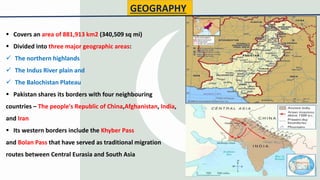
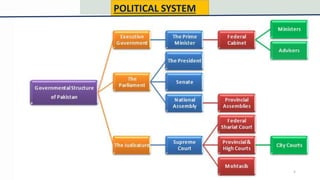
Pakistan is the 5th most populous country with over 210 million people, many of whom are young. It has experienced strong economic growth in recent years. Pakistan faces many internal and external threats to peace and security, including religious extremism and sectarian violence, ethnic clashes, poverty, and tensions with neighboring countries like India and Afghanistan over issues like Kashmir. However, Pakistan has also pursued initiatives to establish peace such as participating in UN peacekeeping missions and attempting to facilitate peace talks in Afghanistan.