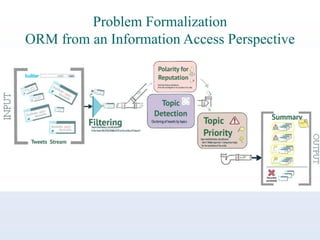
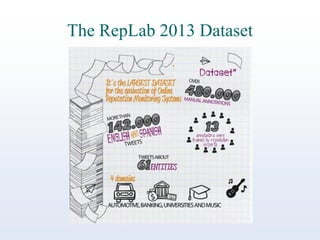
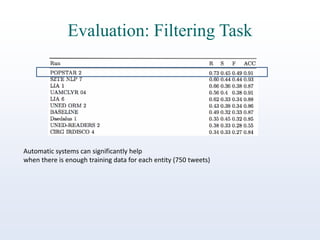
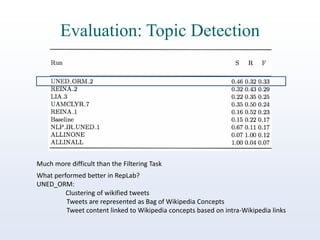
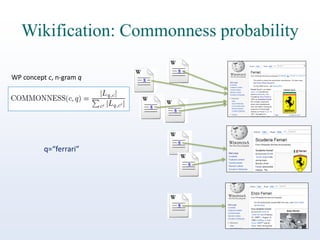
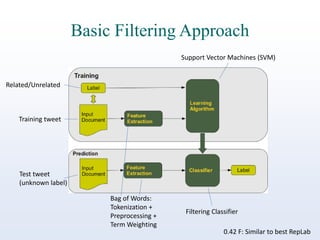
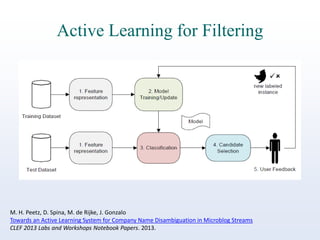
The document discusses online reputation monitoring (ORM) on Twitter, emphasizing its importance for entities like companies and personalities. It outlines the challenges faced in ORM, such as the lack of standard benchmarks and the necessity for both manual and automatic tools for monitoring, filtering, sentiment analysis, and topic detection. The document also presents goals to formalize ORM as scientific challenges, propose automatic solutions, and assess their efficacy through reusable test collections and evaluation campaigns.