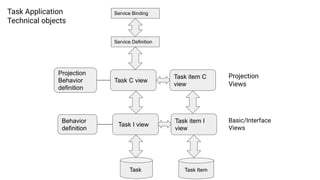
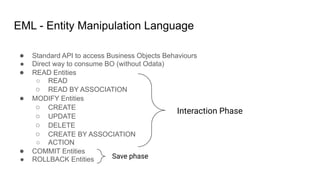
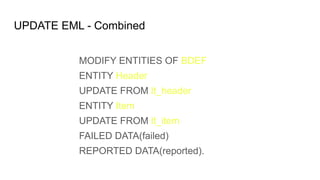
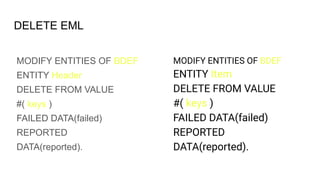
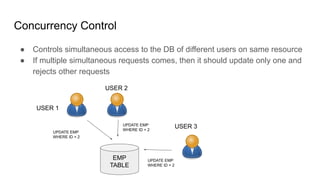
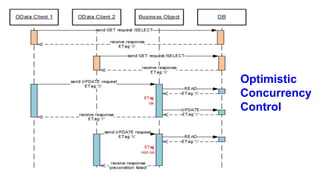
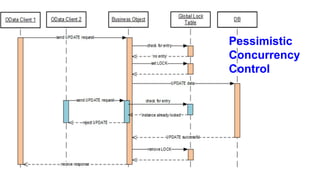
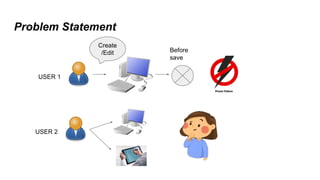
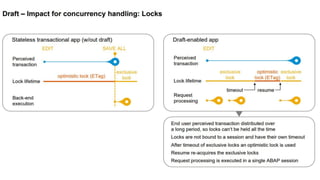
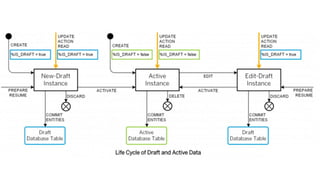
The document provides an overview of Behavior Definition and its components within the RAP (Rapid Application Programming) framework, detailing the behavior characteristics and body associated with business objects (BO). It covers standard operations like CRUD, Entity Manipulation Language (EML) functionalities, validation, and determination processes, alongside concurrency control and draft handling mechanisms. Additionally, it describes the implementation details, syntax, and practical usage of actions, projections, and the RAP generator for deploying applications.