Embed presentation
Download to read offline


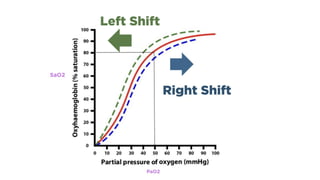



The oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve illustrates the relationship between partial pressure of oxygen (pao2) and hemoglobin saturation (sao2). A rightward shift indicates decreased affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen, leading to easier unloading, while a leftward shift indicates increased affinity and less unloading. External factors can cause these shifts, affecting oxygen transport in the blood.





