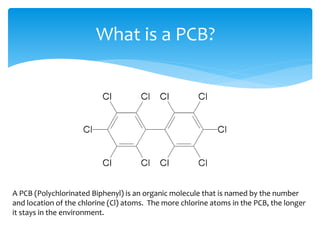
PCBs, or polychlorinated biphenyls, are organic compounds that were widely used as insulating fluids in electrical equipment like transformers and capacitors due to their non-flammability and electrical insulating properties. PCBs are harmful to human and environmental health. They are classified and regulated according to their PCB concentration levels and require special handling, storage, transportation, spill response and disposal procedures due to their toxicity and persistence in the environment.