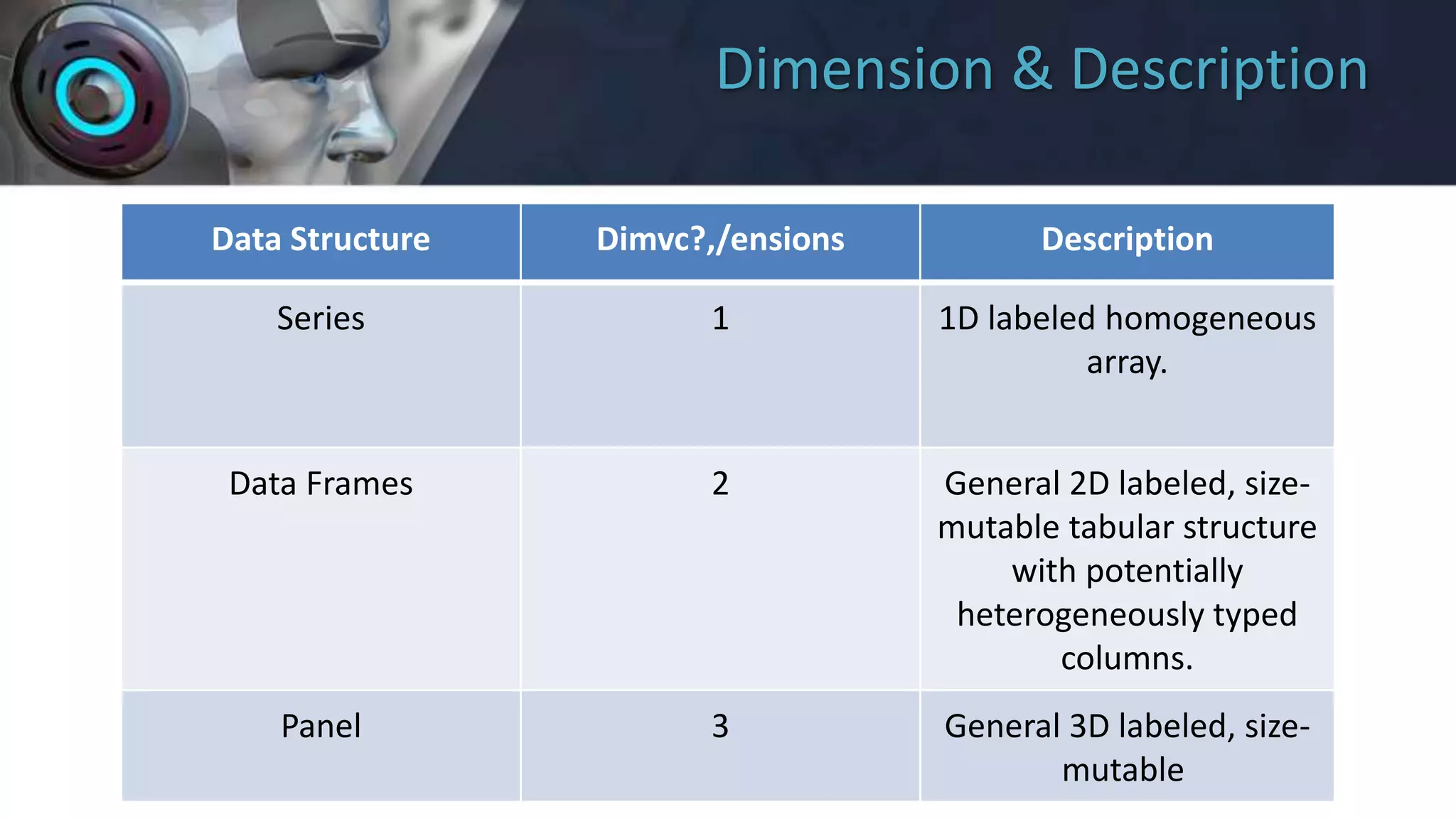
Pandas is a Python library used for working with structured and time series data. It provides data structures like Series (1D array) and DataFrame (2D tabular structure) that are built on NumPy arrays for fast and efficient data manipulation. Key features of Pandas include fast DataFrame objects with indexing, loading data from different formats, handling missing data, reshaping/pivoting datasets, slicing/subsetting large datasets, and merging/joining data. The document provides an overview of Pandas, why it is useful, its main data structures (Series and DataFrame), and how to create and use them.






