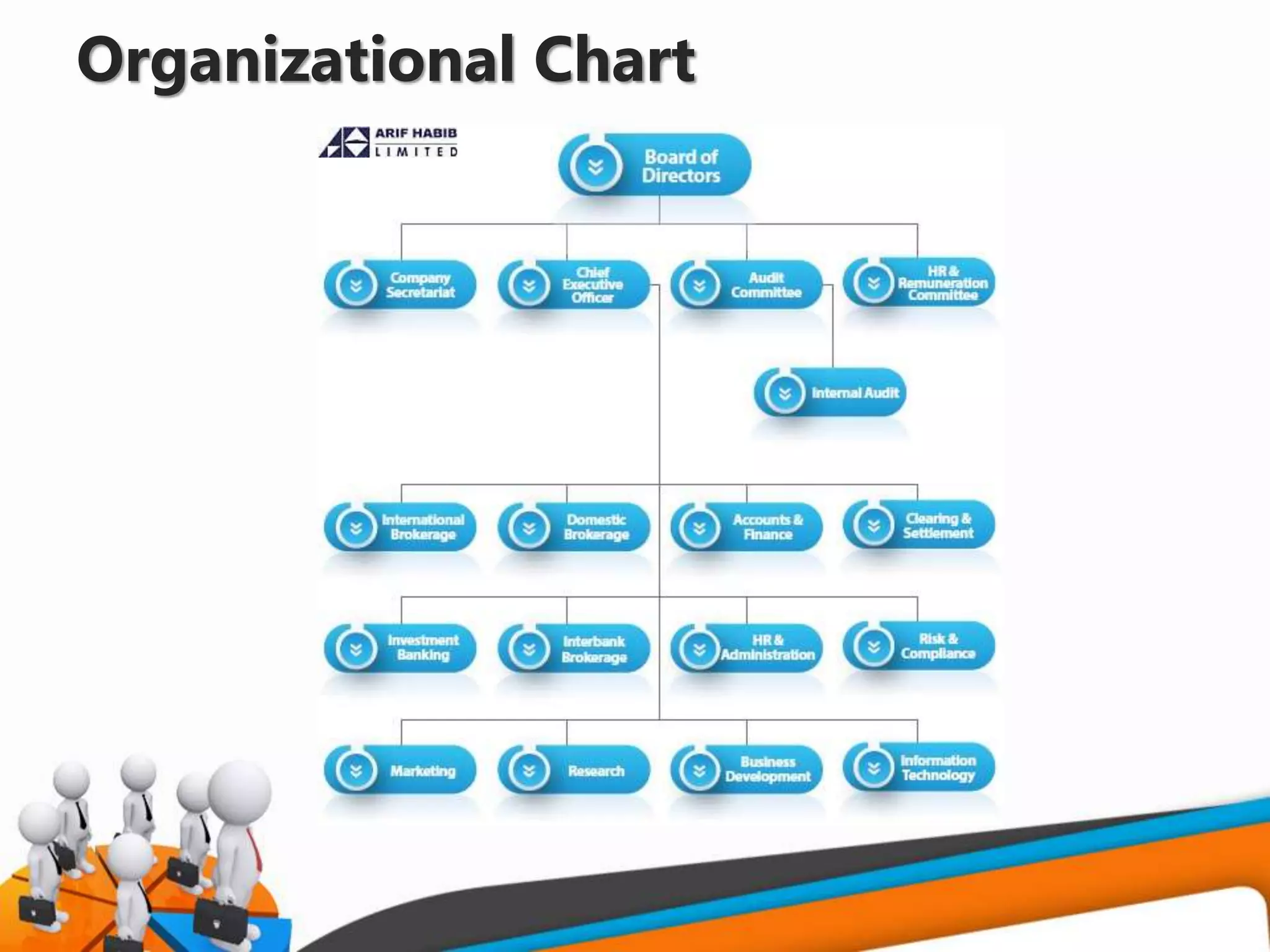
This document discusses six key elements of organizational structure: work specialization, departmentalization, centralization and decentralization, chain of command, span of control, and formalization. It focuses on explaining chain of command and span of control. Chain of command establishes clear reporting relationships within an organization based on authority and responsibility. Span of control refers to the number of subordinates a manager can effectively oversee, which varies depending on the type and complexity of work. The document also provides an example organizational chart and discusses advantages and disadvantages of different spans of control. Finally, it introduces the concept of Holacracy as an alternative organizational structure model based on distributed authority and self-organizing teams.