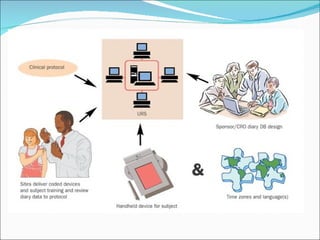
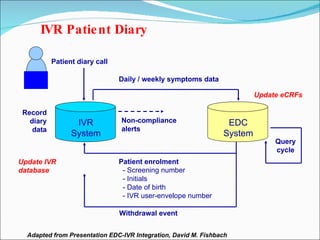
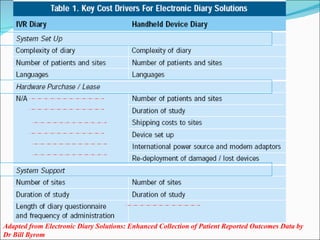
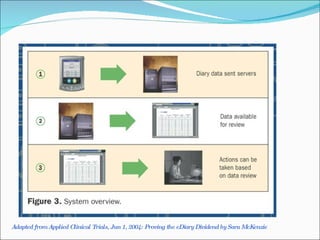
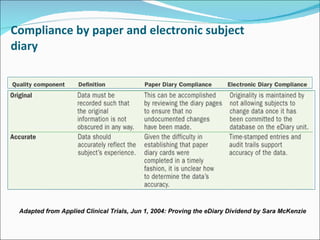
This document discusses patient diaries which are used in clinical trials to record patients' experiences and health status over time. It defines what patient diaries are, who writes in them, and different types including paper-based diaries, electronic diaries using handheld devices, PDAs, mini computers, and IVR systems. The benefits of electronic diaries over paper diaries are outlined, such as improved data quality and compliance. Guidelines are provided on when diaries can be started and how they support clinical research objectives.