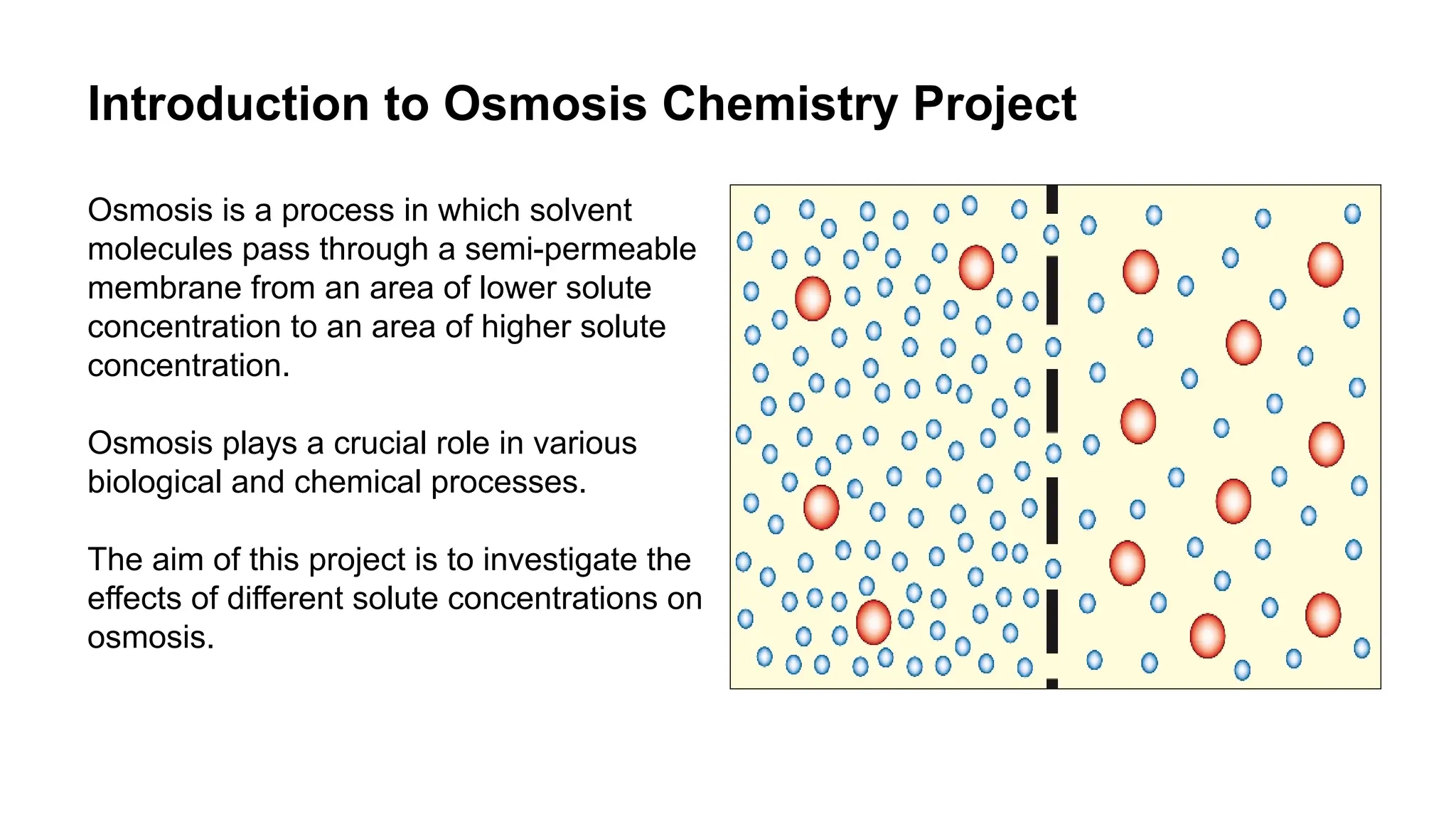
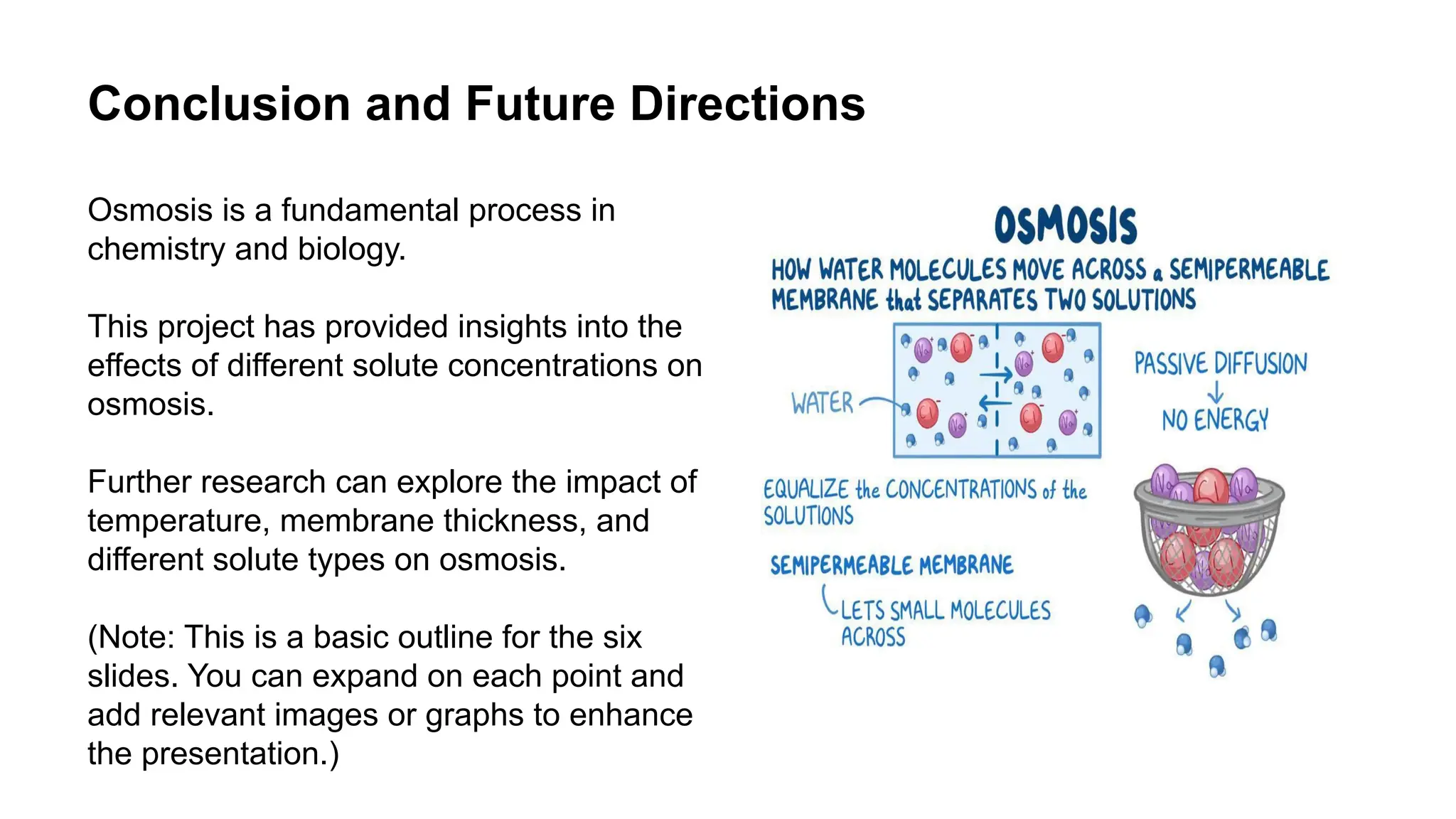
This document outlines an osmosis chemistry project investigating how different solute concentrations affect the process of osmosis. The project uses a semi-permeable membrane, beakers with varying solute solutions, and distilled water to measure the rate of osmosis. The results show that the rate of osmosis increases and the final solvent volume decreases with higher solute concentrations, and distilled water demonstrates the highest rate of osmosis. Analysis indicates osmosis is driven by concentration gradients and helps maintain balance in biological systems. Applications of osmosis include water purification, food preservation, and the pharmaceutical industry. Further research on temperature, membrane thickness, and different solute types could expand understanding of osmosis