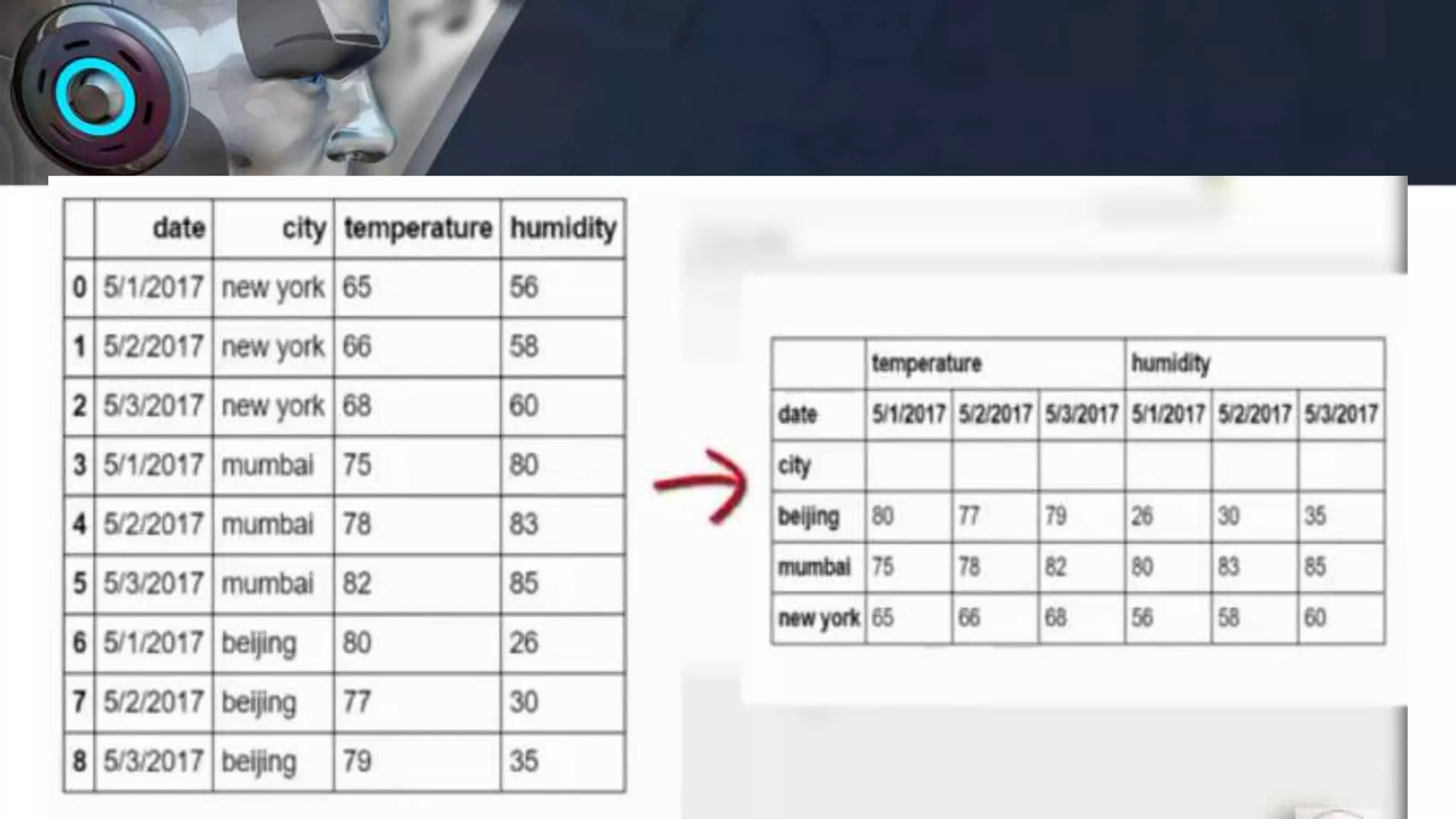




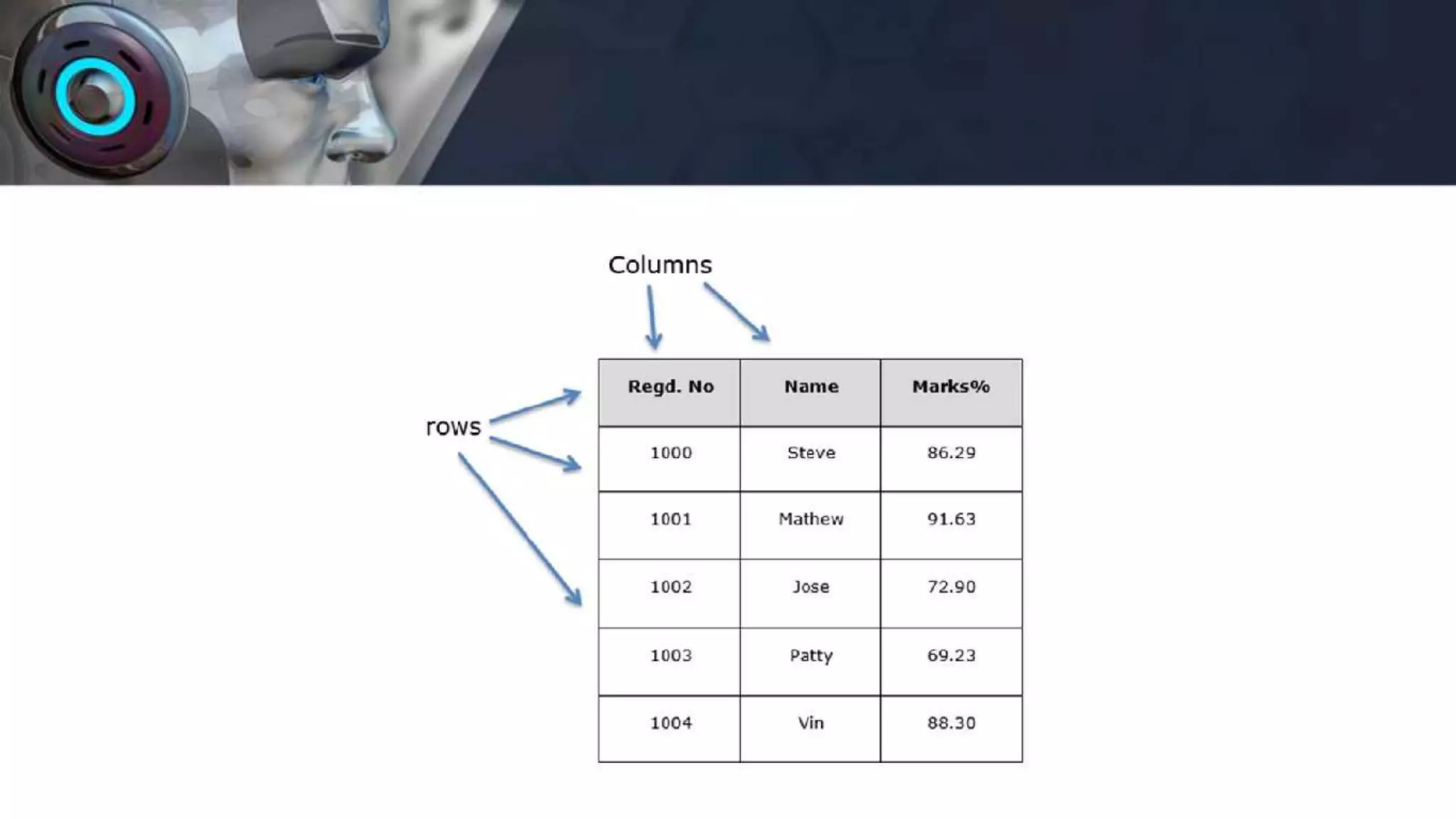
![DataFrame
• Two-dimensional array
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
arr = np.array([1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8])
data = pd.DataFrame(arr)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pandas-200904190409/75/Pandas-14-2048.jpg)
