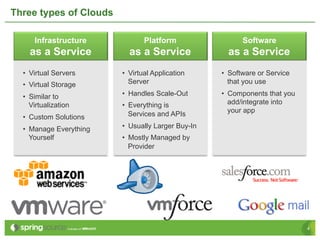
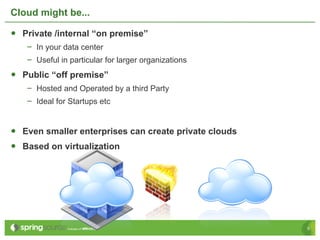
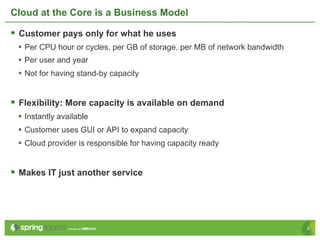
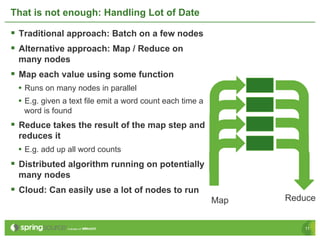
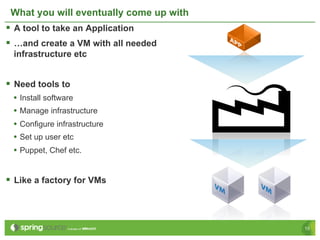
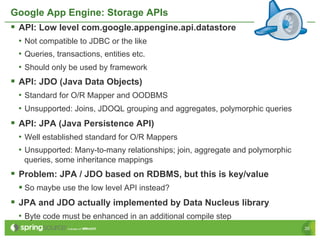
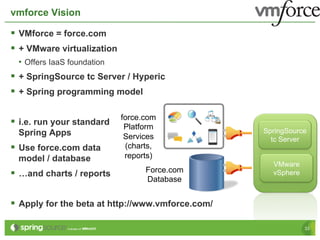
Eberhard Wolff presents an overview of Platform as a Service (PaaS) within cloud computing, outlining the advantages and disadvantages of different service models like IaaS and PaaS. He discusses various examples including Google App Engine, vmforce, and Amazon Beanstalk, emphasizing the need for automatic scaling and the influence of cloud on programming models. The session highlights that while PaaS simplifies cloud utilization for developers, it may restrict customization and flexibility.