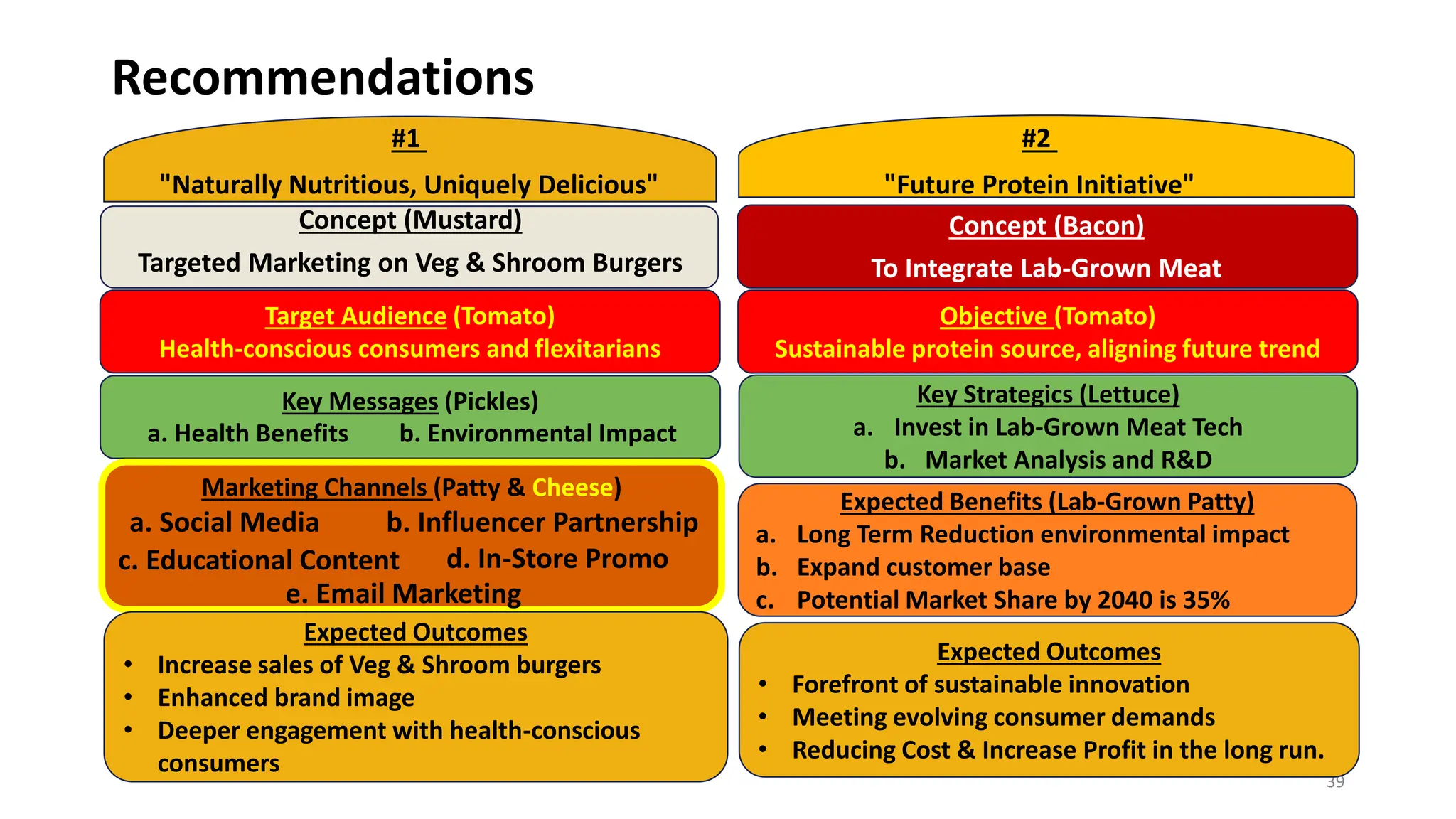
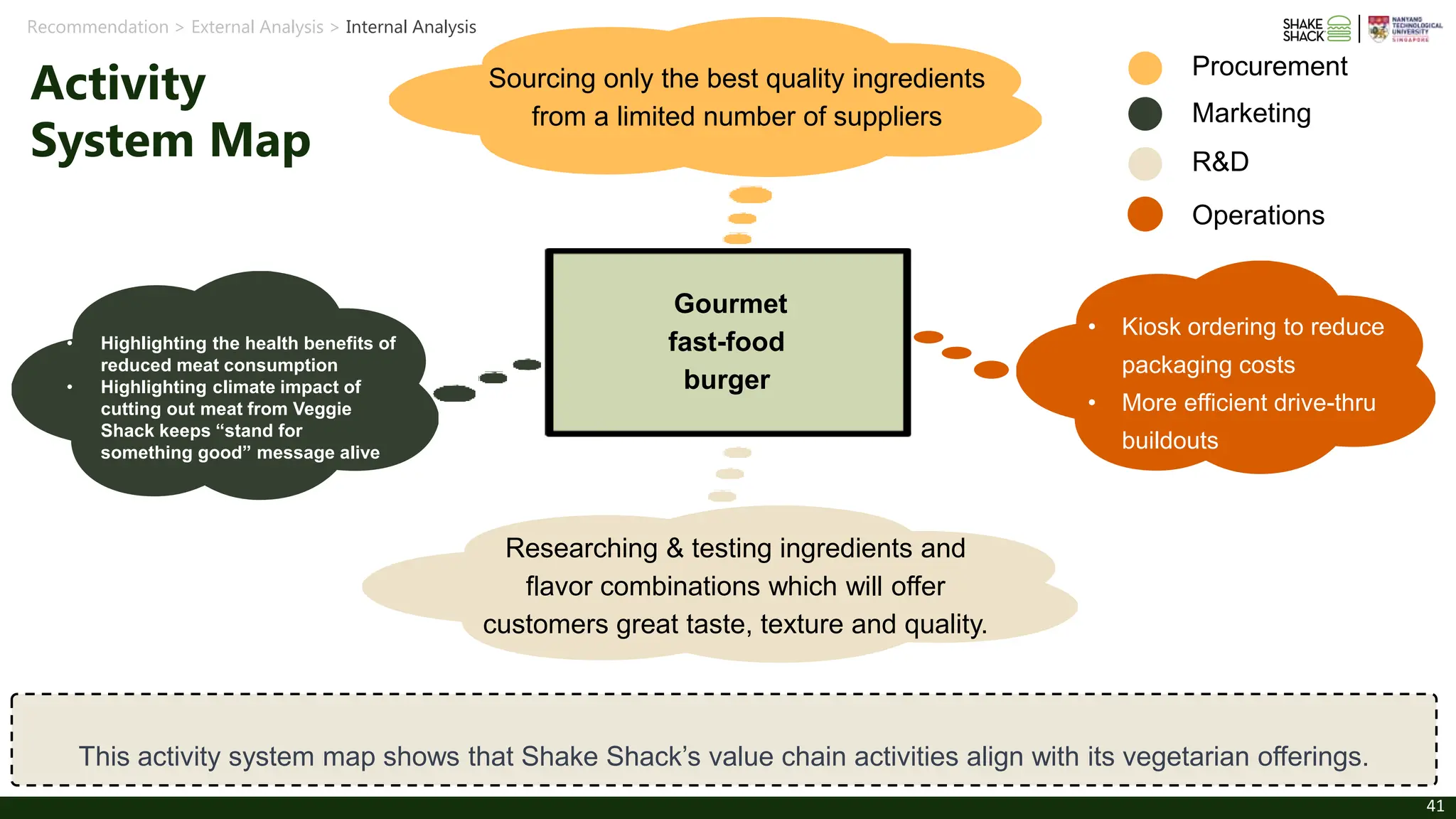
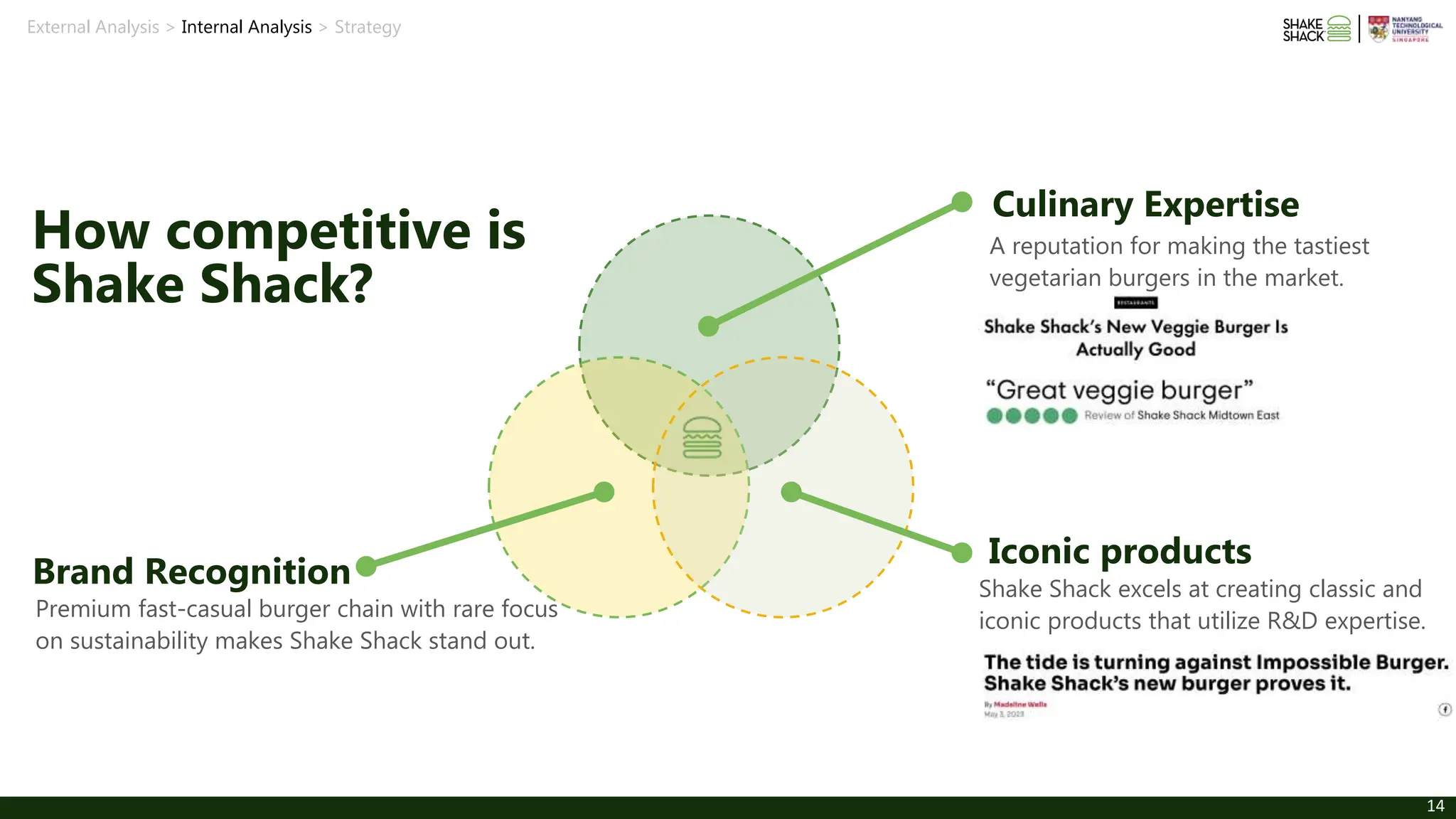
The document discusses Shake Shack's strategy for integrating sustainability into its burger offerings, focusing on short-term and long-term recommendations such as enhancing veggie burger options and investing in lab-grown meat. It analyzes external market trends and internal capabilities, highlighting the potential for profit growth amidst challenges and consumer demand for healthier options. Shake Shack aims to balance profitability with its sustainability mission while navigating a competitive landscape in the fast-casual dining sector.





















![23
*Data from Sec.gov Shake shack’s Securities and Exchange Commission Report [Reference]
* Balance Sheet check [Appendix 4]
1.The majority of profits come from the U.S. market (Revenue exceeds 95%), and it primarily adopts a company-operated
