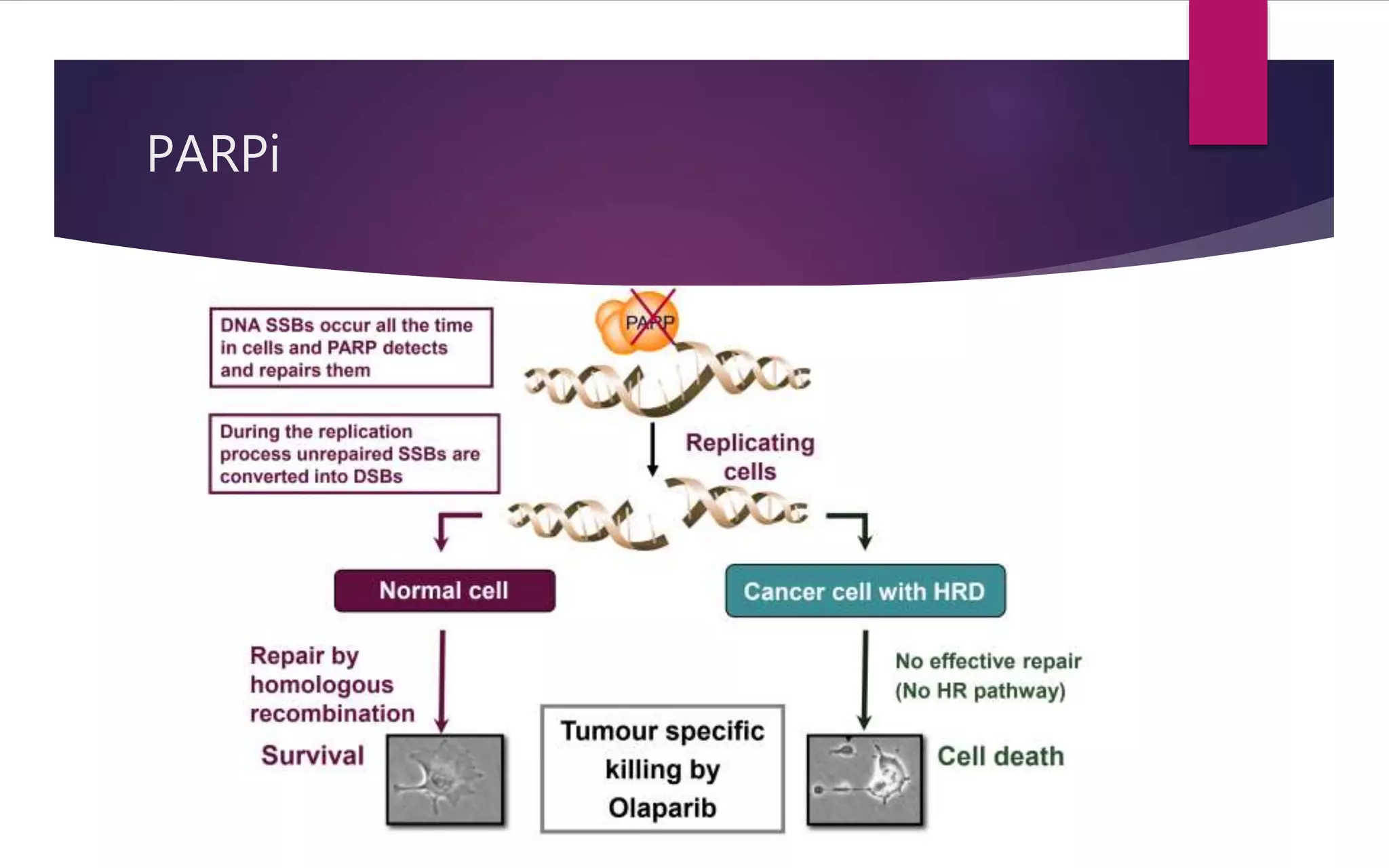
The document discusses the use of PARP inhibitors in the treatment and maintenance of epithelial ovarian cancer, highlighting their effectiveness in prolonging progression-free survival (PFS). It details various studies, including SOLO-1 and others, showing significant benefits of PARP inhibitors like olaparib and niraparib in patients with BRCA mutations and those with high-grade serous ovarian cancer. The challenges of recurrent disease and the importance of tailored maintenance strategies are also addressed.































![Olaparib for the maintenance treatment of PSR OC1-3
Phase III study3
Recurrent BRCAm ovarian cancer after two prior lines of
platinum therapy (n=295)
Maintenance in patients achieving a CR/PR on
platinum therapy
Olaparib tablets PO 300mg BID
Olaparib significantly prolonged PFS compared with placebo
(HR 0.30; 95% CI 0.22 to 0.41; p<0.0001)
Study 19
Phase II study1,2
Recurrent ovarian cancer after two or more prior lines of
platinum therapy (n=265)
Maintenance in patients achieving a CR/PR on
platinum therapy
Olaparib capsules PO 400mg BID
Olaparib significantly prolonged PFS compared with placebo
(HR 0.35; 95% CI 0.25 to 0.49; p<0.00001)
Trend towards benefit for overall survival (HR of 0.73; 95% CI
0.55 to 0.95; nominal p=0.025; statistical significance not reached)
Improvements in PFS and OS were also seen in the non-BRCAm
subgroup (HR 0.54 [95% CI 0.34 to 0.85], p=0·0075; and HR 0.83
[95% CI 0.55 to 1.24], nominal P=0.37; respectively)
BID=twice daily; BRCAm=BRCA1/2 mutation; CI=confidence interval; CR=complete response; HR=hazard ratio; non-BRCAm=no mutations in BRCA1/2; OC=ovarian cancer; OS=overall survival;
PFS=progression-free survival; PO=orally; PR=partial response; PSR=platinum-sensitive relapsed
1. Ledermann J, et al. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(15):1382–1392; 2. Ledermann J, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17(11):1579–1589; 3. Pujade-Lauraine et al. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(9):1274–1284](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parponcowebex-200929131142/75/PARP-inhibitor-in-Ca-Ovary-33-2048.jpg)













![*CR (defined by RECIST v1.1) or PR (defined by RECIST v1.1 and/or a GCIG CA-125 response [CA-125 within normal range]) maintained until entry to ARIEL3 (≤8 weeks of last dose of
chemotherapy). †ATM, ATR, ATRX, BARD1, BLM, BRIP1, CHEK1, CHEK2, FANCA, FANCC, FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCI, FANCL, FANCM, MRE11A, NBN, PALB2, RAD50,
RAD51, RAD51B, RAD51C, RAD51D, RAD52, RAD54L, RPA1.
ARIEL3: Rucaparib in Relapsed Ca Ovary
• HRR status by NGS mutation analysis
BRCA1 or BRCA2
Non-BRCA HRR gene†
None of the above
• Response to recent platinum
CR
PR
• Progression-free interval after
penultimate platinum
6 to <12 months
≥12 months
Patient eligibility Stratification
• High-grade serous or endometrioid
epithelial OC, primary peritoneal, or
fallopian tube cancers
• Sensitive to penultimate platinum
• Responding to most recent platinum
(CR or PR)*
Excludes patients without assessable
disease following second surgery
• CA-125 within normal range
• No restriction on size of residual tumour
• ECOG PS ≤1
• No prior PARP inhibitors
Placebo
BID
n=189
Rucaparib
600 mg BID
n=375
Randomisation2:1
5
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/parponcowebex-200929131142/75/PARP-inhibitor-in-Ca-Ovary-47-2048.jpg)















