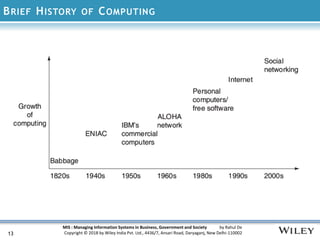
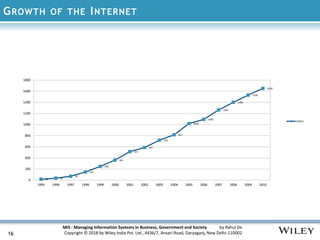
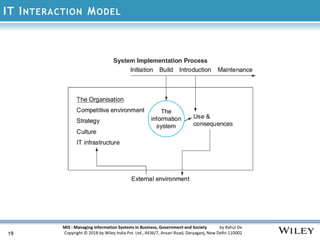
The document discusses the management of information systems in modern organizations, emphasizing their roles and challenges in business, government, and society. It covers the evolution of information technology, the importance of digital networks, and the structure of knowledge organizations. Additionally, it outlines the managerial challenges and considerations when designing and implementing information systems.