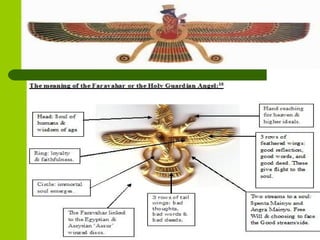
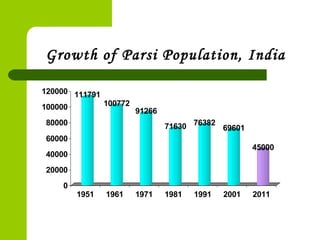
Zoroastrianism, founded by the Persian prophet Zoroaster around 600 B.C. in Northern Iran, is the first monotheistic religion, centered on the worship of Ahura Mazda, the supreme god, and beliefs in duality between good (Ahura Mazda) and evil (Angra Mainyu). The religion emphasizes moral conduct, the sanctity of elements, and rituals, with the Avesta as its holy scripture, comprising teachings, prayers, and ceremonies. Despite its historical prominence, Zoroastrianism faces a declining population today, with significant contributions to various fields but challenges in maintaining their community's numbers and identity.