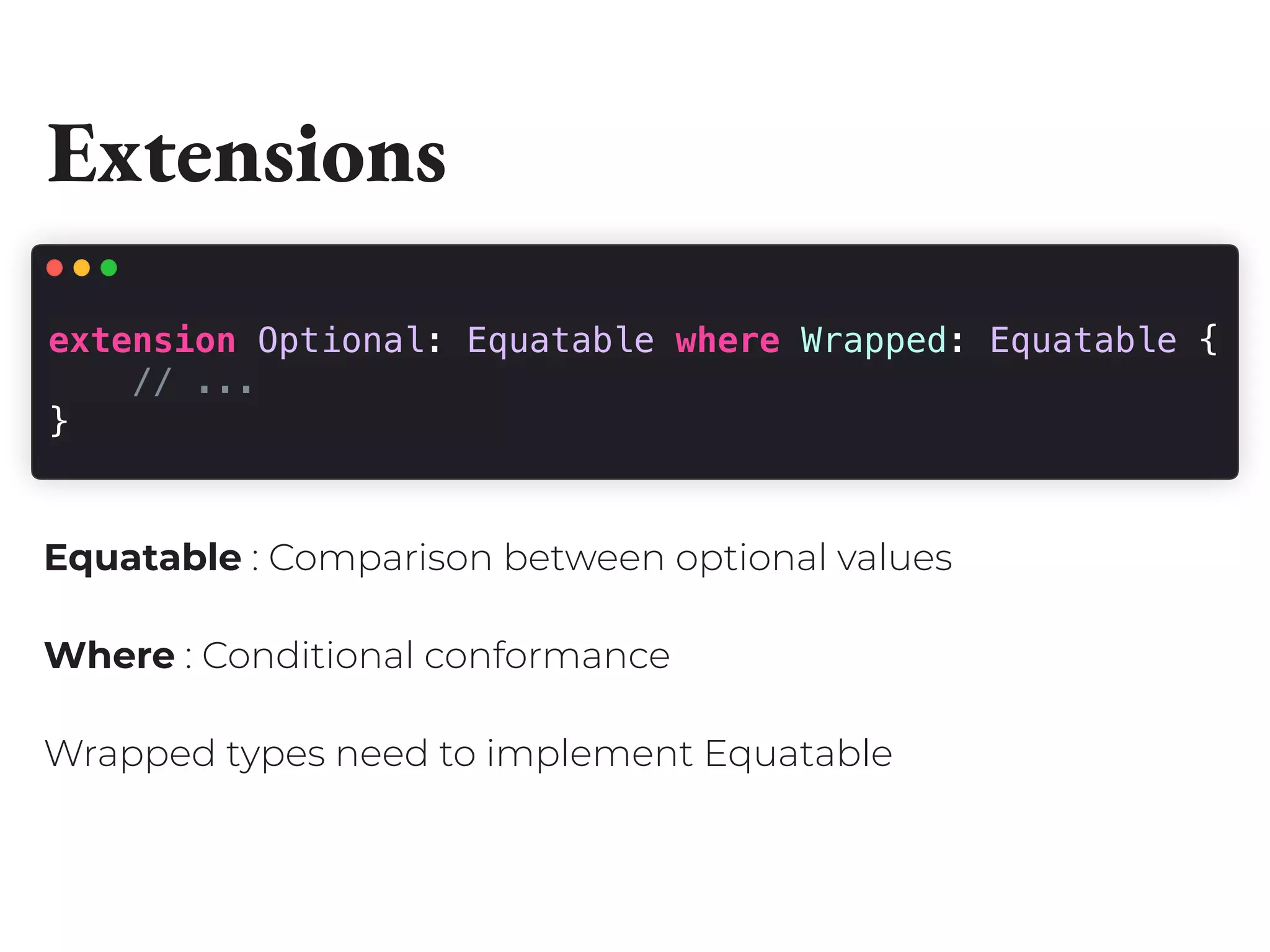
This document discusses optionals in Swift, which represent values that may or may not be present. It begins by providing usage examples of optionals and explaining that they can represent the absence of a value. It then discusses how optionals are implemented behind the scenes using enums, generics, and extensions. The document also covers different techniques for unwrapping optionals safely and unsafely as well as ways to declare, map, and transform optionals. It concludes by presenting some useful optional extensions.


![Usage Example
let users: [Int: String] =
[1: "Johny", 2: "Bernard", 3: "Lucie"]
let user1 = users[1]
let user5 = users[5]
User with id 1?
User with id 5?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-3-2048.jpg)
![Usage Example
let users: [Int: String] =
[1: "Johny", 2: "Bernard", 3: "Lucie"]
let user1 = users[1]
let user5 = users[5]
Optionals = represents either a wrapped value or
the absence of a value](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-4-2048.jpg)
![User with id 1?
User with id 5?
let users: [Int: String] =
[1: "Johny", 2: "Bernard", 3: "Lucie"]
let user1 = users[1]
let user5 = users[5]
//Optional(« Johny")
Usage Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-5-2048.jpg)
![User with id 1?
