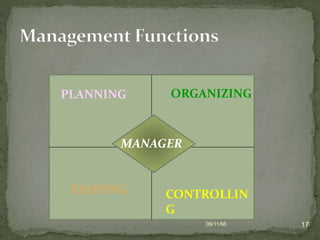
The document discusses the key functions of management which include R&D, marketing, finance, production, and HR. It then defines each function in 1-2 sentences. It also discusses the different levels of management in organizations from top managers down to first-line managers. Finally, it outlines the main functions of a manager as planning, organizing, staffing, and controlling.