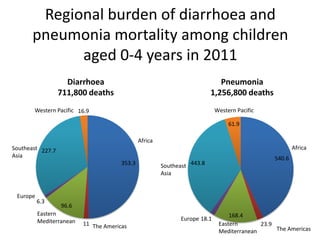
The document reviews the global burden of childhood diarrhea and pneumonia, highlighting that these diseases are significant causes of morbidity and mortality among children under five, with an estimated 2 million deaths in 2011. It emphasizes the need for actionable measures at global and country levels, particularly in high-burden regions like Southeast Asia and Africa, where vaccination and nutritional interventions could prevent a substantial fraction of these cases. Recommendations point towards addressing breastfeeding practices and undernutrition as critical components in combatting these diseases.