Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
Similar to Organ transplant assignment
Similar to Organ transplant assignment (20)
Hsc biology 3.1: genes, mitosis, cell differentiation and specialisation

Hsc biology 3.1: genes, mitosis, cell differentiation and specialisation
Day 4 September 4th 2014 Chapters 2 and 3 Lipids and Cells

Day 4 September 4th 2014 Chapters 2 and 3 Lipids and Cells
Cell signalling and its various types and signal molecules

Cell signalling and its various types and signal molecules
Organ transplant assignment
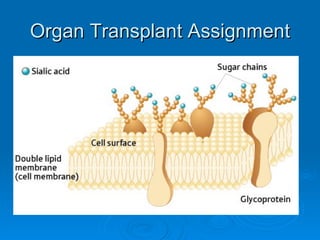
- 4. Various Protein Types Notice how the carbohydrate chain is arranged. The chain is straight then branches off in various directions with various numbers in each mini-chain. This is pattern is unique to each individual.
- 6. Some more examples of chain patterns
- 7. Various chain patterns Some are straight, some are branched, and some are isomers. They often have different numbers of carbohydrates too!
- 8. - Immune system is able to recognize that the foreign tissue’s cells do not have the same glycolipids/proteins as the rest of the body. The immune system will attack the newly received transplant. This is called transplant rejection. To succeed, an individual has to take anti-rejection medication usually for the rest of their life. These medications suppress the Immune system, weakens it, but doesn’t destroy all of the T and B cells. The body can still can fight off most infections. Cons of medication: People who take immunosuppressive drugs are more likely to develop diabetes, kidney disease, infections and cancer. Pros of medication: They get to live! Transplants
- 9. What would your look like??? Cell Fingerprint