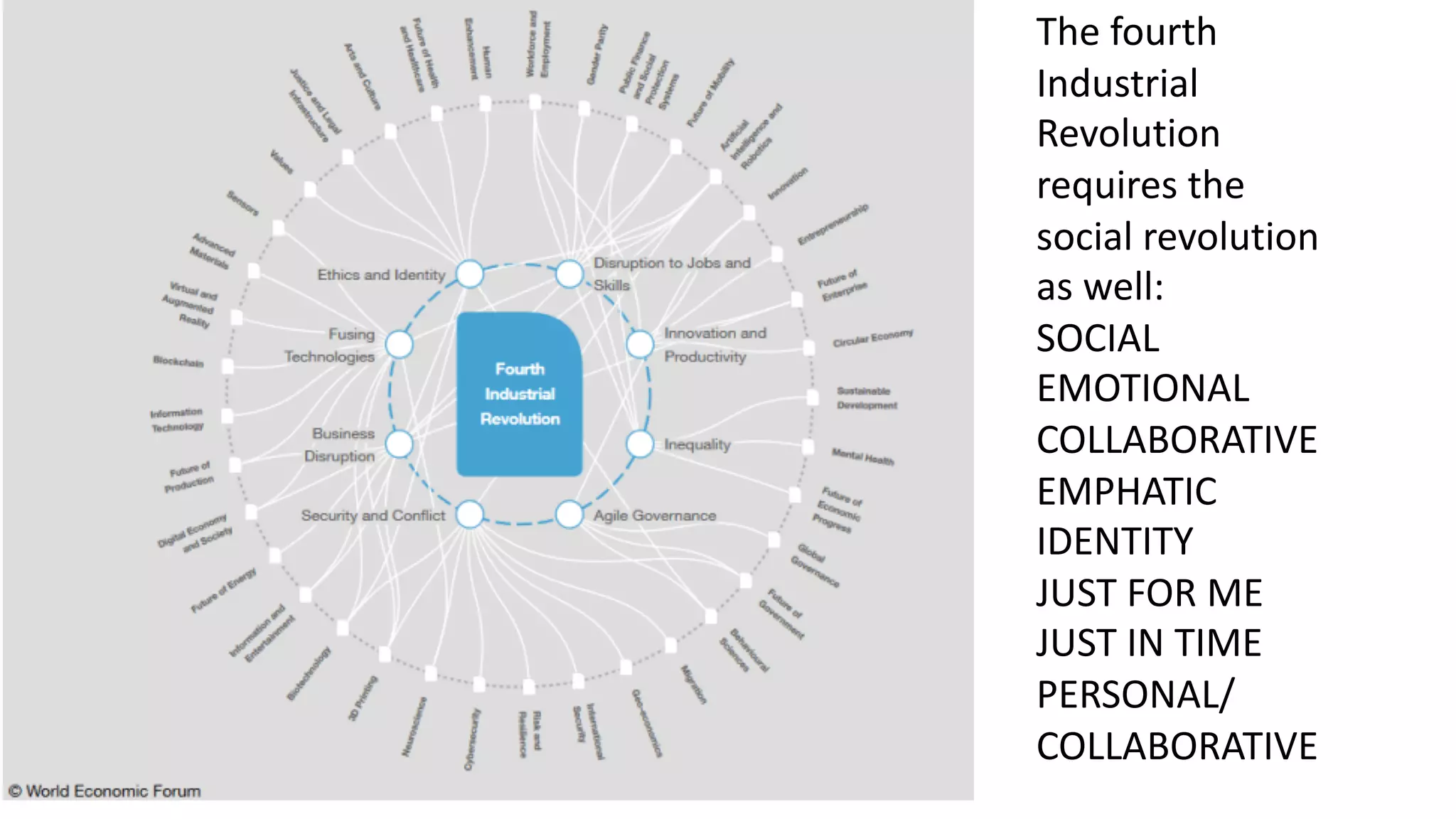
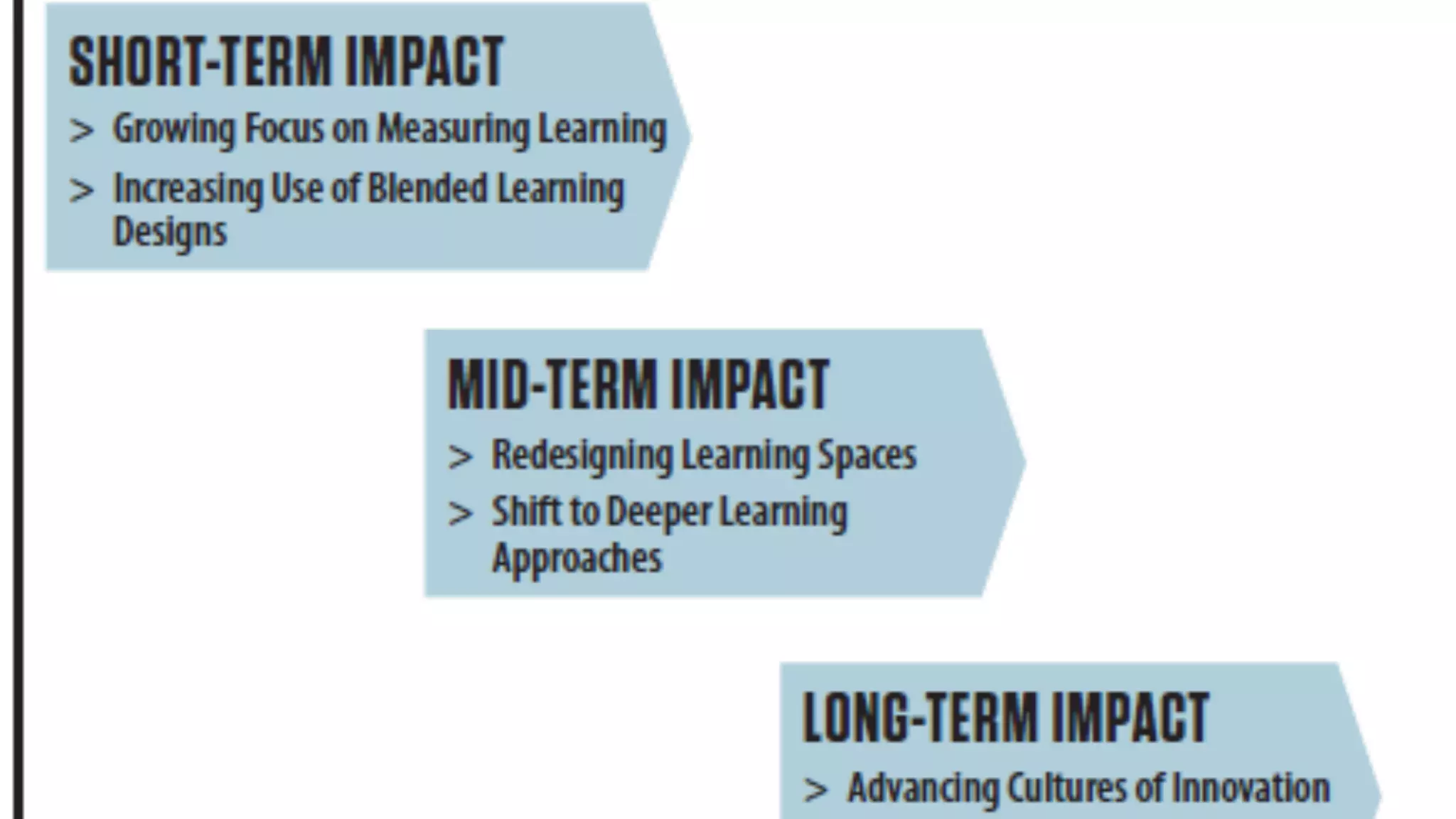
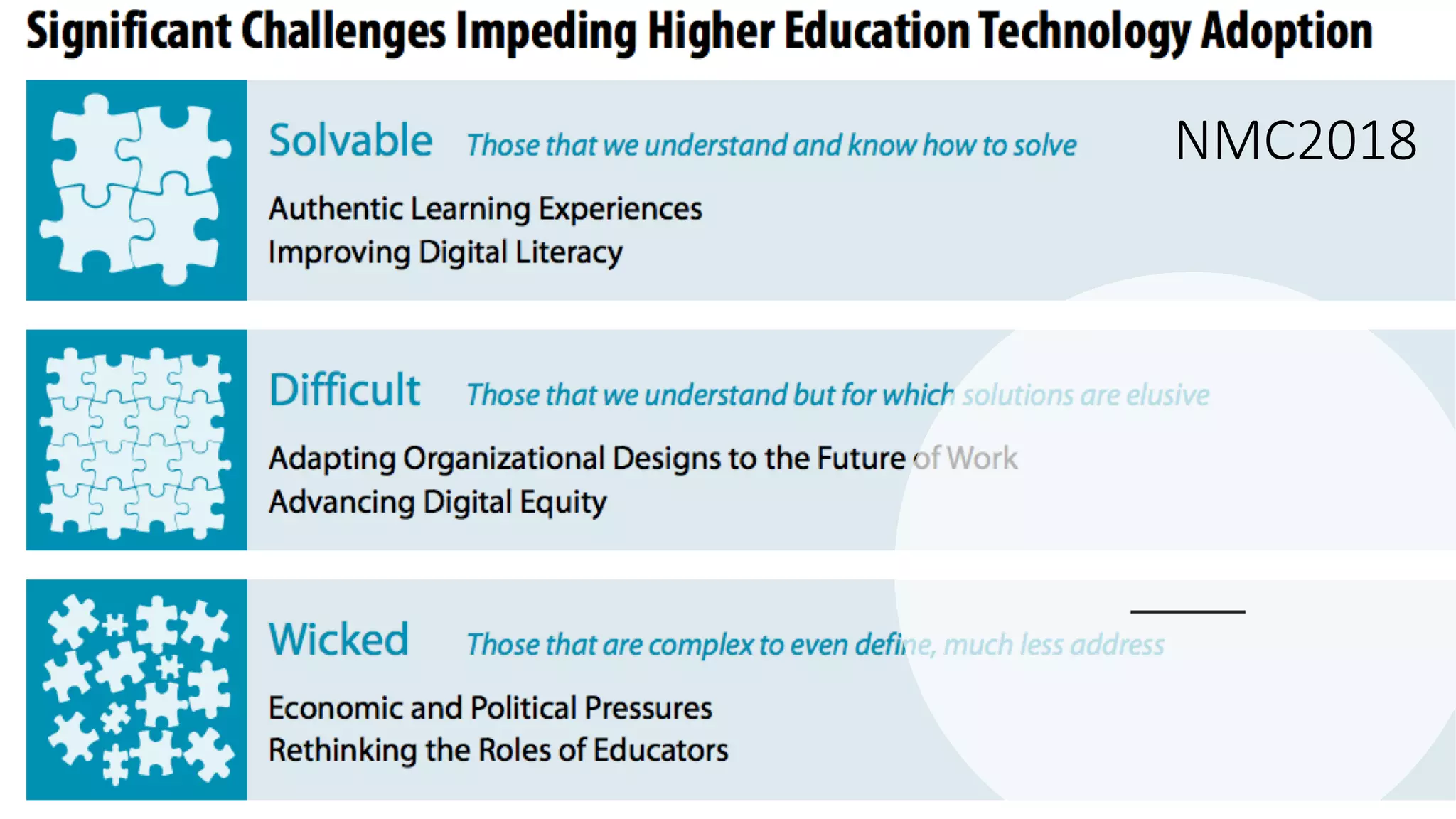
