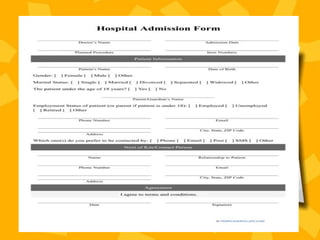
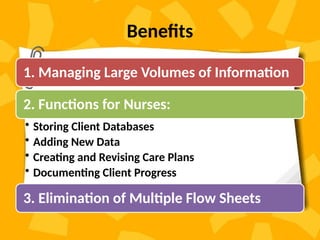
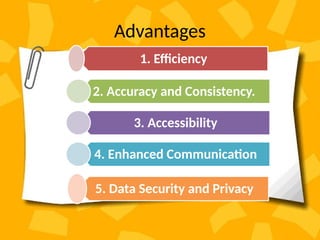
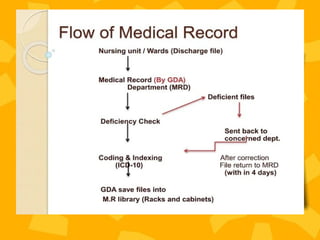
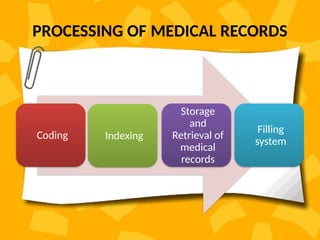
A patient record system is a clinical information system for collecting, storing, and managing clinical data to enhance patient care. It includes various documentation methods, such as paper-based and electronic systems, each with advantages and disadvantages related to organization, communication, and efficiency. The medical records department plays a crucial role in maintaining and processing these records, ensuring accuracy and compliance with regulatory standards.