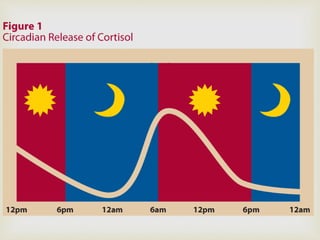
1. Islam considers children to be a sacred trust and obligates parents to raise children righteously.
2. Effective parenting and mentoring techniques include accompanying, sowing, catalyzing, showing, and harvesting. These involve actively participating in a child's learning process.
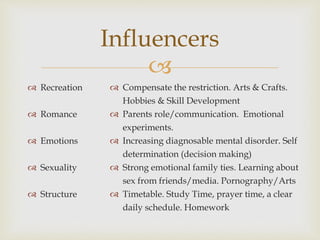
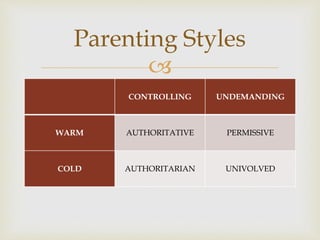
3. Parenting styles and the mentoring approach should depend on a child's situation, mindset, and teachable moments. The goal is to help guide their development from childhood to adulthood.