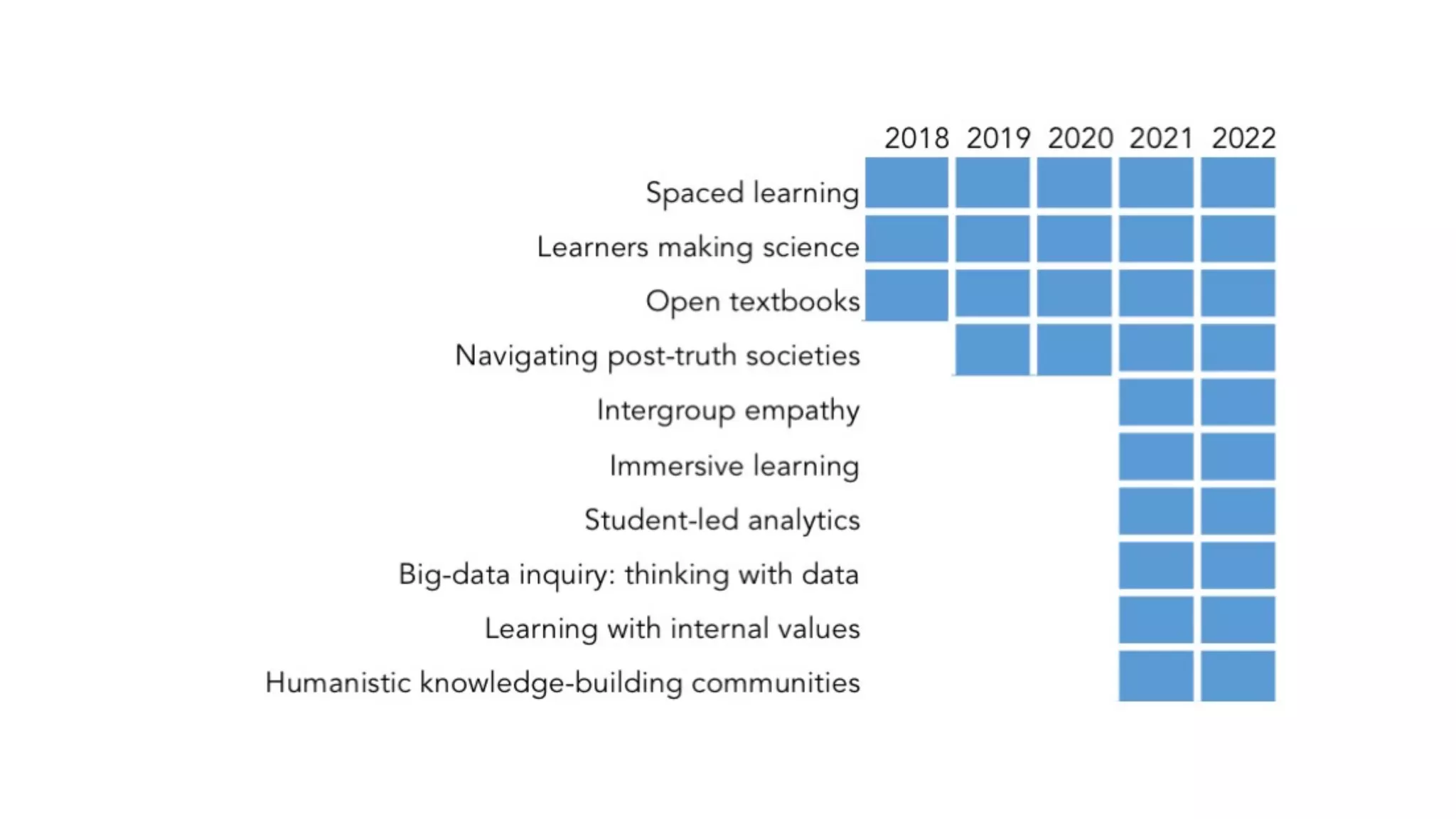
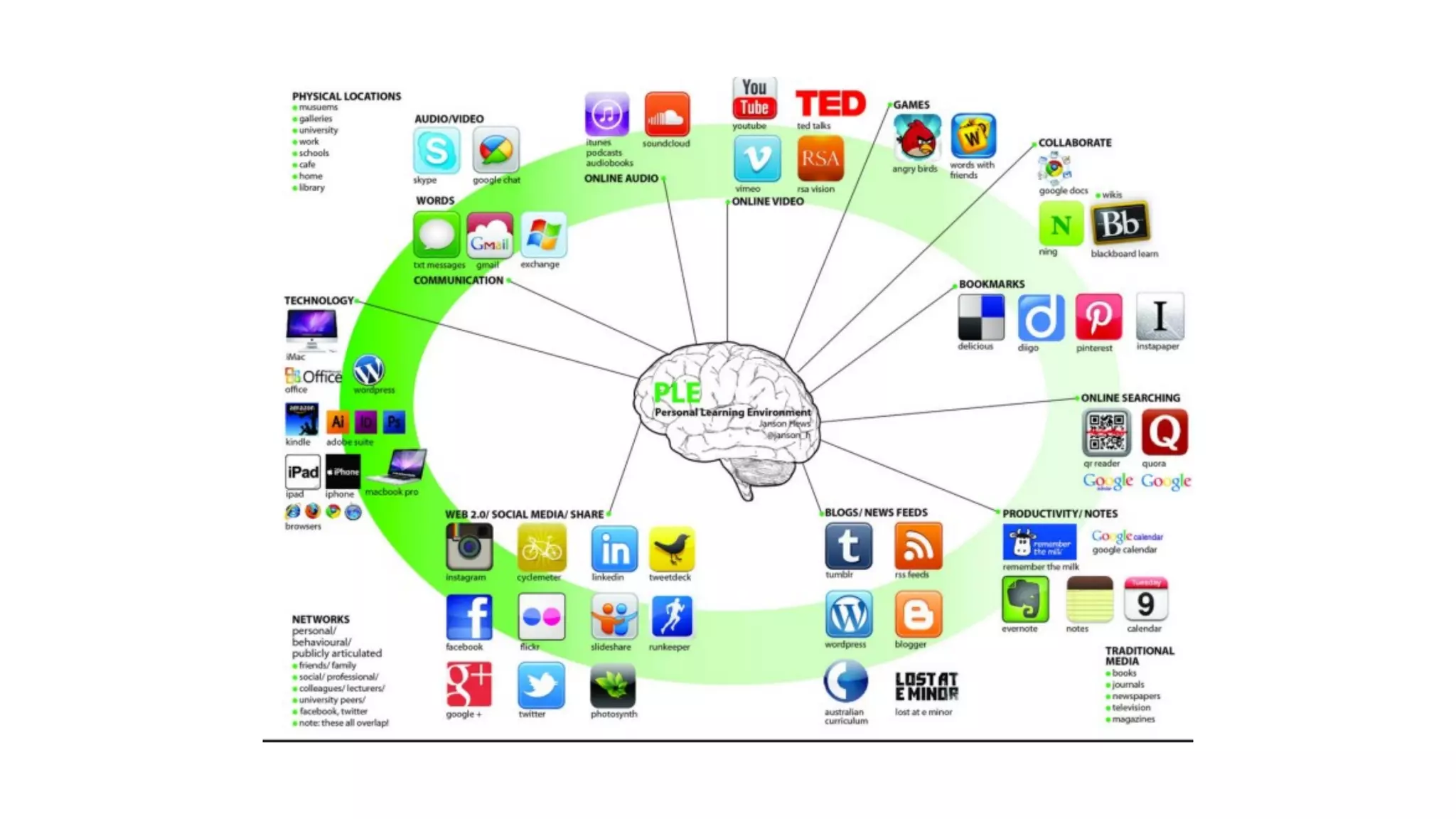
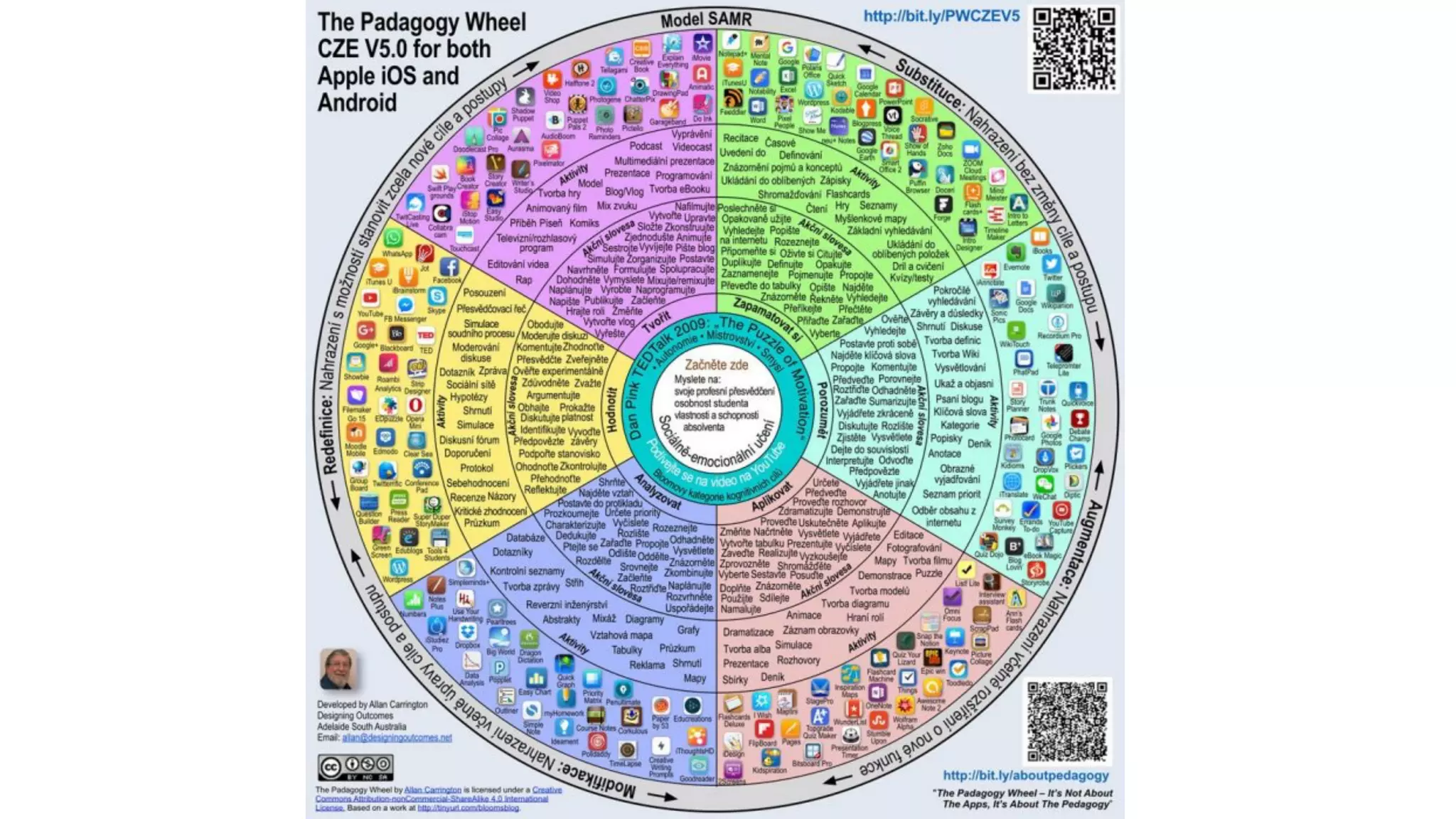
