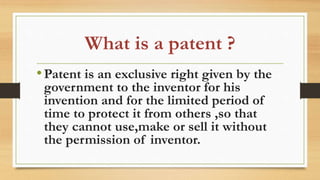
This document discusses patents and the patent process. It defines patents and intellectual property, and outlines the criteria for patentability, including novelty, utility, non-obviousness, and industrial applicability. It describes the different types of patent applications one can file, including provisional, ordinary, convention, and PCT applications. It also explains the patent specification, which contains the technical details of the invention, and patent claims, which define the scope of the invention.