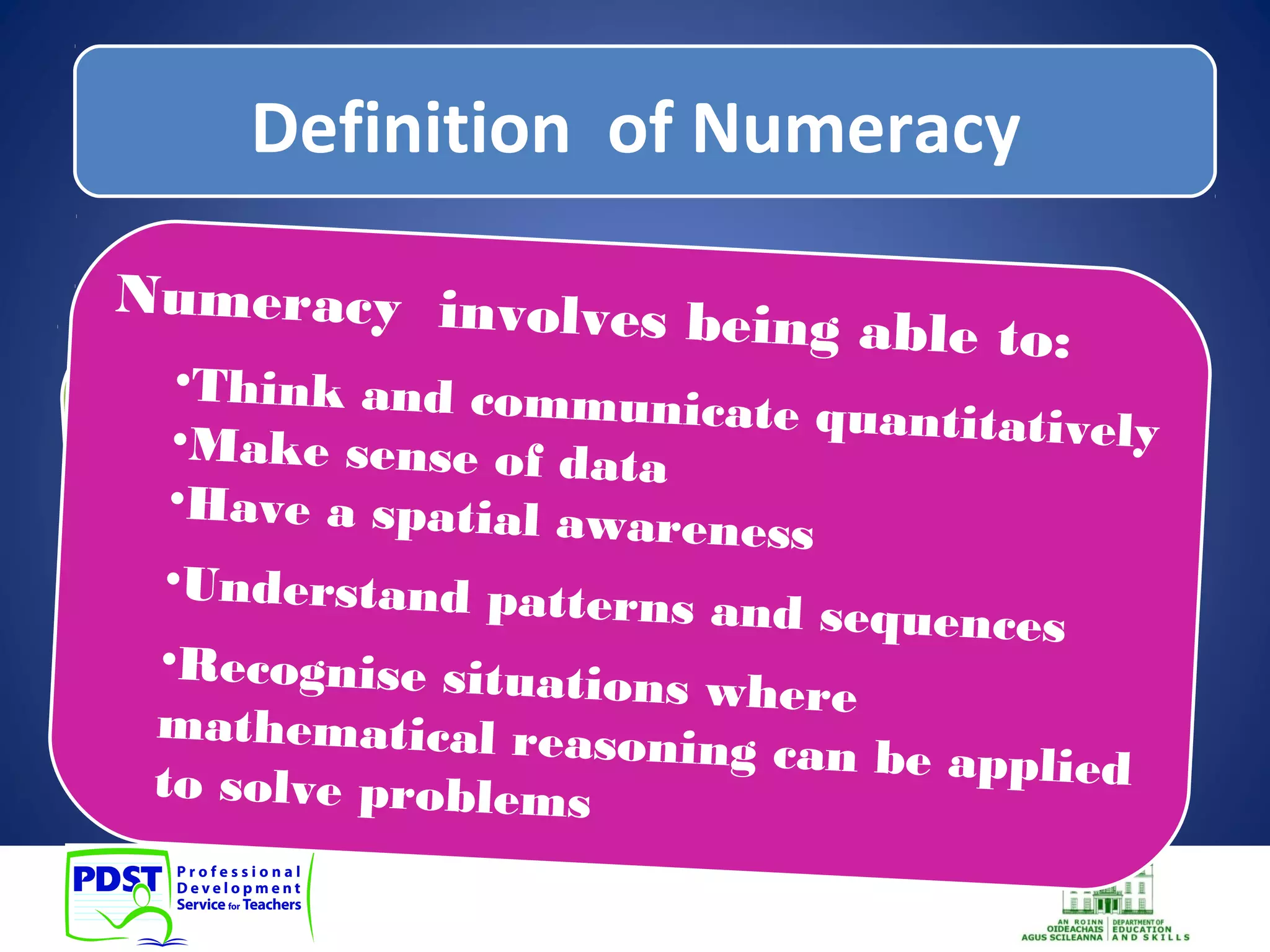
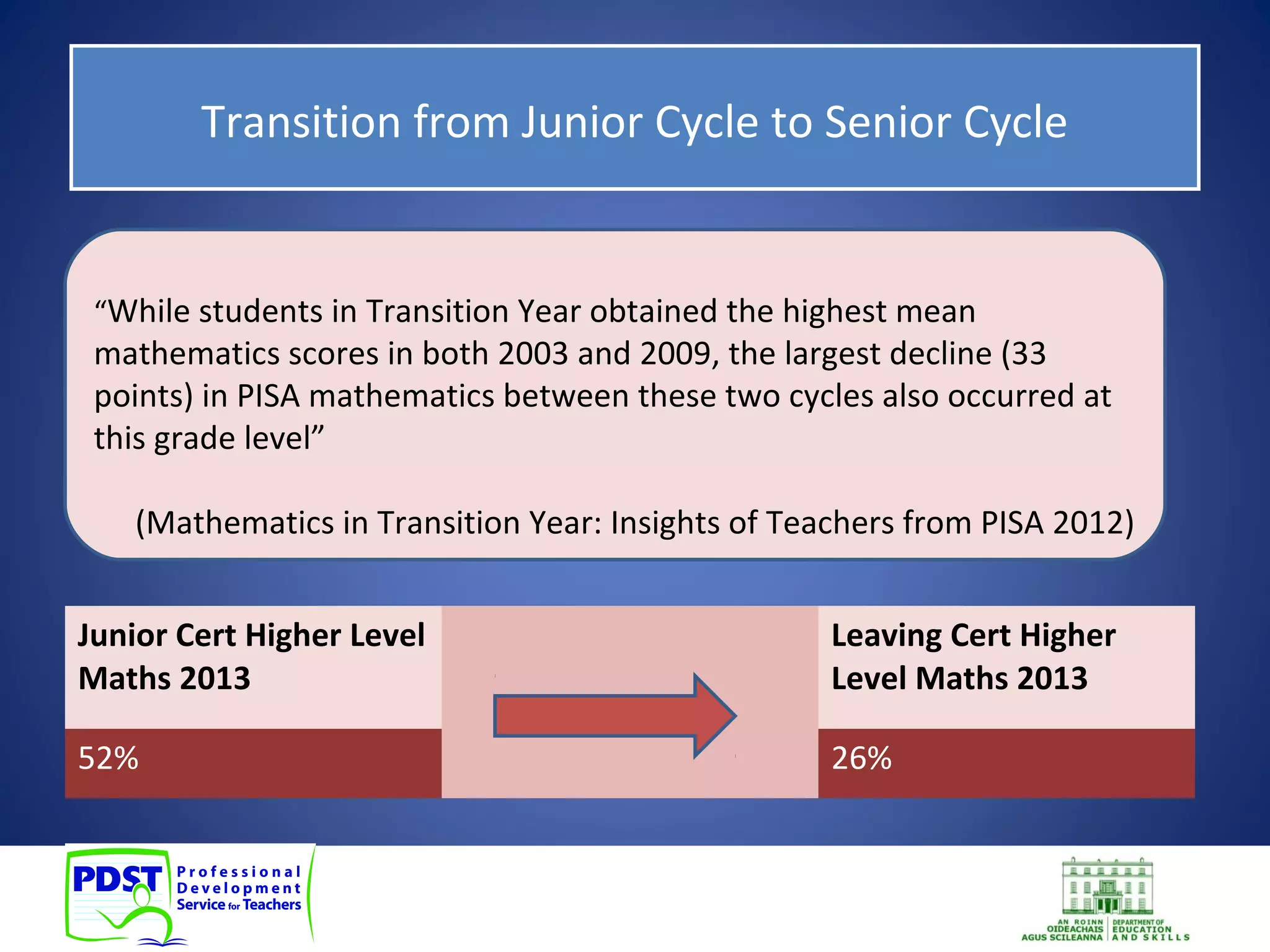
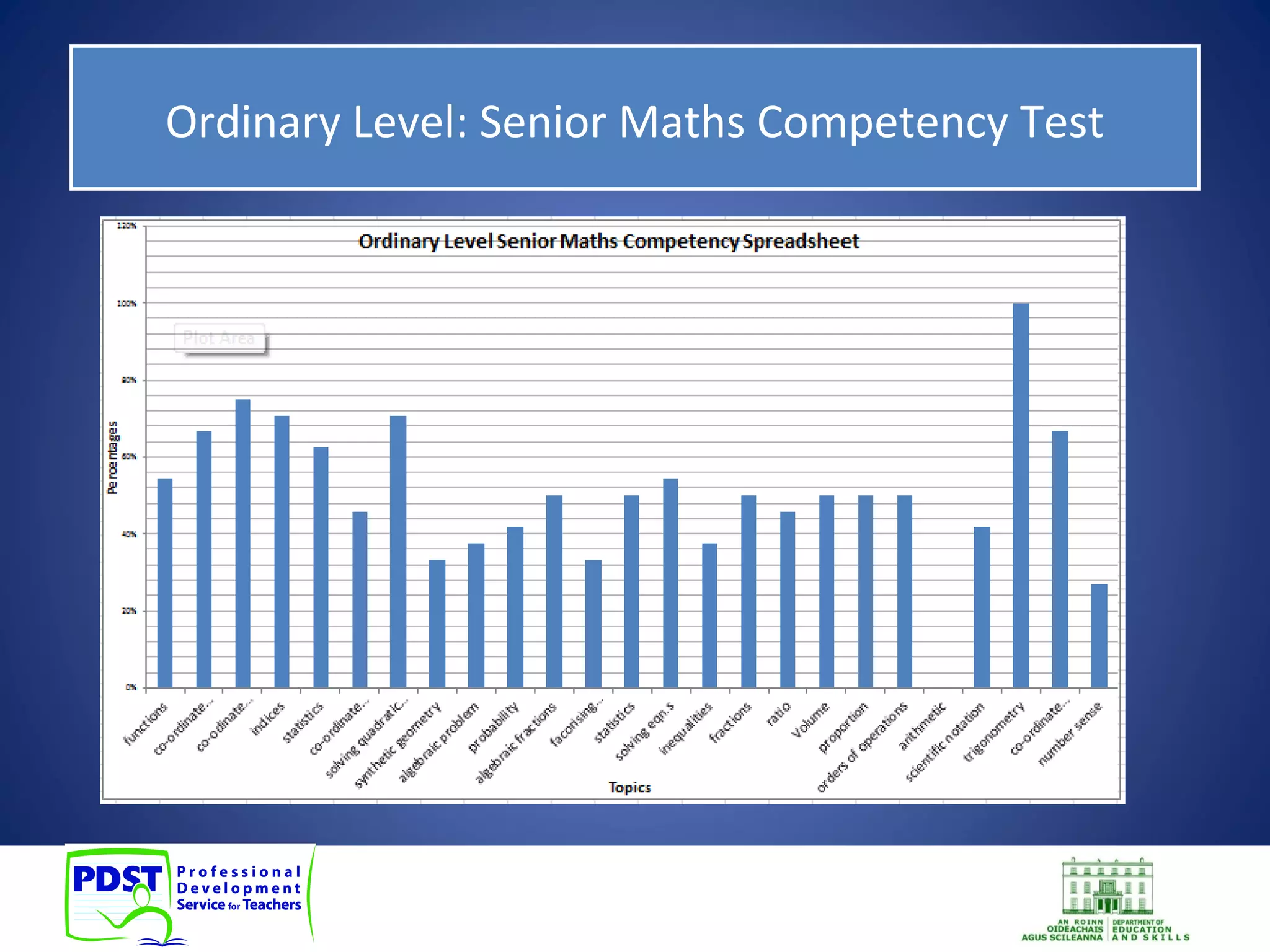
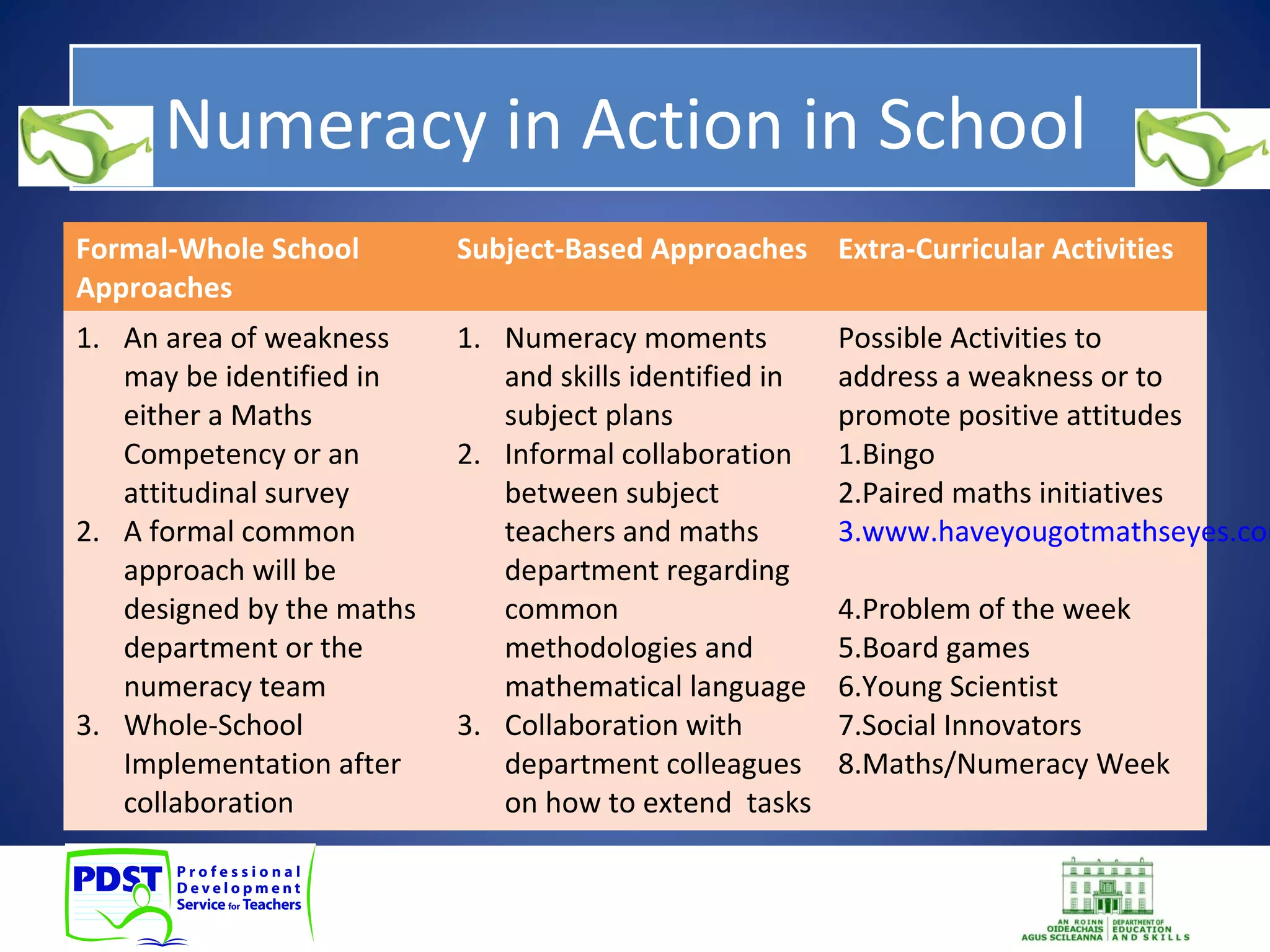