model (with overseas franchising), where direct stores require significant capital investment.
2.Talent development is a priority for Shake Shack, with SG&A expense making up 13.2 % of revenue, partly driven by
salary increases.
Overall Reason
Profitability 2022 YoY 2021
Revenue 900,486 22% 739,893
Gross Margin 42.40% 0.90% 41.40%
EBITDA 7.80% 0.20% 7.60%
Net Profit -2.70% -1.50% -1.20%
Efficiency 2022 YoY 2021
DSO (Days) 5.6 -1.1 6.7
DIO (Days) 2.9 -0.3 3.2
DPO (Days) 14.4 -2.4 16.8
CCC (Cash Conversion Cycle) -5.9 0.9 -6.8
Liquidity 2022 YoY 2021
Current Ratio % 2.3 -1.00 3.4
Quick Ratio % 2.2 -1.10 3.3
Debt / Equity % 2.6 0.20 2.3
*Interest coverage % 50.6 13.5 37
High SG&A & Depreciation Cost
- 40% Gross Margin drop to 7.8% EBITDA
- Report of SG&A & Depreciation from data *Appendix 3
Decent operational efficiency
- Both the Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) and Days Inventory Outstanding
(DIO) cycles are very short.
- The Days Payable Outstanding (DPO) cycle to suppliers is longer than the
sum of the receivables cycle (DSO) and the inventory cycle (DIO), resulting in
a negative Cash Conversion Cycle (CCC).
Have risk to long-term debt repayment if sales growth
and gross margin don't remain strong
- Short-term repayment capability: current assets are 2-3 times current
liabilities, indicating a decent ability to pay off debts.
- Long-term repayment capacity: the Debt/Equity ratio shows that overall debt
is about 2-3 times equity, suggesting some risk to long-term debt repayment
ability.
Conclusions
(USD amount in thousands )
Legend: Good Risk
Financial Analysis
Appendix 2:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shakeshackanalysis-240429113048-f545e554/75/Shake-Shack-A-Sustainable-Burger-Strategy-23-2048.jpg)