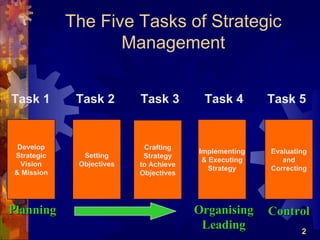
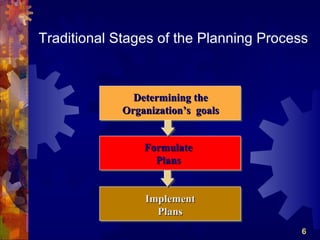
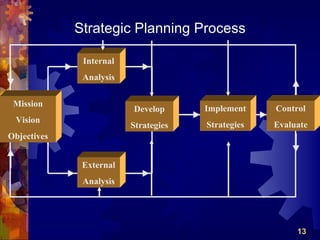
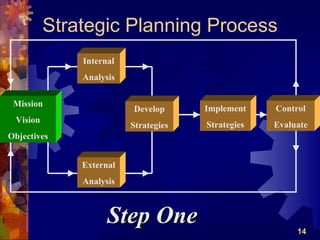
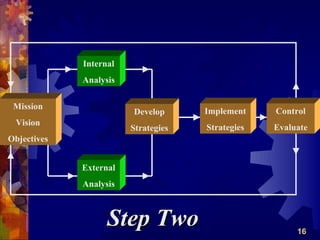
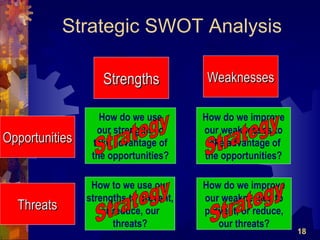
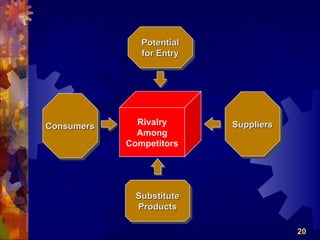
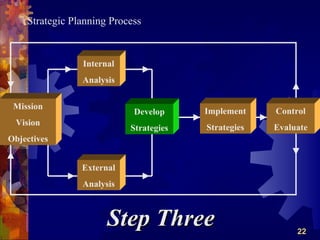
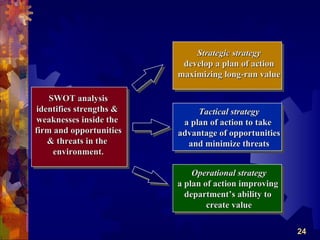
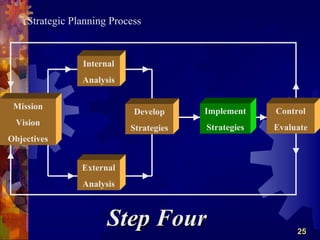
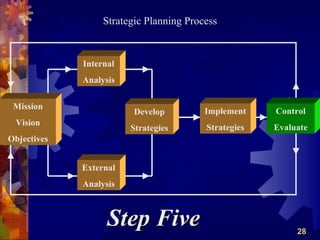
The document discusses the four main functions of management: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It then provides details on each function. Planning involves determining goals and strategies. Organizing is creating an organizational structure. Leading is influencing and motivating others. Controlling monitors performance and makes corrections. The strategic planning process also involves five steps: developing a vision and objectives, analyzing internal and external factors, identifying strategies, implementing strategies, and evaluating performance.