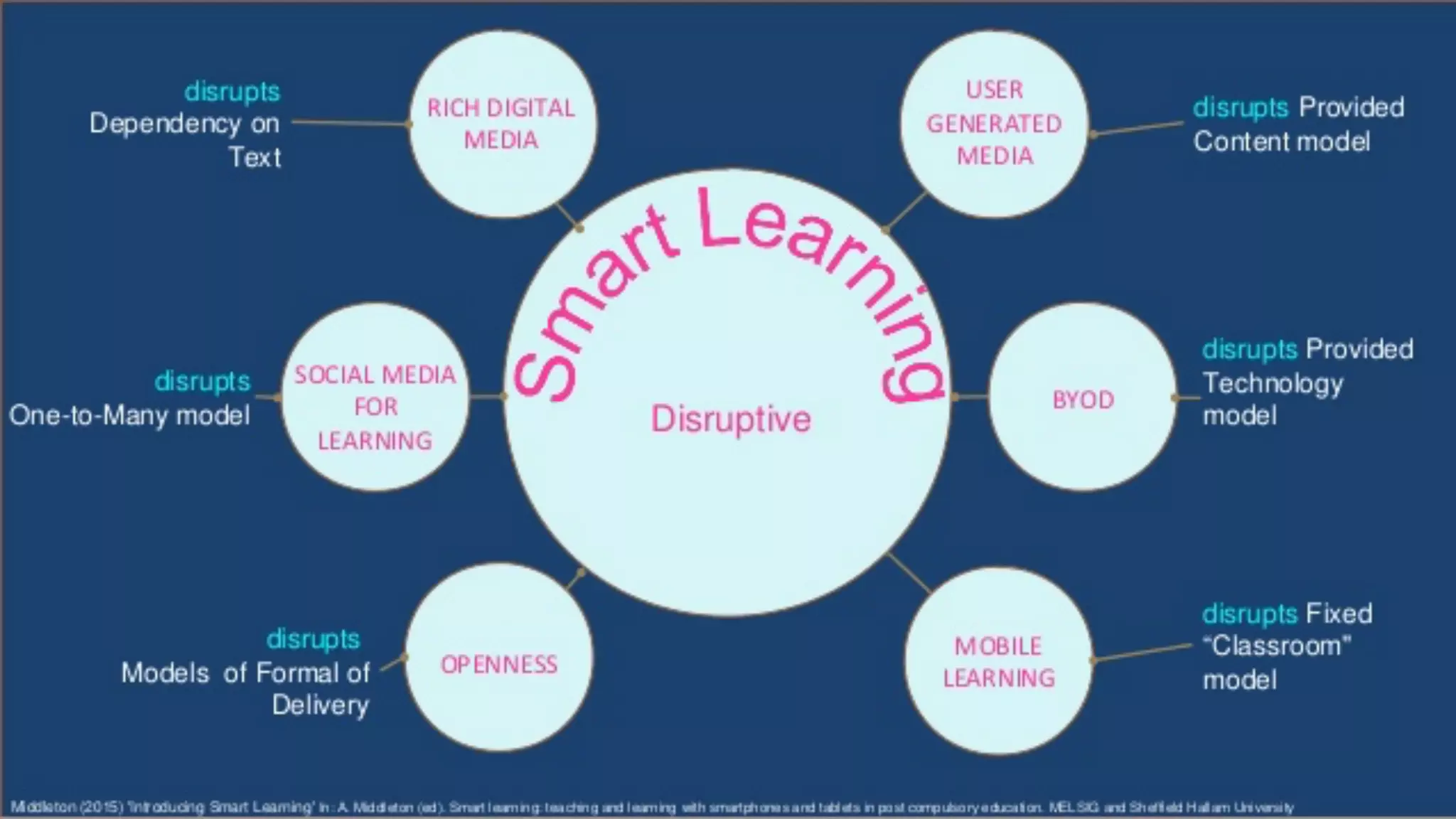
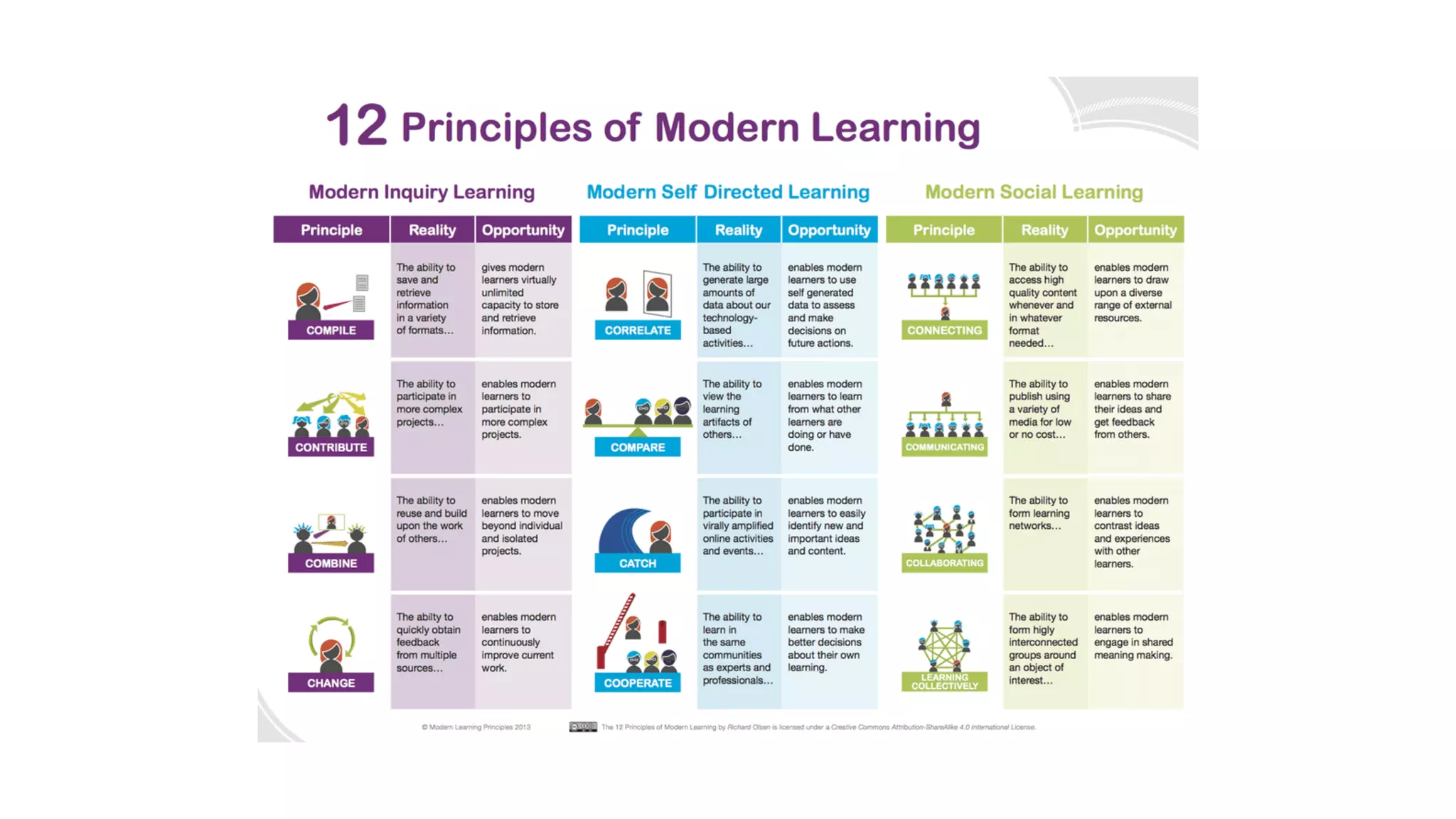
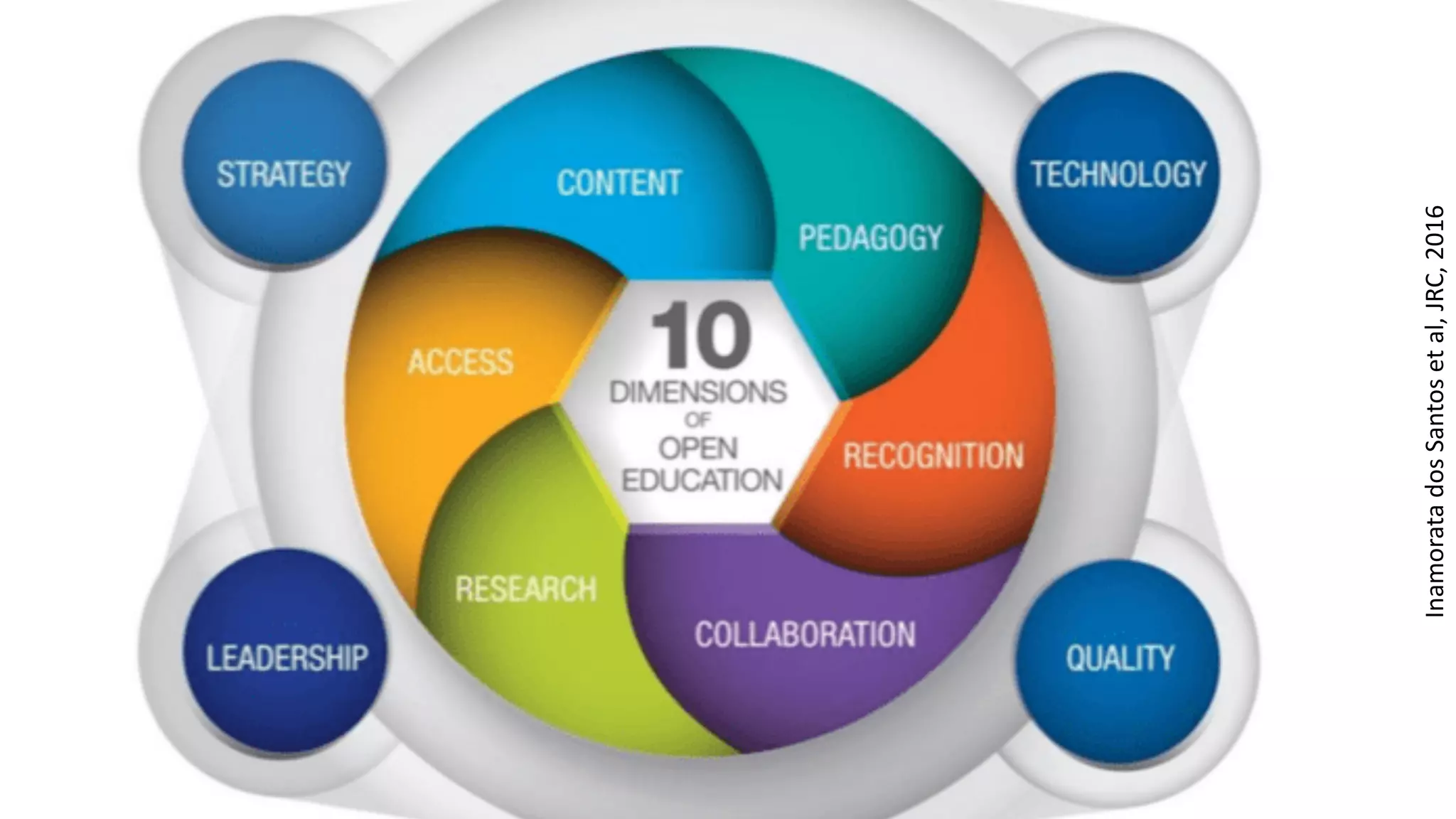