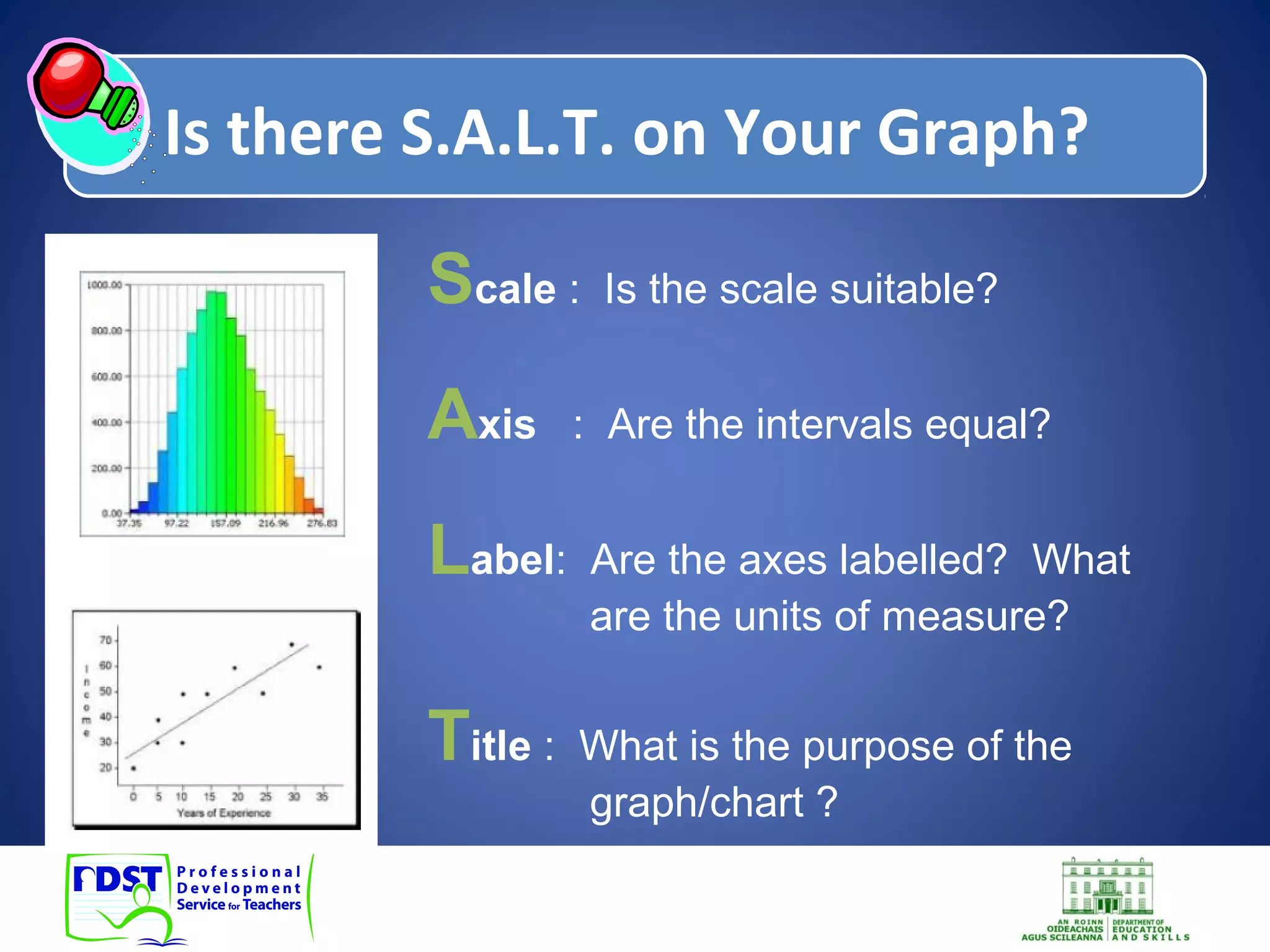
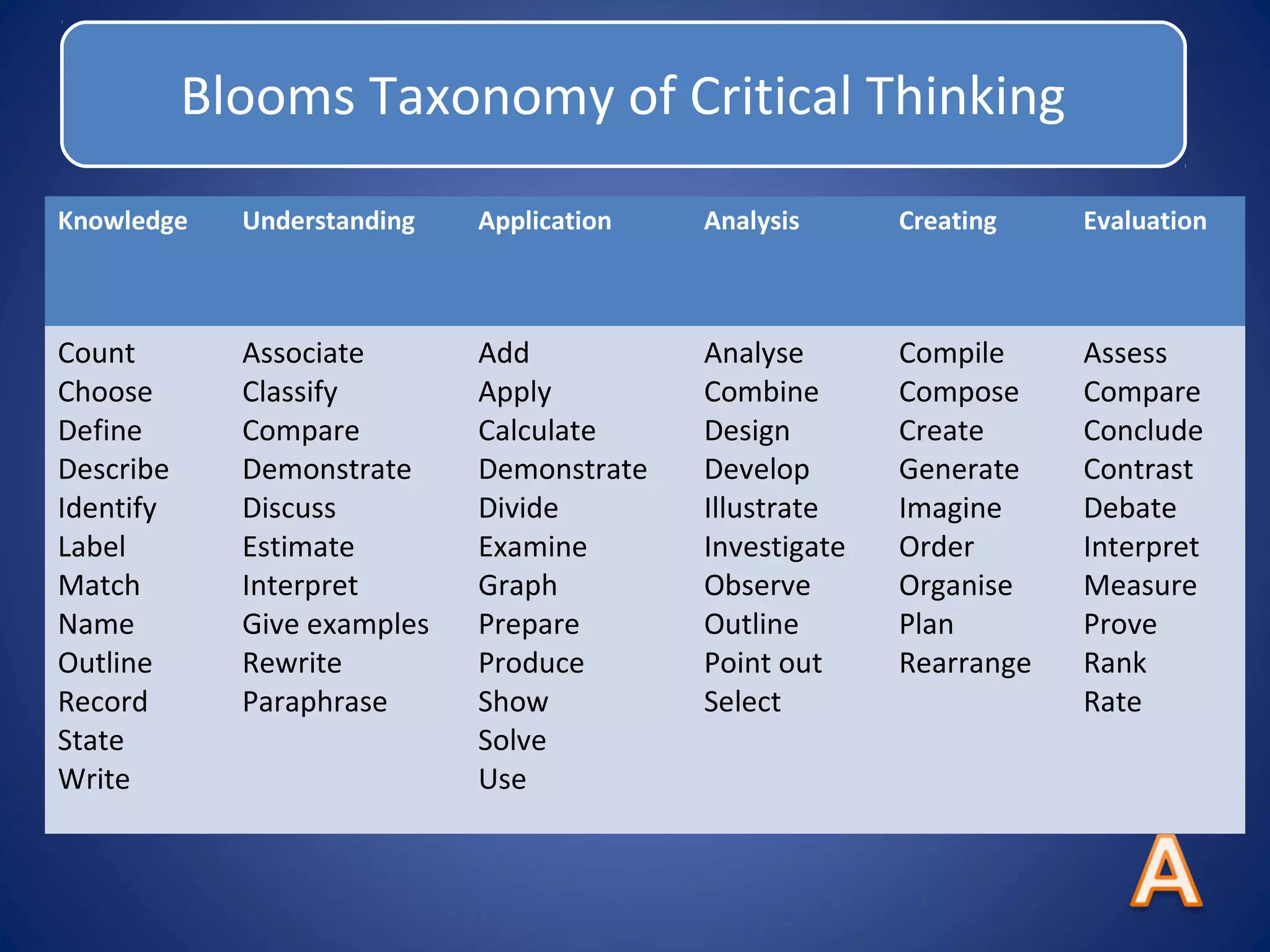
This document discusses numeracy and provides recommendations for developing numeracy in schools. It defines numeracy as involving thinking and communicating quantitatively, making sense of data, understanding patterns and sequences, and recognizing situations where mathematical reasoning can be applied. The document notes a decline in mathematics scores for students in transition year and recommends whole-school, subject-based, and extra-curricular approaches to strengthen numeracy, including identifying weaknesses, collaboration among teachers, and activities to promote positive attitudes toward mathematics.