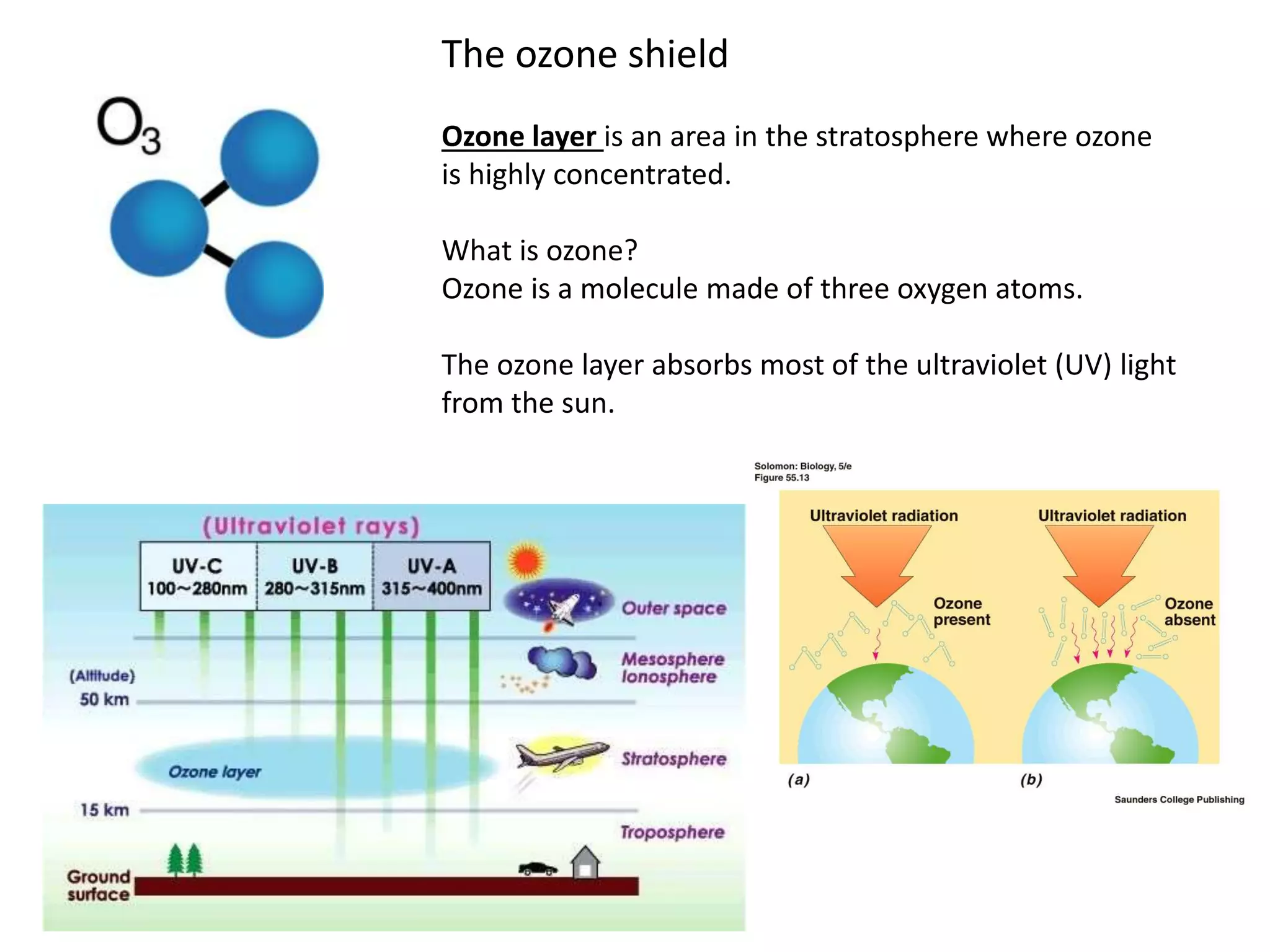
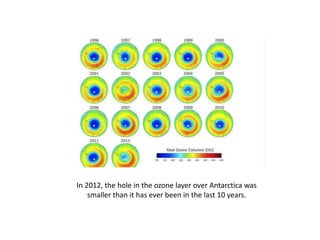
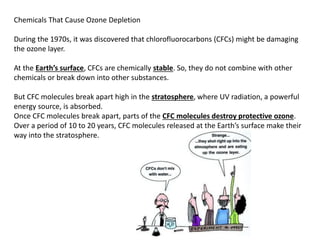
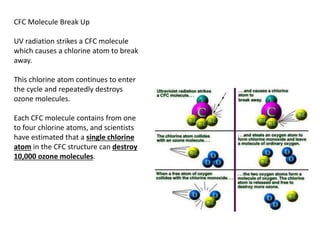
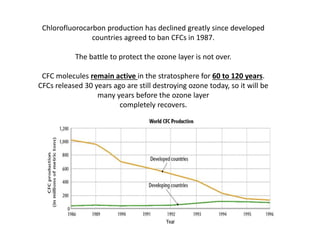
The ozone layer absorbs most UV light from the sun and protects life on Earth. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) released into the atmosphere rise and break down ozone in the stratosphere. In the 1980s, scientists discovered an ozone hole forming over Antarctica each spring due to CFCs, allowing more UV radiation. The 1987 Montreal Protocol banned CFCs to protect the ozone layer, though recovery will take decades as CFCs linger in the atmosphere.