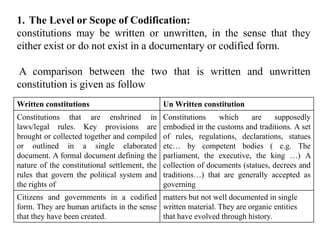
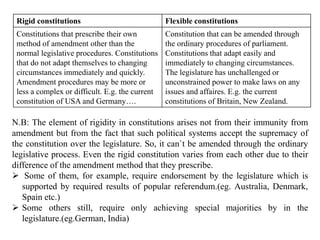
Chapter seven discusses the nature of constitutions and constitutionalism, defining a constitution as the fundamental law that organizes government, establishes powers, and outlines relationships between the state and individuals. It differentiates between written and unwritten constitutions while emphasizing the importance of public participation in their creation, and outlines the rigidity and flexibility of amendment processes. Overall, it illustrates the variability in constitutional frameworks across different political systems and the characteristics that define them.