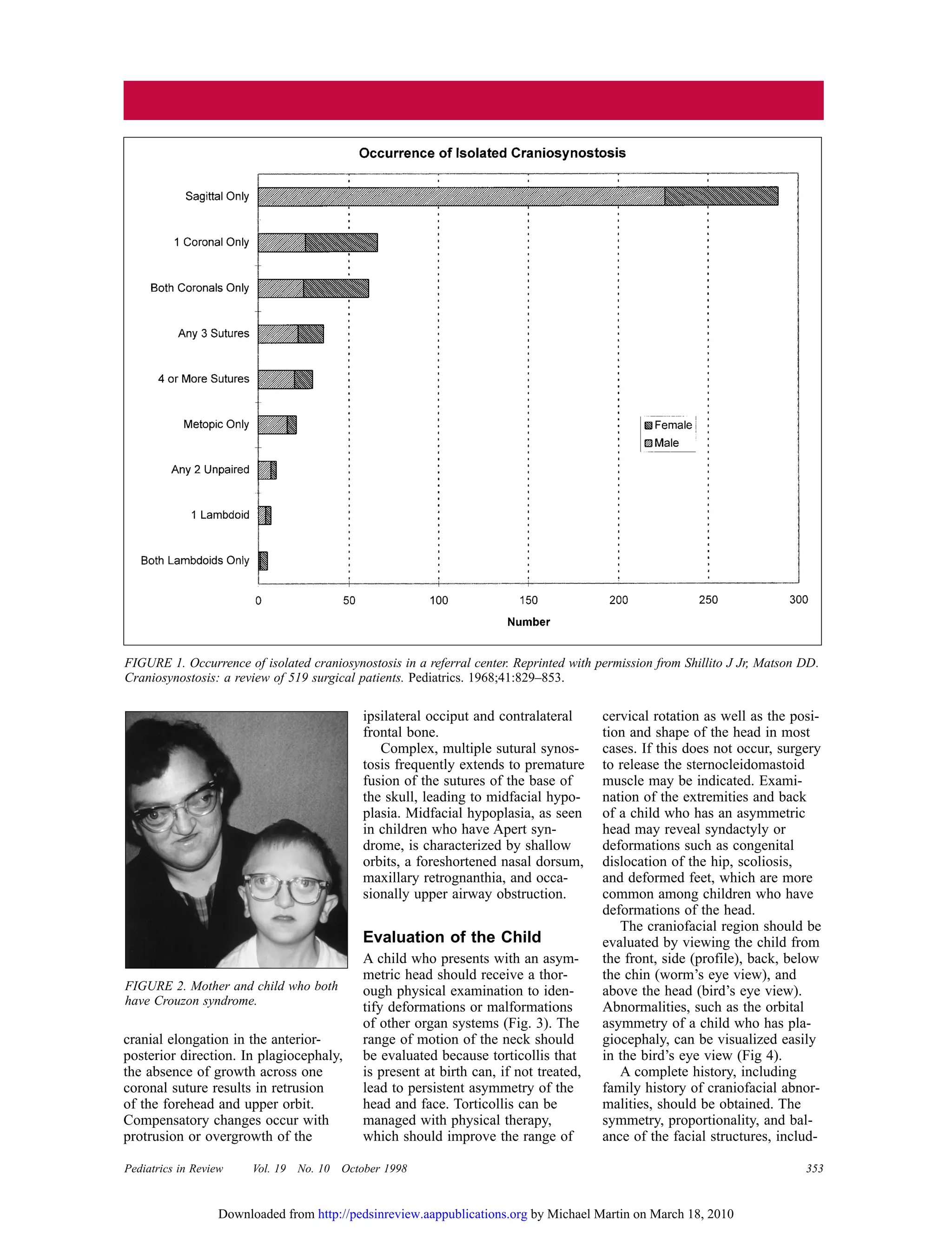
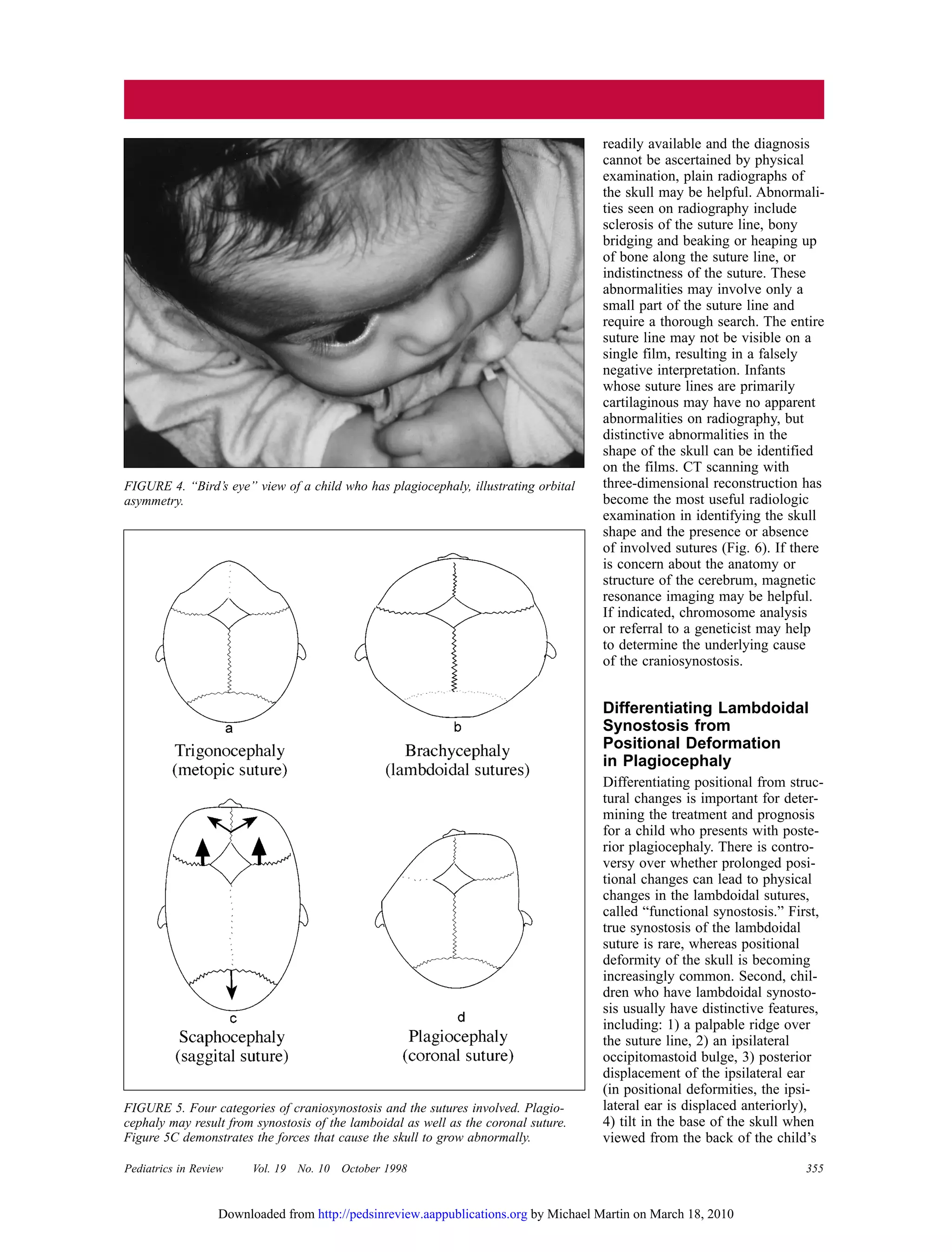
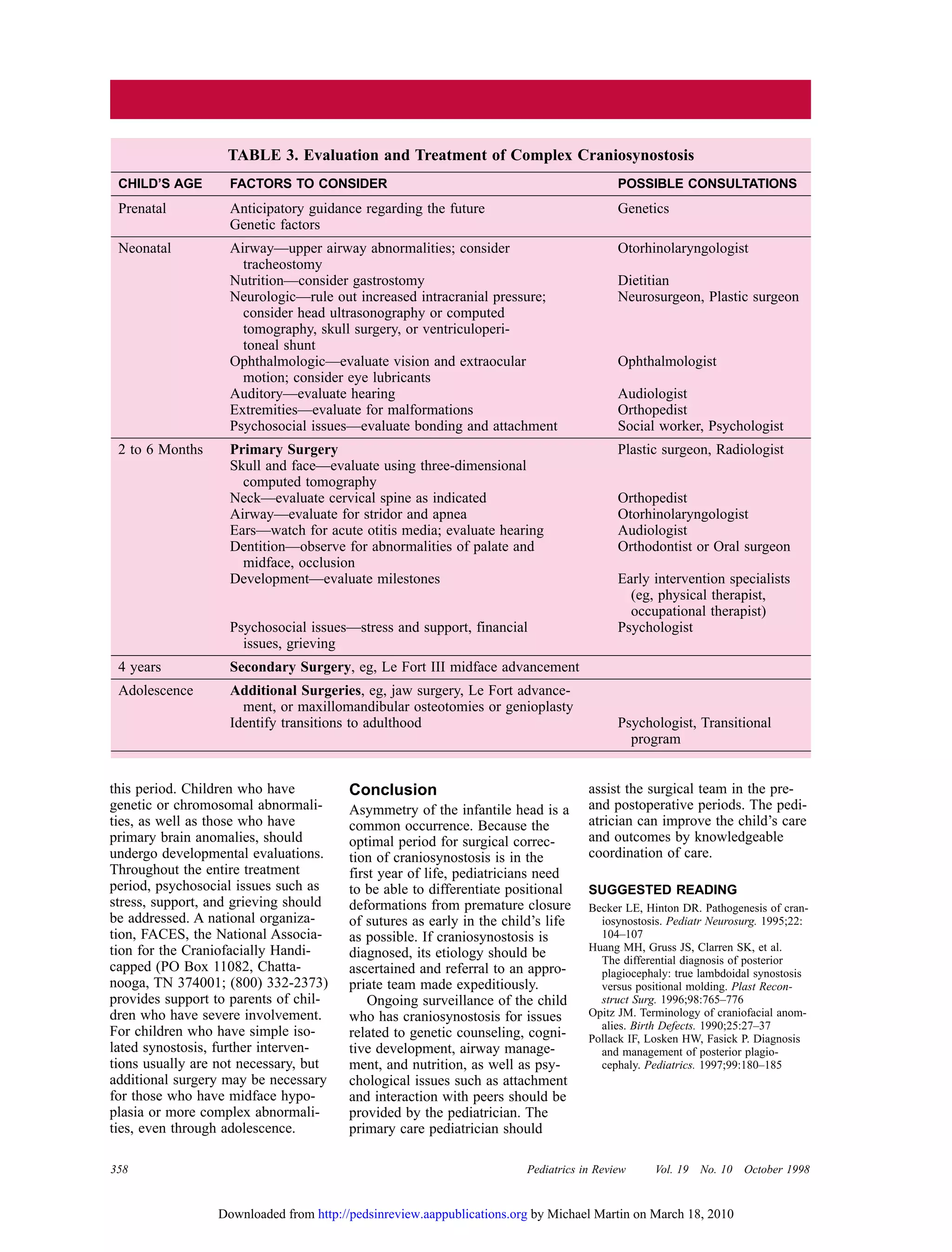
This document discusses craniosynostosis, which is the premature fusion of skull bones. It occurs in about 1 in 2,000 births. The document describes the evaluation and treatment of craniosynostosis, including physical examination, imaging tests, genetic testing, and surgical intervention if needed. Craniosynostosis can range from mild and cosmetic to severe, causing increased intracranial pressure. The document also discusses differentiating between positional skull deformities and true cranial bone fusion.