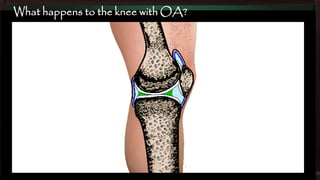
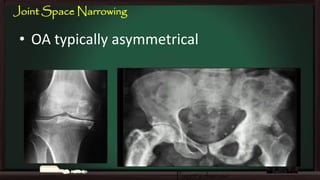
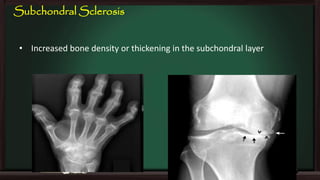
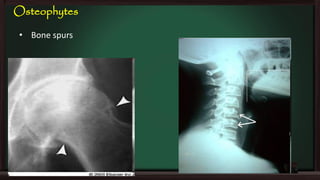
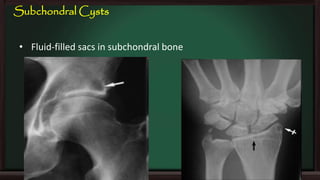
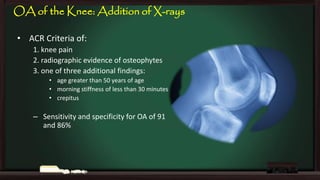
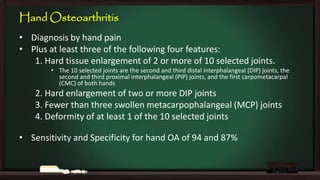
This document provides an overview of osteoarthritis (OA), including its definition, risk factors, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment options, and management goals. OA results from cartilage failure induced by genetic and biomechanical factors. It is diagnosed based on symptoms like pain and stiffness, along with physical exam findings and radiographic evidence. Treatment includes non-pharmacological options like exercise, braces, and weight loss as well as pharmacological options like acetaminophen, NSAIDs, and corticosteroid injections. Surgical options like joint replacement are considered if conservative treatments fail to control pain and functional limitations. The overall goals of treatment are to reduce pain and disability, improve quality of life, and prevent disease progression.