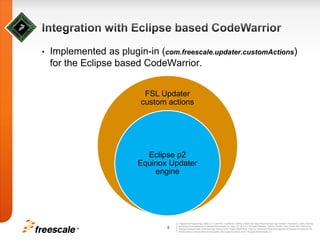
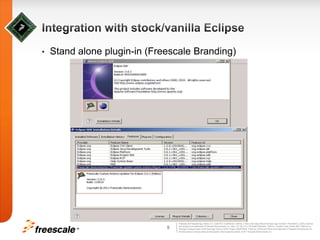
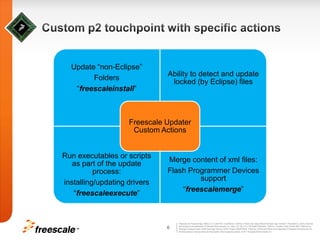
This document discusses extending the capabilities of the Eclipse p2 framework by adding custom installation steps. It describes implementing a custom p2 touchpoint and action for the CodeWarrior IDE to provide a "Multi User Install" capability. This allows installing Eclipse files in both administrator-level and user-level locations to support multiple users accessing the same installation. The goal is to continue enhancing the p2 updater functionality to better manage external Eclipse files, include uninstall support for external files, and synchronize with new p2 releases from the Eclipse project.




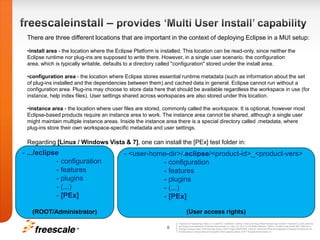

![instance area - the location where user files are stored, commonly called the workspace. It is optional, however most Eclipse-based products require an instance area to work. The instance area cannot be shared, although a single user might maintain multiple instance areas. Inside the instance area there is a special directory called .metadata, where plug-ins store their own workspace-specific metadata and user settings. Regarding [Linux / Windows Vista & 7], one can install the [PEx] test folder in:- .../eclipse - configuration - features - plugins - (...) - [PEx](ROOT/Administrator)- <user-home-dir>/.eclipse/<product-id>_<product-vers> - configuration - features - plugins - (...) - [PEx](User access rights)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/peeclipsedemocampbucharest2011-110628064612-phpapp02/85/Extend-Eclipse-p2-framework-capabilities-Add-your-custom-installation-steps-10-320.jpg)