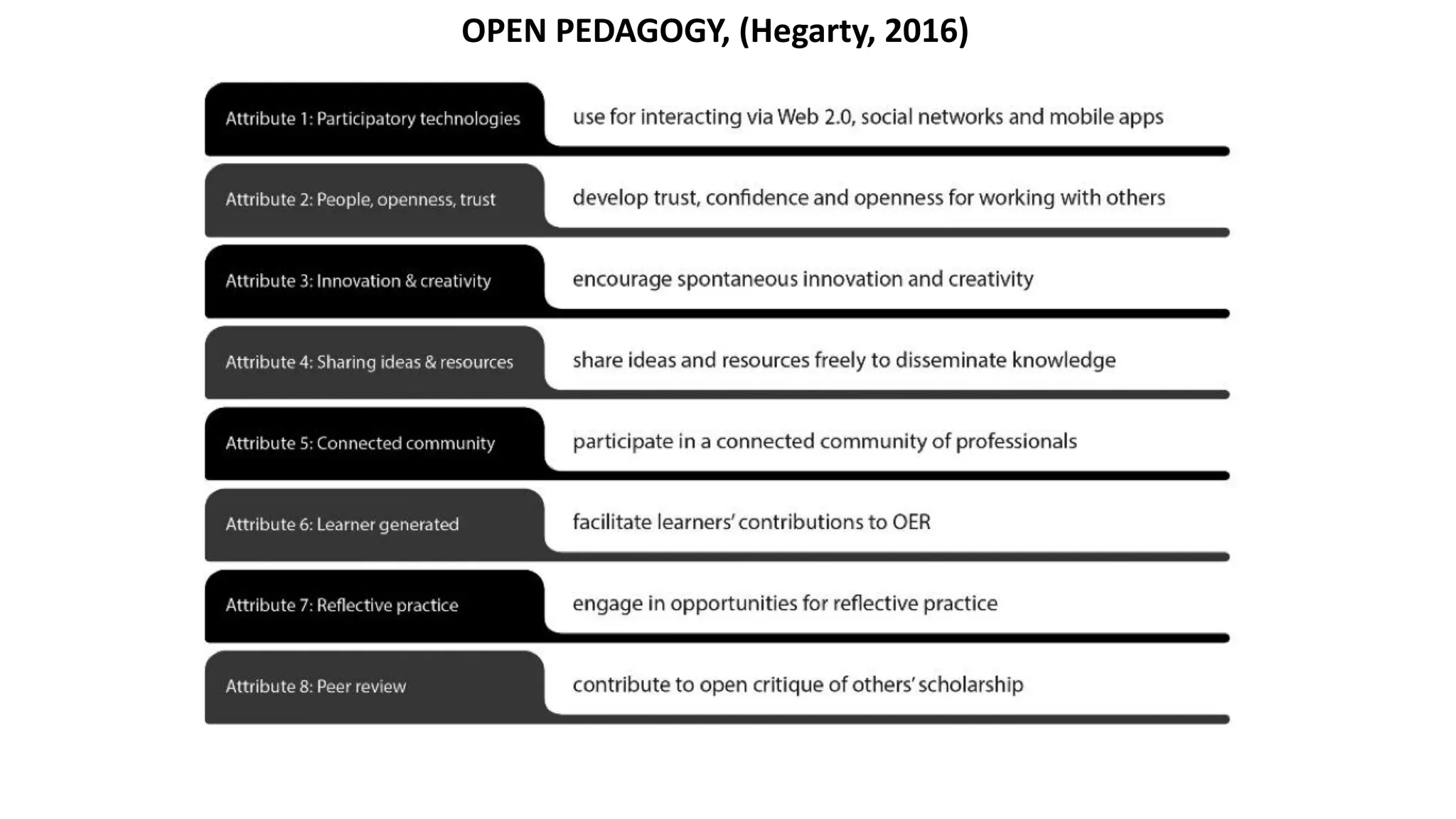
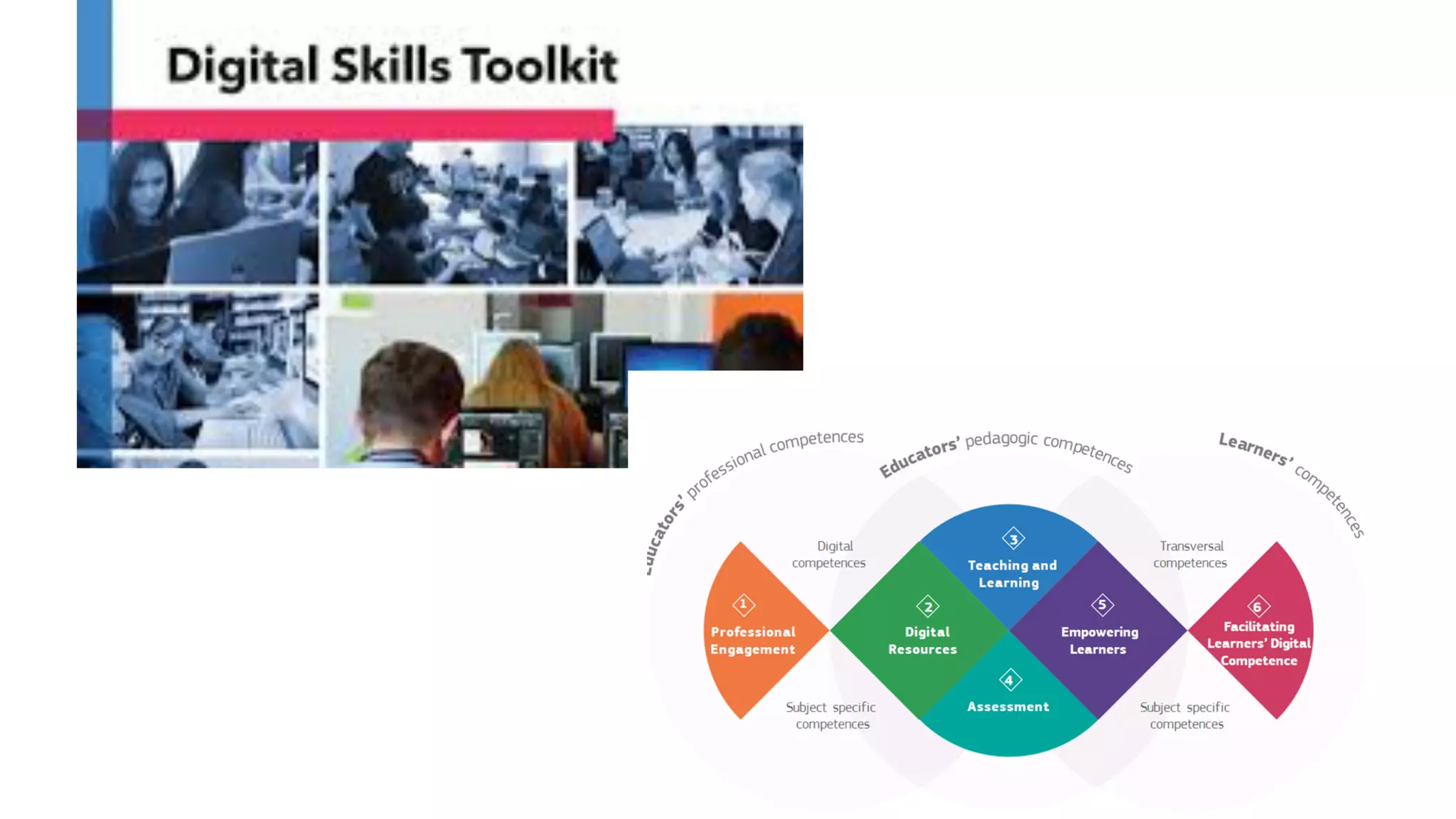
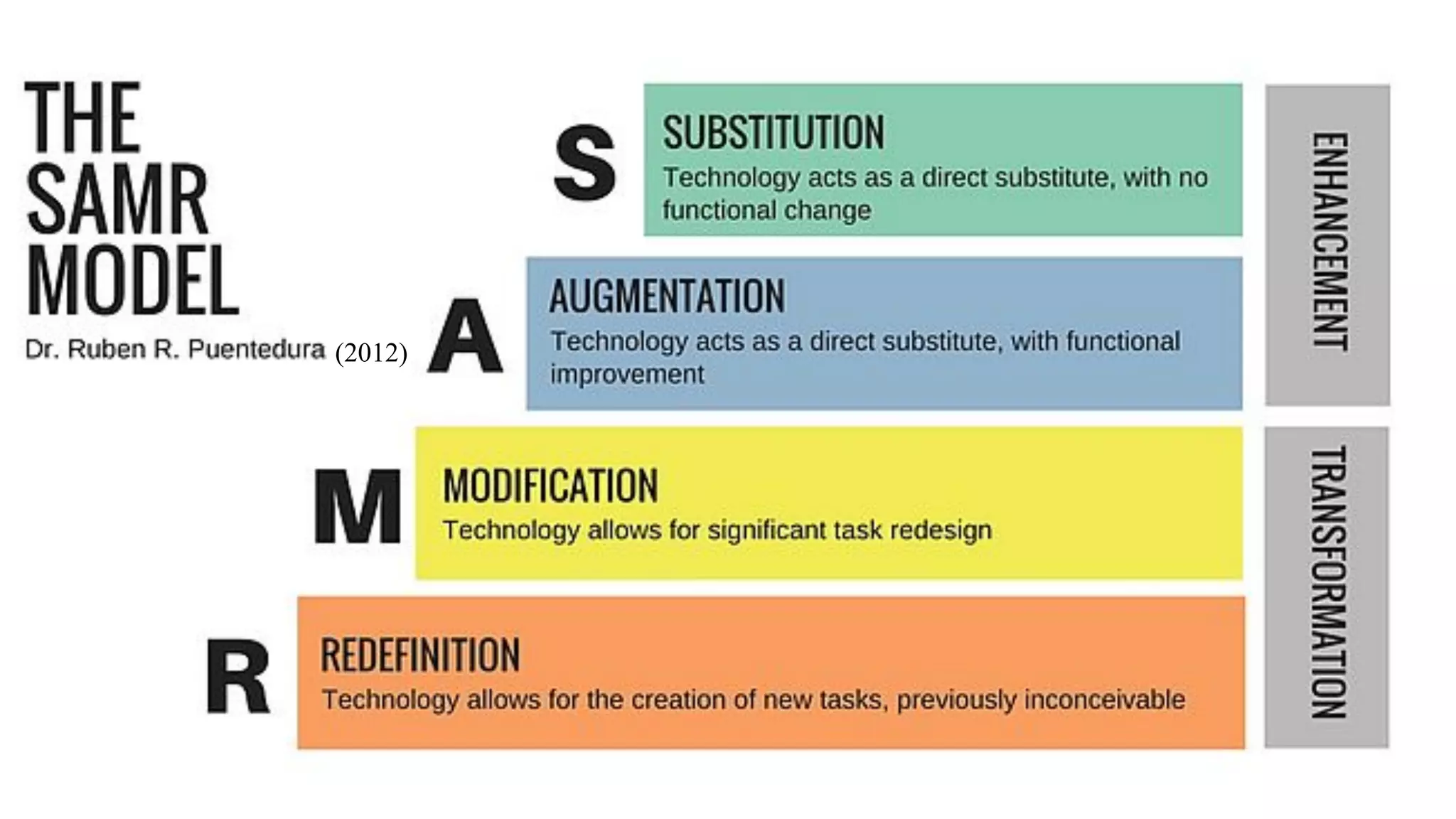
The OEB 2018 pre-conference workshop focuses on creating innovative learning spaces to meet the demands of the 21st century educational environment, emphasizing critical skills like collaboration and digital literacy. The agenda includes discussions on how physical and virtual spaces, along with technology, can enhance learning outcomes and adapt pedagogy to better engage learners. Leadership plays a crucial role in fostering a culture of innovation in educational settings by monitoring and supporting teaching and learning initiatives.