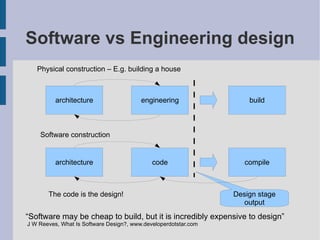
This document discusses various design patterns in Python and how they compare to their implementations in other languages like C++. It provides examples of how common patterns from the Gang of Four book like Singleton, Observer, Strategy, and Decorator are simplified or invisible in Python due to features like first-class functions and duck typing. The document aims to illustrate Pythonic ways to implement these patterns without unnecessary complexity.







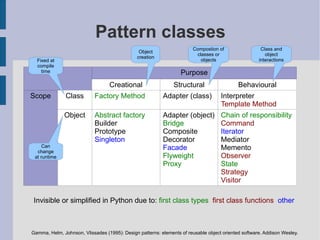


![Motivation “ 16 of 23 [GoF] patterns have a qualitatively simpler implementation in Lisp or Dylan than in C++, for at least some uses of each pattern” Peter Norvig (http://norvig.com/design-patterns/) “ Patterns are not needed in Python because design patterns are a sign of a deficiency of a language” … ... for the purpose that the design pattern addresses. How is observer implemented in Python? (equivalent to Boost.Signals, Qt Slot/Signals, .NET events) Coming from C++ or Java, if you already know the GoF patterns then it would be informative to see how they are implemented in Python. This talk documents part of my journey from C++ to Ptyhon.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramsey2011-patterns-clean-111002165039-phpapp02/85/Patterns-in-Python-12-320.jpg)

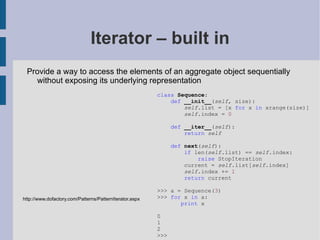















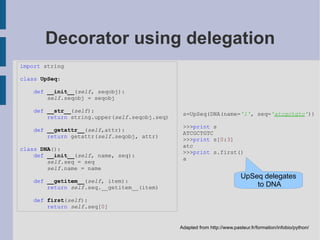



![If you need to do something special. E.g. # Put in const.py...: class _const : class ConstError (TypeError): pass def __setattr__ ( self ,name,value): if self .__dict__.has_key(name): raise self .ConstError, "Can't rebind const (%s)" %name self .__dict__[name]=value import sys sys.modules[__name__]=_const() # that's all -- now any client-code can import const # and bind an attribute ONCE: const.magic = 23 # but NOT re-bind it: const.magic = 88 # raises const.ConstError # you may also want to add the obvious __delattr__ Alex Martelli http://code.activestate.com/recipes/65207-constants-in-python/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramsey2011-patterns-clean-111002165039-phpapp02/85/Patterns-in-Python-37-320.jpg)
![Iterator – built in Provide a way to access the elements of an aggregate object sequentially without exposing its underlying representation class Sequence : def __init__ ( self , size): self .list = [x for x in xrange(size)] self .index = 0 def __iter__ ( self ): return self def next ( self ): if len( self .list) == self .index: raise StopIteration current = self .list[ self .index] self .index += 1 return current >>> a = Sequence( 3 ) >>> for x in a: print x 0 1 2 >>> http://www.dofactory.com/Patterns/PatternIterator.aspx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramsey2011-patterns-clean-111002165039-phpapp02/85/Patterns-in-Python-38-320.jpg)





![Command in Python def greet (who): print "Hello %s" % who greet_command = lambda : greet( "World" ) # pass the callable around, and invoke it later greet_command() class MoveFileCommand (object): def __init__ ( self , src, dest): self .src = src self .dest = dest self () def __call__ ( self ): os.rename( self .src, self .dest) def undo ( self ): os.rename( self .dest, self .src) undo_stack = [] undo_stack.append(MoveFileCommand( 'foo.txt' , 'bar.txt' )) undo_stack.append(MoveFileCommand( 'bar.txt' , 'baz.txt' )) # foo.txt is now renamed to baz.txt undo_stack.pop().undo() # Now it's bar.txt undo_stack.pop().undo() # and back to foo.txt http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1494442/general-command-pattern-and-command-dispatch-pattern-in-python (Ants Aasma) Simple case: Just use a callable More complex case: Use a command object but no need for a base class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ramsey2011-patterns-clean-111002165039-phpapp02/85/Patterns-in-Python-44-320.jpg)