User with id 5?
let users: [Int: String] =
[1: "Johny", 2: "Bernard", 3: "Lucie"]
let user1 = users[1]
let user5 = users[5]
//Optional(« Johny")
//nil
Usage Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-6-2048.jpg)
























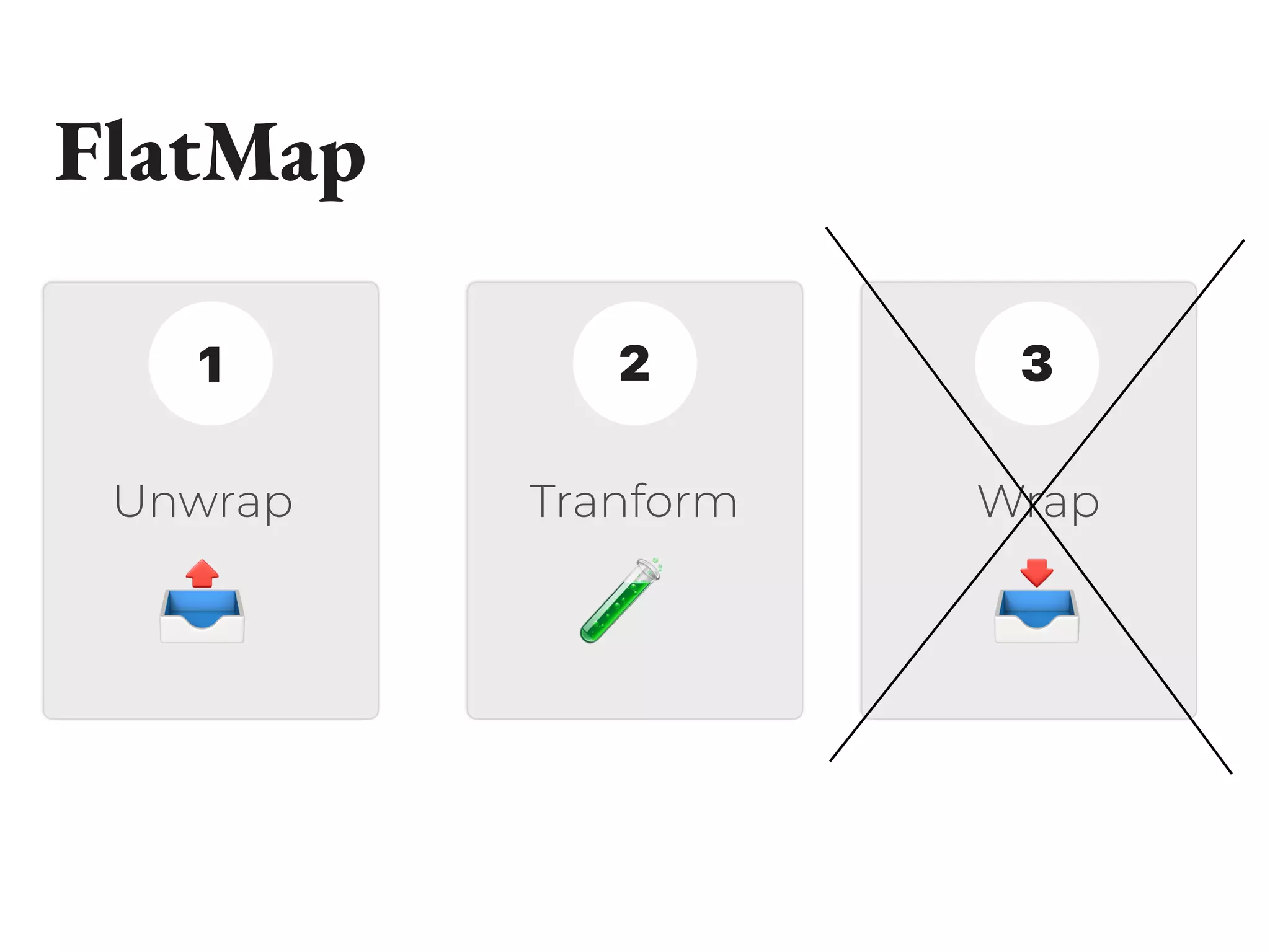
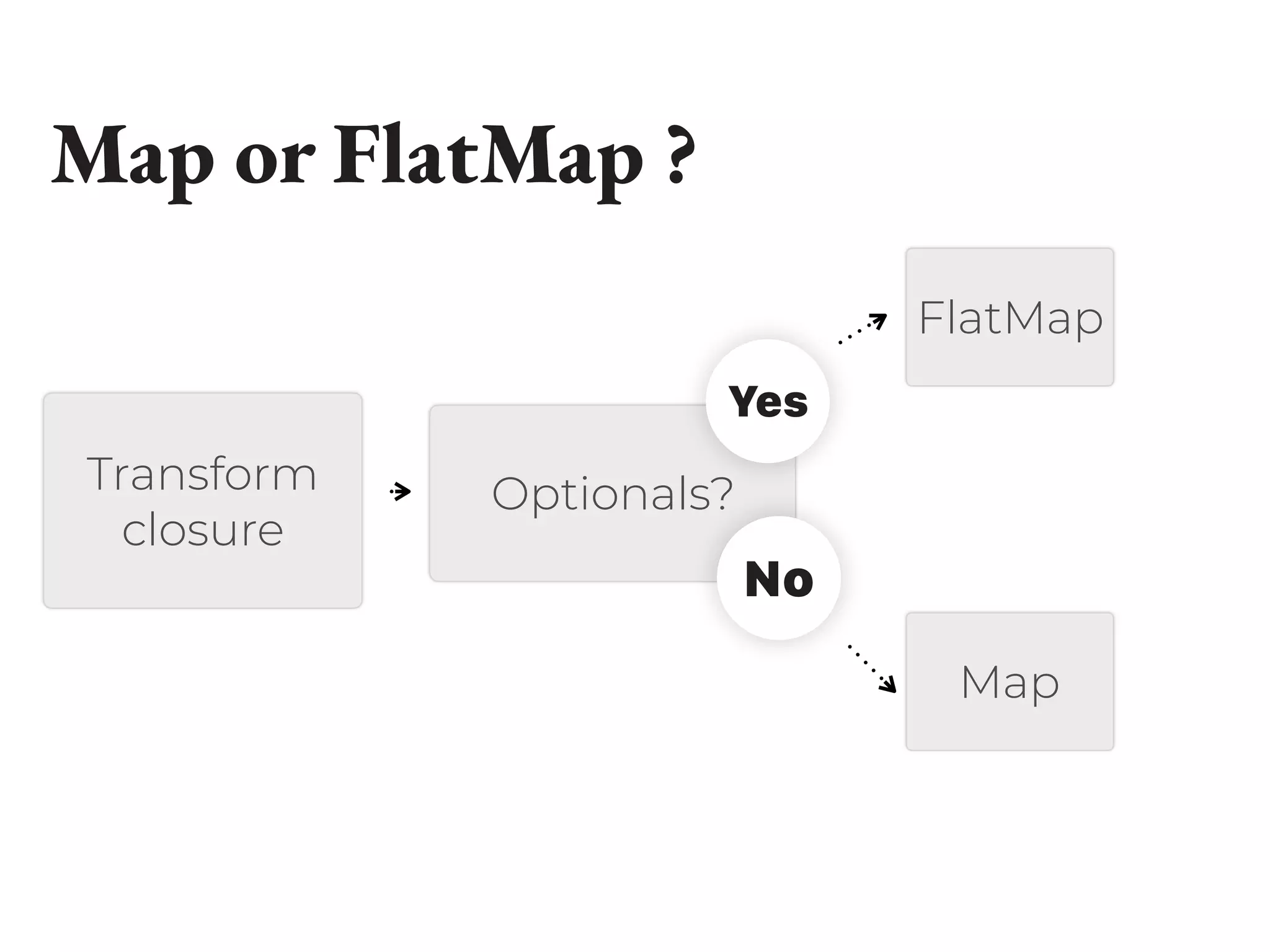
![Example 2
enum AccessType {
case read
case write
}
struct Admin {
func grantAccess(to: AccessType)
throws -> [AccessType] {
//...
}
}
let admin: Admin? = Admin()
let adminAccess = try? admin?.grantAccess(to: .read)
Type of adminAccess ? [AccessType]? or [AccessType]??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-33-2048.jpg)
![Example 2
enum AccessType {
case read
case write
}
struct Admin {
func grantAccess(to: AccessType)
throws -> [AccessType] {
//...
}
}
let admin: Admin? = Admin()
let adminAccess = try? admin?.grantAccess(to: .read) //[AccessType]??
Swift 4 and less
Type of adminAccess ? [AccessType]? or [AccessType]??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-34-2048.jpg)
![Example 2
enum AccessType {
case read
case write
}
struct Admin {
func grantAccess(to: AccessType)
throws -> [AccessType] {
//...
}
}
let admin: Admin? = Admin()
let adminAccess = try? admin?.grantAccess(to: .read)
Swift 5
Type of adminAccess ? [AccessType]? or [AccessType]??
//[AccessType]?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-35-2048.jpg)
![Example 3
let users: [String: Int?] = ["theo@gmail.com": 21,
"lucille@gmail.com": 45,
"charles@laposte.net" : nil]
let theoAge = users["theo@gmail.com"]
Type of theoAge ? Int? or Int??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-36-2048.jpg)
![Example 3
let users: [String: Int?] = ["theo@gmail.com": 21,
"lucille@gmail.com": 45,
"charles@laposte.net" : nil]
let theoAge = users["theo@gmail.com"] //Int??
Type of theoAge ? Int? or Int??](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optionals-200302130342/75/Optionals-Swift-Swift-Paris-Junior-3-37-2048.jpg)